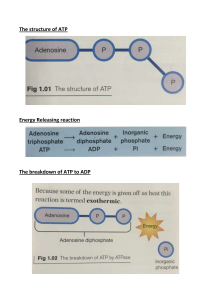
Energy Transformation In the process of cellular respiration, the energy in food is changed into energy that can be used by the body's cells. The flow of energy starts with the sun. There are two organelles that participate in the energy flow from the sun through living things. Countless chemical reactions are occurring in cells to do essential life functions with the help of ATP as the energy currency of the cells. What are the tasks of ATP? • Chemical work: ATP is used for building macromolecules • Transport work: ATP is used for transporting ions membranes • Mechanical work: ATP is used for mechanical processes such as muscle contraction, cilia movement In our cells, the energy released from the oxidation of the food we eat is stored in the form of a “highenergy” compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). • Adenine – is a nitrogenous base and a part of many substances in the body that give energy to cells. • Ribose – is a sugar and the ratelimiting compound in the production of energy compounds called Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), which are like fuel for the cells. • Phosphate Group - The phosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source which the cell taps. Available energy is contained in the bonds between the phosphates and is released when they are broken, which occurs through the addition of a water molecule (a process called hydrolysis). Why are the phosphoanhydride bonds considered high-energy? When energy is needed inside living cells, the enzyme ATPase hydrolyses the bond between the second and third phosphate group in ATP, removing the third group and leaving only two. The ATP molecule is hydrolsed into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate ion with the release of chemical energy. HYDROLYSIS OF ATP The bonds between the phosphate groups of ATP can be broken by hydrolysis. When the terminal phosphate bond is broken by addition of a water molecule, a molecule of inorganic phosphate leaves the ATP, which becomes adenosine diphosphate, or ADP. Every mole of ATP that is hydrolysed releases 30.6kJ when the bond is broken. Chemical reactions can be classified as either exergonic (energy outward) or endergonic (energy inward). • An exergonic reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy. • An endergonic reaction is one that absorbs free energy from its surroundings. • If a chemical process is exergonic (downhill), releasing energy in one direction, then the reverse process must be endergonic (uphill), using energy. A reversible process cannot be downhill in both directions. ATP - ADP CYCLE When ATP is broken down, energy is released and ADP is formed. When ADP binds with another phosphate group, energy is stored and ATP is formed. • Every task of the body requires the use of energy. At the cellular level, body cells need a steady supply of energy to keep the organism alive. • Energy is also required to produce and breakdown molecules, as well as to transport products in and out of the cell. Removing pathogenic microbes and exporting wastes out of the cell also require the use of energy. • Bioenergetics is the branch of biochemistry that focuses on how cells transform energy, often by producing, storing or consuming adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Energy coupling is the transfer of energy from one chemical reaction to another. An energetically favorable reaction is directly linked with an energetically unfavorable reaction. Through energy coupling, the cell can perform nearly all of the tasks it needs to function.