Lab Values Reference Sheet: Normal Ranges & Clinical Significance
advertisement
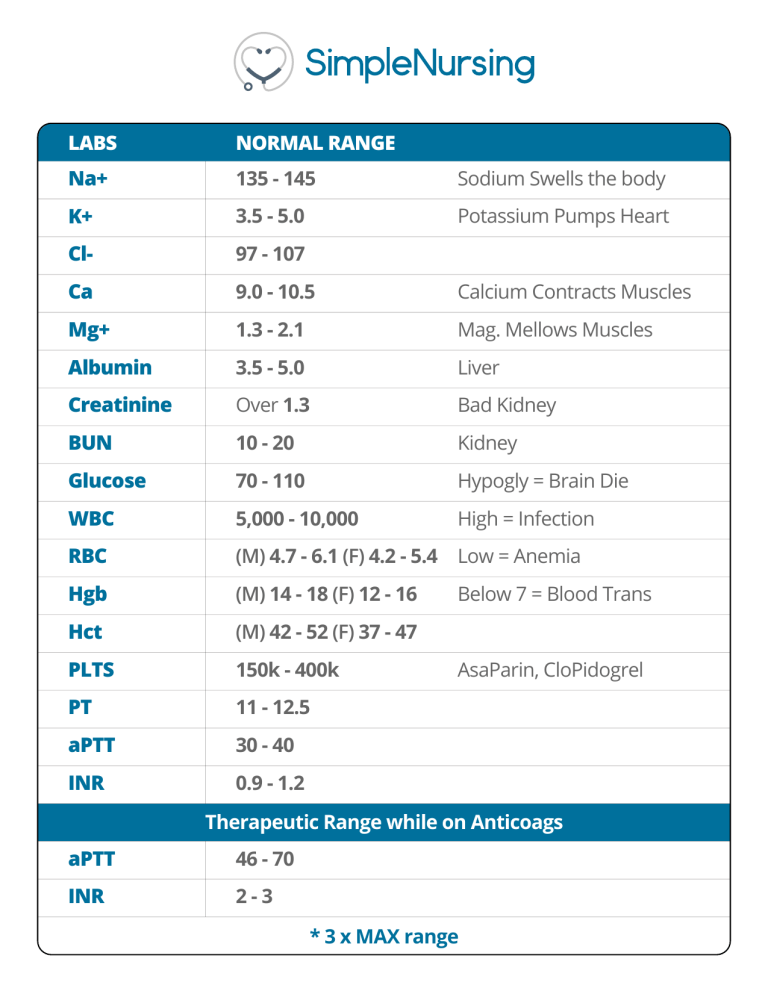
LABS NORMAL RANGE Na+ 135 - 145 Sodium Swells the body K+ 3.5 - 5.0 Potassium Pumps Heart Cl- 97 - 107 Ca 9.0 - 10.5 Calcium Contracts Muscles Mg+ 1.3 - 2.1 Mag. Mellows Muscles Albumin 3.5 - 5.0 Liver Creatinine Over 1.3 Bad Kidney BUN 10 - 20 Kidney Glucose 70 - 110 Hypogly = Brain Die WBC 5,000 - 10,000 High = Infection RBC (M) 4.7 - 6.1 (F) 4.2 - 5.4 Low = Anemia Hgb (M) 14 - 18 (F) 12 - 16 Hct (M) 42 - 52 (F) 37 - 47 PLTS 150k - 400k PT 11 - 12.5 aPTT 30 - 40 INR 0.9 - 1.2 Below 7 = Blood Trans AsaParin, CloPidogrel Therapeutic Range while on Anticoags aPTT 46 - 70 INR 2-3 * 3 x MAX range Lab Values Memory Trick The kidneys filter out HUC, since the kidneys sort of look like a pirate hook. H+ U C Hydrogen Ions = High Acid Are very acidic & too much can push the body into Acidosis. Renal failure & infection causes a back up of H+ Ions pH BELOW 7.35 Urea H+ H+ H+ BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) 10 - 20 Max Byproduct of protein waste. Think of a protein bar wrapper, it is trash that the body tosses out. This trash comes in the form of ammonia, which the liver converts into UREA, then it’s pushed into blood & excreted by the kidneys. Hence the name blood UREA nitrogen. Creatinine > 1.3 Creatinine = Critical Kidney Lab! Key Numbers: Over 1.3 = Bad Kidney Urine Output 30 ml/hr or Less = Kidney distress BUN/Creatinine Higher creatinine levels in the blood = Higher renal impairment. Creatinine is a waste product produced by the muscles coming from the normal everyday wear & tear. Common NCLEX Questions List of clients MOST at risk for Metabolic Acidosis? Select all that apply. 1. Renal failure 2. Pyelonephritis 3. Patient waiting for hemodialysis 4. Hyperventilation related to anxiety attack 5.Child with diarrhea x 2 days Client with an infected toe due to diabetes is scheduled for cardiac catheterization with contrast, which lab value should the nurse report to 1. Blood Urea Nitrogen level of 19 2. Blood glucose of 155 3. Creatinine level of 1.9 4. White blood cell count of 14,500

