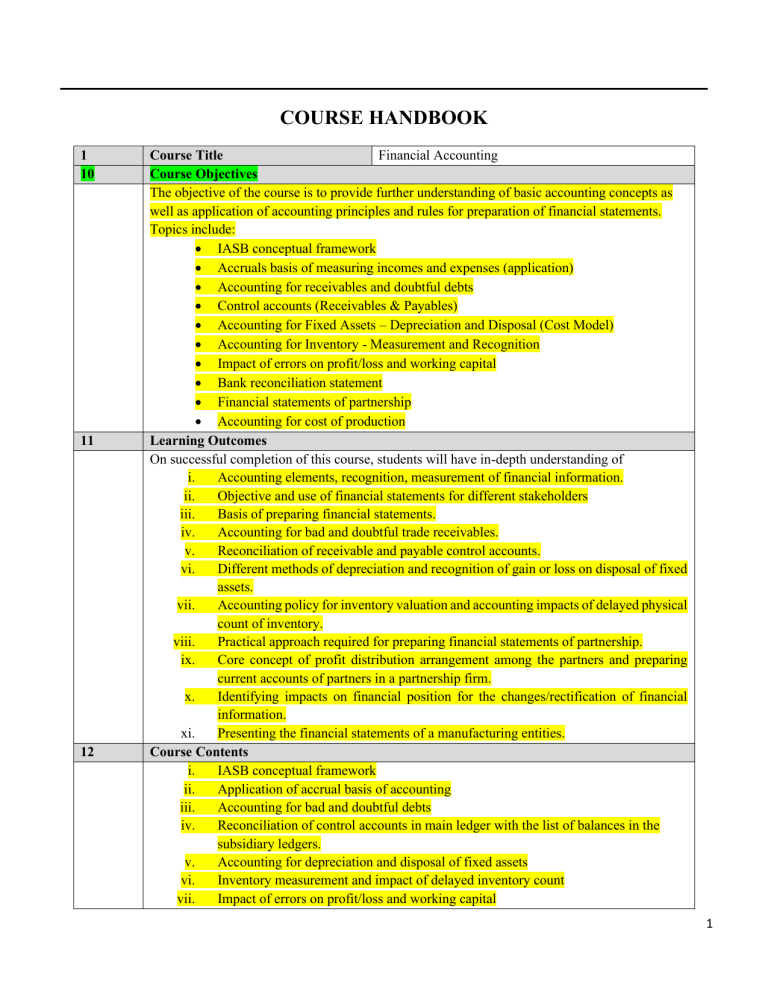
COURSE HANDBOOK 1 10 11 12 Course Title Financial Accounting Course Objectives The objective of the course is to provide further understanding of basic accounting concepts as well as application of accounting principles and rules for preparation of financial statements. Topics include: • IASB conceptual framework • Accruals basis of measuring incomes and expenses (application) • Accounting for receivables and doubtful debts • Control accounts (Receivables & Payables) • Accounting for Fixed Assets – Depreciation and Disposal (Cost Model) • Accounting for Inventory - Measurement and Recognition • Impact of errors on profit/loss and working capital • Bank reconciliation statement • Financial statements of partnership • Accounting for cost of production Learning Outcomes On successful completion of this course, students will have in-depth understanding of i. Accounting elements, recognition, measurement of financial information. ii. Objective and use of financial statements for different stakeholders iii. Basis of preparing financial statements. iv. Accounting for bad and doubtful trade receivables. v. Reconciliation of receivable and payable control accounts. vi. Different methods of depreciation and recognition of gain or loss on disposal of fixed assets. vii. Accounting policy for inventory valuation and accounting impacts of delayed physical count of inventory. viii. Practical approach required for preparing financial statements of partnership. ix. Core concept of profit distribution arrangement among the partners and preparing current accounts of partners in a partnership firm. x. Identifying impacts on financial position for the changes/rectification of financial information. xi. Presenting the financial statements of a manufacturing entities. Course Contents i. IASB conceptual framework ii. Application of accrual basis of accounting iii. Accounting for bad and doubtful debts iv. Reconciliation of control accounts in main ledger with the list of balances in the subsidiary ledgers. v. Accounting for depreciation and disposal of fixed assets vi. Inventory measurement and impact of delayed inventory count vii. Impact of errors on profit/loss and working capital 1 13 Week 1. Week 2. Week 3. viii. Adjusted trial balance and financial statements of partnership. ix. Profit distribution statement and current accounts of partnership firm x. Cost flow in a manufacturing entity Outline of Weekly Lectures & Reading list/Recommendations Books IASB conceptual framework Reading Interpretation and application of IFRS by Wiley, Notes & Handouts. Accrued and prepaid expenses (opening and closing balances) impact on SOPL and SOFP Reading Business Accounting by Frank Wood, Financial Accounting by Sir Kieso, Financial Accounting by M. Hanif and A. Mukherjee, Notes & Hand-outs. Accounting entries for bad and doubtful debts, increase and decrease in allowances for doubtful debts, presentation in financial statements. Week 4. Accounting entries for bad and doubtful debts, increase and decrease in allowances for doubtful debts, presentation in financial statements. Week 5. Posting process from the sales daybook and purchase daybook into the subsidiary ledgers and the main ledger. Reconciliation of receivable ledger control account balance with the list balance of sales ledger. Reconciliation of payable ledger control account balance with the list balance of purchase ledger. Calculation of depreciation charge for the year under different methods, accounting entries, change in methods, change in useful life and presentation in financial statements. Accounting for disposal of fixed asset, proportionate depreciation on the asset purchased or sold during the year. Loss on disposal of asset covered by insurance company and trade in allowance in case of part exchange. Calculation of cost (FIFO & W.Avg) and net realizable value of inventory. Accounting policy for inventory measurement as per IAS 2. Write-down and reversal of write-down of inventory. Periodic and perpetual system of accounting. Impact of delayed inventory count on SOFP and SOPL. Impact of errors on SOPL and Working Capital. Difference between rectifying entries, adjusting entries and closing entries. Impact of year-end adjustments and rectification of errors on trial balance, creating adjusted trial balance. Preparation of SOPL and SOFP from the adjusted trial balance for partnership entities. Week 6. Week 7. Week 8. Week 9. Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Week 13 Reasons of difference between cash book balance and bank statement balance. Adjusting entries in the adjusted cash book. Preparing bank reconciliation statement. Preparing bank reconciliation statement. Week 14 Cost elements their characteristics and behavior. Cost of goods manufactured and sold statement and SOPL. Week 15 Cost of goods manufactured and sold statement and SOPL. Week 16 Pre final Exams and course revision Reading list/Recommended Books 1. Anthony, R. N., Hawkins, D. F., & Merchant, K. A. (2011). Accounting-Texts and Cases (11th ed.). 2. Mukherjee, A., & Hanif, M. (n.d.). Modern Accountancy-Volume-I. 2 3. Williams, J. R., Haka, S. F., & Bettner, M. S. (2014). Financial and Managerial Accounting-The Basis for Business Decisions-International Edition (14th ed.). 4. Practical Illustrations provided by the concerned Teacher (n.d.). 5. Shukla, M. C. (n.d.). Advance Accounting. 6. Gupta, R. L. (n.d.). Advance Accounting. 14 Assessment Policy The assessment of this module shall have following evaluation components: Quizzes, Assignments, Attendance 30% Mid Term Test 20% Final Examination 50% The minimum pass marks for each course are 50%. 15 Assessment Schedule Practice questions as Assignment. a. IASB conceptual framework and Application of accrual basis of accounting (due in week 2) b. Accounting for bad and doubtful debts (due in week 4) c. Accounting for depreciation and disposal of fixed assets (due in week 6) d. Inventory measurement and impact of delayed inventory count (due in week 8) e. Impact of errors on profit/loss and working capital and adjusted trial balance and financial statements of sole proprietor (due in week 11) f. Statement of cash flows of sole proprietor. g. Profit distribution statement and current accounts of partnership firm (due in week 13) 30% th Mid Term Test (8 week) 20% Final Semester Exam (20% theory 80% numerical) 50% 16 Attendance Policy ● Attendance must be at least 80 percent to be eligible to appear in the final semester exams. ● In live lectures, attendance will be marked by the teacher. ● For students with limited or no internet connectivity, attendance will be assignment based. On weekly basis, such students will submit a review/report related to all theory and practical questions to be discussed in that week. 3 • • • • • • 12 Internal Control System and Constituents. General and Special Auditing Techniques i.e., Performing Audit. Key International Standards on Auditing. Legal and Regulatory Framework for Auditing in Pakistan. Understanding and Developing Audit Reports; and Terminologies developed by International Auditing and Assurance Standard Board Course Contents This course covers on the following course contents: • Introduction to Auditing. • Internal Control System and its Constituents. • Objectives of Internal Auditing and Techniques. • Legal and Professional Considerations. • Audit Planning and Control. • Audit Procedures and Techniques. • Audit Documentation and Evidence. • Performance of Audit, Audit Risk and Management. • Audit Completion and Audit Reporting; 13 Week 1 &2 Outline of Weekly Lectures & Reading List GOAL 1: INTRODUCTION TO AUDITING i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. x. Week 3 Nature, Definition, Scope, Objective and Principles of an Audit Classification (kinds/types) of an Audit Need for, and usefulness of an Audit. Distinction and Relationship between Accounting and Auditing Concepts of reasonable assurance, audit risk and materiality, true and fair view, recurring Audit Management Responsibility for Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statements Legal and Regulatory Framework for Auditing in Pakistan Responsibility of an Auditor, and his Role as a detector of Error/Mistake/Fraud/Misrepresentation Postulates of Auditing Glossary of Terms for Auditing attached with ISAs issued by IAASB/IFAC GOAL 2: UNDERSTANDING THE INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEM i. ii. iii. iv. v. Definition/Meaning, Objectives, Types, Principles and Techniques of Key Components and/or Essential Elements of Internal Control Features of an Effective Internal Control System Limitations on the Effectiveness of Internal Control/Audit Internal Control in an EDP Environment 4 Week 4 GOAL 3 : INTERNAL AUDIT i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. Scope, Limitations and Types of Internal Audit Responsibilities of Internal Auditor Impact of Internal Controls and Audit Work, and Issuance of Management Letter Internal Audit VS External Audit Audit Working Papers Functions of Chief Internal Auditor Week 5 & GOAL 4 : LEGAL AND PROFESSIONAL CONSIDERATIONS 6 i. Appointment, Remuneration, Resignation, Removal, Rights, Powers, Duties, Liabilities, Qualification and Disqualification of an Auditor ii. procedure for appointment of first and subsequent auditors under Companies Act 2017 iii. International Standards on Auditing (ISAs) and guidelines, Standard Accounting and Auditing Practices and Technical Releases by Local Professional Institutes of Pakistan iv. ‘Code of Conduct for Professional Accountants’ issued by IFAC and Week 7 GOAL 5: AUDIT PLANNING AND CONTROL i. Concept & Benefits of, and the Need for Audit Planning ii. Planning Procedure: overall Audit Strategy, Review of the Client’s Business, Accounting System, Financial Procedures etc. iii. Audit Risk, Audit Plans, Programs and Procedures iv. Documentation of Audit Plan, Audit Timeliness, and Changes in Audit Plans Week 8 Week 9 Mid-Term Exams GOAL 6: AUDIT ENGAGEMENT, PROCEDURES AND TECHNIQUES i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. Terms of audit engagement, engagement letter and its contents Types of Audit Procedures and Techniques Management Representation, and Reliance on it, and Judgment by Auditor Vouching and Verification of Assets and Liabilities Financial Statements Analysis Use of Computer Assisted Audit Techniques (CAATs) i.e., IT Auditing Week 10 GOAL 7: AUDIT DOCUMENTATION AND EVIDENCE i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. Terms of audit engagement, engagement letter and its contents Types of Audit Procedures and Techniques Management Representation, and Reliance on it, and Judgment by Auditor Vouching and Verification of Assets and Liabilities Financial Statements Analysis Use of Computer Assisted Audit Techniques (CAATs) i.e., IT Auditing 5 Week 11 GOAL 8: PERFORMING AUDIT, AND AUDIT RISK CONSIDERATIONS & 12 i. Precautions, Assumptions and Judgment by the Auditor ii. Analysis of Internal Control System, People, IT Infrastructure, Procedures etc. iii. Developing a suitable Audit Program, and ensuring its implementation in a professional way iv. Identifying the applicable risks, and classifying the same for Audit Purposes v. Materiality Assessment, and Audit Sampling vi. Applying applicable ISA’s provisions in dealing with the organizational risks vii. Preparing risk management documentation and reports thereupon. viii. IT based risks, their influence and dealing with them. Week 13 GOAL 9: COMPLETION OF AN AUDIT i. Audit Completion/Closing Procedures, and Filing ii. Informing Management about completion, flaws/loopholes and areas of internal control requiring improvement iii. Letter of representation to the Management iv. Attending the upcoming AGM v. fulfilling the applicable legal and professional formalities Week 14 GOAL 10: AUDIT OPINION & ITS FORMS, AND AUDIT REPORT & ITS COMPONENTS i. Audit Report, its Template and Components ii. Types of Audit Opinion as per ISAs iii. Statement of Compliance with the Code of Corporate Governance iv. Date and Signatories of the Auditors’ Report v. Audit Report of a Listed Company Week 15 GOALs 1-10: Revision / Overview of the whole Course, and Q&As Reading List: Week 16 Final-Term Exams Reading List/Rec ommend ed Books 1. International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board. (2018). Handbook of International Quality Control, Auditing, Review, Other Assurance, and Related Services Pronouncements. Retrieved April 3, 2023, from https://www.iaasb.org/publications/2018-handbook-international-quality-controlauditing-review-other-assurance-and-related-services-26 2. Millichamp, A. H. (2002). Auditing. Cengage Learning Emea. 3. Ainapure, V., & Ainapure, M. (2009). Auditing and assurance. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.. 4. Gomez, C. (2012). Auditing and assurance: Theory and practice. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. 5. Graham, L. (2015). Internal control audit and compliance: Documentation and testing under the new COSO framework. John Wiley & Sons. 6 6. Coderre, D. (2009). Internal audit: Efficiency through automation (Vol. 11). John Wiley & Sons. 7. https://www.secp.gov.pk/document/companies-act2017/?wpdmdl=28472&refresh=5ed02a6ae274f1590700650 8. Hayes, R., Wallage, P., & Gortemaker, H. (2014). Principles of auditing: An introduction to international standards on auditing. Pearson Higher Ed. 9. Davis, C., & Schiller, M. (2011). IT Auditing: Using Controls to Protect Information Assets. McGraw Hill, 2nd Edition. 10. Hayes, R., Wallage, P., & Gortemaker, H. (2014). Principles of Auditing: An Introduction to International Standards on Auditing. Pearson Higher Ed. 11. Chambers, A., & Rand, G. (2011). The Operational Auditing Handbook: Auditing Business and IT Processes. John Wiley & Sons. 12 Assessment Policy 7

