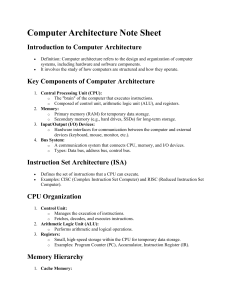
Computer Architecture Bus Data connection between two or more devices connected to the computer. eg. the connection between the registers in a CPU and the memory Cell Unit of main memory Typically 1 byte Address String of numbers that uniquely identifies a cells in main memory DRAM Dynamic memory Volatile Sector Subdivision of a track on a magnetic disk Cache Memory Computer memory stored closest to the CPU, hence fastest memory Stores recent instructions that are used repeatedly Volatile Stored Program Concept Programmed encoded as bit patterns in main memory (machine instruction) CPU can extract the instructions and easily execute and run them Instruction Set Architecture Provides commands to the processor Contains addressing modes, instructions, native data types, registers, memory architecture, interrupt and exception handling, external I/O Instruction Sets examples ADD - Add two numbers together COMPARE - Compare numbers IN - Input information from a device OUT - Output information to a device JUMP - Jump to a designated RAM address (function) JUMP IF - Conditional statement that jumps to a designated RAM address LOAD - Load information from the RAM to the CPU OUT - Output information to a device STORE - Store information to RAM Machine Language Philosophies Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) Few, simple, efficient and fast instructions PowerPC - Apple/IBM/Motorola, SPARC - Sun Microsystems Complex Instruction Set Computing (CISC) Many, convenient, and powerful instructions Pentium - Intel, Ryzen - AMD Machine Instruction types Data Transfer Arithmetic/Logic Control Machine Instruction parts Op-Code Specifies which operation to execute Operand Gives more detailed information about the operation Interpretation depends on op-code eg. 1000 0200 0300 0400 meaning ADD A, B, C where ADD is the op-code Program Execution Program Counter Register in a CPU that contains the address of the next instruction Instruction Register Register in a CPU that contains the address of the current instruction Machine Cycle Fetch Retrieve the next instruction from memory by the program counter and increment it Decode Decode the bit pattern in the instruction register Execute Perform the action required in the instruction register Communicating with other devices Controller Intermediary apparatus that handles communication between the computer and device Specialized Controllers General Purpose Controllers (USB and FireWire) Port Point at which a device connects to a computer Memory-mapped I/O CPU communicated with peripherals as if they were memory cells Direct Memory Access (DMA) Main memory access by a controller over the bus Von Neumann Bottleneck Insufficient bus speed impedes peformance Handshaking The process of coordinating the transfer of data between components Parallel Communication Several communication paths transfer bits simultaneously Serial Communication Single communication paths transfer bits one after another Bandwidth Maximum available rate of data transfer Architectures Pipelining Overlap steps of a machine cycle Parallel Procesing Use multiple processors simultaneously MIMD (Multiple Instructions, Multiple Data) SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) Performs the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously Clock Speed/Rate The speed at which the microprocessor executes each instruction The CPU requires a fixed number of cycles to execute each instruction Clock speeds are measured in MHz, 1 MHz representing 1 million cycles per second