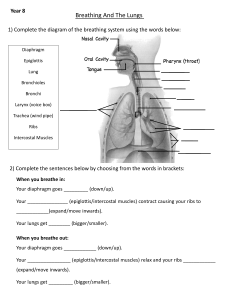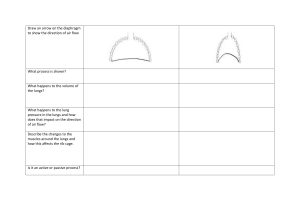
MECHANICS OF BREATHING WHAT ARE THE MECHANICS OF BREATHING? ▪ The diaphragm flattens and moves downwards and the intercostal muscles move the rib cage upwards and out. ▪ This increase in size decreases the internal air pressure and so air from the outside (at a now higher pressure than inside the thorax) rushes into the lungs to balance the pressures. ▪ Inspiration occurs when the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles contract. ▪ Expiration occurs when the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles relax. ▪ The contraction or relaxation of muscles around the lungs changes the entire volume of air inside the lungs, and so does the pressure. As seen, the diaphragm has contracted in the first diagram to make space for the lungs, and the diaphragm has relaxed in the second diagram as the chest contracts. INTERCOSTAL MUSCLES ▪ The intercostal muscles are found between the ribs and they control rib movement. ▪ 1) Diaphragm contracts and moves downwards. ▪ 2) Intercostal muscles contract and move the ribs upwards and outwards. These muscles help in rib functioning during breathing ROLE OF MUSCLES DURING NORMAL BREATHING There are 2 types of muscles involved Muscles of inspiration Muscles of expiration END OF PRESENTATION