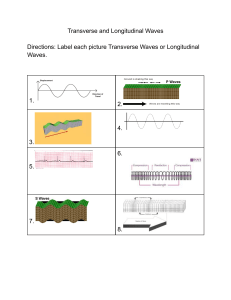
Types of Waves: Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Transverse, Longitudinal
advertisement

TYPES OF WAVES A wave is the process by which a disturbance at one point in space is spread through an elastic medium to another point further from the source. Waves transport energy without transporting matter. Waves are formed because of the individual motion of the particles that make up the medium through which the wave propagates through. Waves can be classified, as shown below. 5 identify that mechanical waves require a medium for propagation while electromagnetic waves do not WAVES ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES …………………………................. Do NOT require medium for transmission. ALL TRANSVERSE ……………………….…………. Alternating electric and magnetic fields operating perpendicularly to the direction of wave travel. MECHANICAL WAVES ……………………………… Do require a medium for transmission. TRANSVERSE WAVES ................................................... Particles of medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation. LONGITUDINAL WAVES ................................................... Particles of medium vibrate in the same direction of the wave propagation. EXAMPLES ................................................... Water and earthquake waves and waves in ropes and springs. EXAMPLES ................................................... Sound waves and waves in springs. We can use diagrams to demonstrate the differences between these waves. 8 present diagrammatic information about transverse and longitudinal waves, direction of particle movement and the direction of propagation TRANSVERSE WAVE LONGITUDINAL WAVE 6 describe the relationship between particle motion and the direction of energy propagation in transverse and longitudinal waves The direction of energy flow is in the same direction that the wave propagates through a medium. This motion is PERPENDICULAR to the oscillation of the particles of the medium that the wave moves through. The direction of energy flow is in the same direction that the wave propagates through a medium. This motion is PARALLEL to the oscillation of the particles of the medium that the wave moves through.