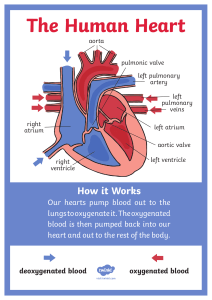
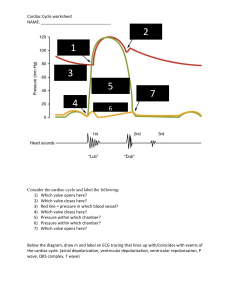
<3 Anatomy Review / ekg Blood flow vena cava right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle pulmonary valve pulmonary artery lungs pulmonary veins left atrium mitral valve left ventricle aortic valve aorta and the tissues of the body <3 sounds S1 – AV valves closing (mitral and tricuspid) – Corresponds with pulse - heard at apex of left side of heart S2 – Semilunar valve closing (aortic and pulmonary) – heard at the 2 ICS space at the sternal border S3 – ventricles filling S4 – atrial contraction in presence of Cardiac Cells Automaticity – ability to fire off on it’s own Excitability – ability to respond to impulses Conductivity – cardiac muscles conduct the impulses to different areas Contractility – cardiac muscles contract and relax Pacemakers SA NODE – upper right atrium (natural pacemaker) Purpose: firing impulses Rate: 60 – 100 AV NODE - (gatekeeper) Purpose: delays impulses from SA node to ventricles--> to allow the atrium to contract properly. Rate – 40 - 60 PREKINJE FIBERS BUNDLE OF HIS – Rate: 20 – 40 bpm EKG Depolarization – contraction Repolarization – relaxation Pwave = depolarization of the atria QRS Complex = depolarization of the ventricles and repolarization of the atria TWave = repolarization of the ventricles – may also have a UWave Uwave = repolarization of the Purkinje fibers. (not always seen) EKG Paper PWave = depolarization of the atria PR Interval = time taken from SA node impulse to reach ventricle Normal Measurement = .12 - .20 seconds Measured at the beginning of the p wave, and the beginning of the R. / QRS = JPoint = QT Interval = atria and ventricular repolarization, and electrical depolarization R-R Segments = Sinus Rhythms Normal Sinus