Biology Worksheet: Photosynthesis, Respiration, Cell Division
advertisement

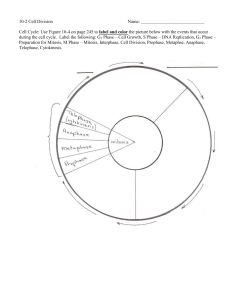
2nd Trimester – Worksheet Revision for the Final exam 2023-2024 Subject: Biology Name: _________________________ Grade: _____9_____ Date: _________________ I-Ordering Question 1-Place the steps of photosynthesis into the correct order from top to bottom. Carbon dioxide is used to create glucose molecules. Hydrogen ions move through the ATP synthase converting ADP into ATP. Light energy breaks down water into oxygen and hydrogen ions. Electrons move through the electron transport and convert NADP+ into NADPH. NADPH and ATP are used in the Calvin cycle. 2-Place the steps of electron transport in order from beginning to end. Light energy excites electrons in photosystem II causing a water molecule to split and releasing an electron into the electron transport system. The excited electrons move from photosystem II to an electron-acceptor molecule in the thylakoid membrane. The electron-acceptor molecule transfers the electrons along a series of electron-carriers to photosystem I. In the presence of light, photosystem I transfers the electrons to a protein called ferrodoxin. The electrons lost by photosystem I are replaced by electrons shuttled from photosystem II. Ferrodoxin transfers the electrons to the electron carrier NADP+, forming the energy-storage molecule NADPH. 3-Place the steps of the Calvin cycle in the correct order from beginning to end. Six carbon dioxide molecules combine with six 5-carbon compounds to form twelve 3-carbon molecules called 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA). The chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH is transferred to 3-PGA molecules to form high-energy molecules called glyceraldehyde 3-phosphates (G3P). Two G3P molecules leave the cycle to be used for the production of glucose and other organic compounds. Rubisco converts ten G3P molecules into 5-carbon molecules called ribulose 1, 5bisphosphates (RuBP). Ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphates (RuBP) molecules combine with new carbon dioxide molecules to continue the cycle. 4-Place the steps of the Krebs cycle in order from beginning to end. Acetyl CoA combines with a 4-carbon compound to form a 6-carbon compound known as citric acid. Citric acid is broken down in the next series of steps, releasing two molecules of carbon dioxide and generating one ATP, three NADH, and one FADH2. Acetyl CoA and citric acid are generated and the cycle continues. 5-Place the steps involved in glycolysis in order from beginning to end. Two phosphate groups, derived from two molecules of ATP, are joined to glucose. The 6-carbon glucose molecule is broken down into two 3-carbon compounds. Two phosphates are added and electrons and hydrogen ions (H+) combine with two NAD+ molecules to form two NADH molecules. The two 3-carbon compounds are converted into two molecules of pyruvate. At the same time, four molecules of ATP are produced. II-Fill in the Blank Question 1-Chlorophylls absorb most strongly in the violet-blue region of the visible light spectrum and reflect light in the ___________________ region of the spectrum. 2-In photosynthesis, ___________ is the major electron carrier involved in electron transport. 3-The second phase of photosynthesis in which energy is stored in organic molecules such as glucose is called the _____________ 4-In the final step of the Calvin cycle, an enzyme called __________ converts G3P molecules into 5-carbon molecules called ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphates (RuBP). 5-__________________ plants allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaves only at night, when the plants fix carbon dioxide into organic compounds. During the day, carbon dioxide is released from these compounds and enters the Calvin cycle. 6-The ________________ in which an organism lives can impact the organism’s ability to carry out photosynthesis. As a result, many plants in extreme climates have alternative photosynthesis pathways to maximize energy conversion. 7-Plants, such as sugarcane and corn, that fix carbon dioxide into four-carbon compounds instead of threecarbon molecules during the Calvin cycle are called _______ plants. 8-In cellular respiration, NAD+ is an example of a(n) _______________ , a substance that temporarily stores energy. 9- the __ _______________ occurs prior to the Krebs cycle. 9-The net total of ATP produced by prokaryotic cells that undergo aerobic respiration is ______ ATP, as opposed to the 36 ATP molecules produced under ideal conditions in eukaryotic cells. 10-In _______________ fermentation, enzymes convert the pyruvate made during glycolysis to lactic acid. 11-________________ fermentation occurs when pyruvate is converted to ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. 12-______________ ___occurs in the cytoplasm and regenerates the cell’s supply of NAD+ while producing a small amount of ATP. 13-__ _____________ is the stage of the cell cycle during which the cell's nucleus and nuclear material divide. 14-The phosphate groups in DNA create a negative charge, which attracts the DNA to the positively charged histone proteins and form a_____ ________________ 15-Cells reproduce by a cycle of growing and dividing called the ___ _____________ 16-_____ ______________is the stage of the cell cycle during which the cell grows, develops into a mature, functioning cell, and duplicates its DNA in preparation for division. 17-Cells in___ ______________ carry out various metabolic processes, including the replication of DNA. 18-During the __ ___________ _stage of interphase, a cell copies its DNA in preparation for cell division. 19-During the ___ ______________ stage of interphase, a cell is growing, carrying out normal cell functions, and preparing to replicate DNA. 20-During the ____ _____________ stage of interphase, a cell prepares for the division of its nucleus and takes inventory to make sure it is ready to continue with mitosis. 21-The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase _____________ and __ _____________ 22-The first stage and longest stage of mitosis is called____ ____________ 23-___________________ ___are structures that contain identical copies of DNA. 24-The structure at the center of the chromosome where the sister chromatids are attached is called the ___ ____________________ 25-During the second stage of mitosis, ___________________, the sister chromatids are pulled by motor proteins along the spindle apparatus to the cell's equator. 26-The structure made of spindle fibers, centrioles, and aster fibers is called the_________________________ 27-The chromatids are pulled apart during ______________________resulting in the equal separation of replicated and identical DNA. 28-_______________________ is the last stage of mitosis. III-True false question. 1-True or false: Many plants in extreme climates have alternative photosynthesis pathways to maximize energy conversion. 2-True or false: In both lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation, NADH donates electrons during this reaction and NAD+ is regenerated. 3-True or false: For most normal, actively-dividing animal cells, the cell cycle takes approximately 12–24 hours. 4-True or false: The human body's process of healing a cut to the skin involves mitosis. True false question. IV-Multiple Choice Question 1-Which accessory pigments absorb light mainly in the blue and green regions of the spectrum, while reflecting most light in the yellow, orange, and red regions? a-Chlorophyll a b-Chlorophyll b c-Carotenoids 2-In photosynthesis, which is the major electron carrier involved in electron transport? Multiple choice question. a-ATP b-NADPH c-H2O d-NADP+ 3-Which best describes the process of chemiosmosis? a-The mechanism by which ATP is produced as a result of the flow of electrons down a concentration gradient. b-The mechanism by which ATP is produced as a result of the flow of electrons against a concentration gradient. c-The enzyme rubisco converts organic carbon dioxide molecules into inorganic molecules that can be used by the cell. d-The enzyme rubisco converts inorganic carbon dioxide molecules into organic molecules that can be used by the cell. 4-Select the statements about carotenoids that are true. a-Carotenoids produce the colors in carrots and sweet potatoes because they reflect light in the yellow, orange, and red regions of the spectrum. b-Carotenoids absorb most strongly in the violet-blue region of the visible light spectrum and reflect light in the green region of the spectrum. c-Carotenoids are accessory pigments that absorb light in the blue and green regions of the spectrum. 5-Which statements about chemiosmosis are true? a-The chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH is transferred to 3-phosphoglycerate molecules to form high-energy molecules. b-It is the mechanism by which ATP is produced as a result of the flow of electrons down a concentration gradient. c-As hydrogen ions (protons) move through ion channels across the thylakoid membrane, ATP is formed in the stroma. d-The breakdown of water is essential for providing the protons (H+) necessary to drive ATP synthesis during chemiosmosis. f-Six carbon dioxide molecules combine with six 5-carbon compounds to form twelve 3-carbon molecules called 3-phosphoglycerate. 6-Which is the first step in electron transport? a-Light energy excites electrons in photosystem II, releasing an electron into the electron transport system. b-The electron-acceptor molecule transfers the electrons along a series of electron-carriers to photosystem c-Photosystem I transfers the electrons to a protein called ferrodoxin. 7-What term describes the second phase of photosynthesis in which energy is stored in organic molecules such as glucose? a-Calvin cycle b-Krebs cycle c-chemiosmosis 8-What does the diagram show? a-the steps involved in the Krebs cycle b-the steps involved in glycolysis c-the steps involved in electron transport d-the steps involved in the Calvin cycle 9-Plant parts that contain chlorophyll appear green to the human eye because chlorophylls absorb most strongly in the a-blue-green region of the visible light spectrum and reflect light in the red region of the spectrum. b-yellow-orange region of the visible light spectrum and reflect light in the blue-green region of the spectrum. c-violet-blue region of the visible light spectrum and reflect light in the green region of the spectrum. 10-which type of plants fix carbon dioxide into four-carbon compounds instead of three-carbon molecules during the Calvin cycle? A-CAM plants B-C4 plants C-Calvin plants 11-In the final step of the Calvin cycle, which enzyme converts G3P molecules into 5-carbon molecules called ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphates (RuBP)? A-Lactase B-ATPase C-Rubisco 12-Which is true about the CAM pathway? a-CAM plants allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaves only at night when the plants fix carbon dioxide into organic compounds. b-CAM plants fix carbon dioxide into four-carbon compounds instead of three-carbon molecules during the Calvin cycle. c-It is used by plants such as cacti, orchids, and pineapples. d-During the day, CAM plants release carbon dioxide from organic compounds and where enters the Calvin cycle. 13-Which is the series of reactions in which pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide? a-Glycolysis b-Lactic acid fermentation c-Krebs cycle 14-Which happen during the preparatory reaction? a-carbon dioxide is given off by the cell b-NAD+ is converted to NADH c-three-carbon pyruvate reacts with coenzyme A d-citric acid is broken down 15-Which is true about the equation for cellular respiration? a-It shows energy being released. b-It is the same as the equation for photosynthesis. c-Oxygen, water, and glucose are reactants. 16-During which step of the Krebs cycle are electron carriers used? a-Acetyl CoA and citric acid are generated and the cycle continues. b-Acetyl CoA combines with a 4-carbon compound to form a 6-carbon compound known as citric acid. c-Citric acid is broken down, releasing two molecules of carbon dioxide and generating one ATP, three NADH, and one FADH2. 17-Which step in glycolysis involves electron carriers? a-Two phosphate groups, derived from two molecules of ATP, are joined to glucose. b-Two phosphates are added to two molecules of ADP and electrons and hydrogen ions (H+) combine with two NAD+ molecules to form two NADH molecules. c-Two 3-carbon compounds are converted into two molecules of pyruvate. At the same time, four molecules of ATP are produced. 18-The equation for which process shows the breakdown of glucose to release energy? a-Cellular respiration b-Fermentation c-Photosynthesis 19-What is the role of electron carriers in cellular respiration? a-to produce energy b-to carry glucose through the cell membrane c-to temporarily store energy 20-Which occurs in the cytoplasm and regenerates the cell’s supply of NAD+ while producing a small amount of ATP? a-Fermentation b-Glycolysis c-Cellular respiration 21-In prokaryotic cells that undergo aerobic respiration, the location of electron transport is along the a-cellular membrane. b-mitochondrial membrane. c-cell wall. 22-Select the similarities between lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation. a-Both reactions convert glucose to pyruvate through the process of glycolysis. b-Both reactions convert pyruvate to alcohol and carbon dioxide. c-During both reactions, NADH donates electrons and NAD+ is regenerated. d-Both reactions convert pyruvate to lactic acid. 23-Which describes lactic acid fermentation? Pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide and acetyl CoA. Enzymes convert the pyruvate made during glycolysis to lactic acid. Pyruvate is converted to ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. 24-Which describes how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are related? The products of photosynthesis are the reactants for cellular respiration. The products of cellular respiration are the reactants for photosynthesis. Cellular respiration releases oxygen into the atmosphere. The oxygen is then used by plants to carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthesis releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. The carbon dioxide is then used by organisms to carry out cellular respiration. 25-Yeast and some bacteria convert pyruvate to ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. This process is called alcohol fermentation. lactic acid fermentation. cellular respiration. 26-Select the three main stages of the cell cycle. Mitosis Interphase Cytokinesis Gap 2 Synthesis 27-For most normal, actively-dividing animal cells, the cell cycle takes approximately 1 year. 12 to 24 minutes. 12 to 24 hours. 8 days. 28-What is formed when the phosphate groups in DNA create a negative charge, which attracts the DNA to the positively charged histone proteins? nucleosome centromere chromatin 29-Which are the primary stages of the cell cycle? Interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis G1, Synthesis, G2 Interphase, G1, Synthesis Mitosis, Synthesis, Cytokinesis 30-Which is the stage of the cell cycle during which the cell grows, develops into a mature, functioning cell, and duplicates its DNA in preparation for division? mitosis cytokinesis interphase 31-Which are the stages of interphase? G1, S, and G2 G1, mitosis, and S synthesis, mitosis, and G2 32-Which term describes the cycle of growing and dividing by which cells reproduce? synthesis interphase and mitosis cytokinesis cell cycle 33-Select events that occur in a cell during interphase. Cells in interphase form nuclei around chromosomes. Cells in interphase divide into two cells. Cells in interphase carry out normal cell functions. Cells in interphase replicate DNA. 34-Which occurs during the S stage of interphase? A cell prepares for the division of its nucleus and takes inventory to make sure it is ready to continue with mitosis. A cell grows, carries out normal cell functions, and prepares to replicate DNA. A cell copies its DNA in preparation for cell division. 35-Which occurs during the G1 stage of interphase? A cell copies its DNA in preparation for cell division. A cell prepares for the division of its nucleus and takes inventory to make sure it is ready to continue with mitosis. A cell grows, carries out normal cell functions, and prepares to replicate DNA. 36-Which occurs during the G2 stage of interphase? A cell copies its DNA in preparation for cell division. A cell grows, carries out normal cell functions, and prepares to replicate DNA. A cell prepares for the division of its nucleus and takes inventory. 37-Which are the four stages of mitosis? Synthesis, interphase, prophase, and metaphase Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase Cytokinesis, interphase, synthesis, and telophase Interphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase 38-Which is the first stage and longest stage of mitosis? Prophase Metaphase Telophase Anaphase 39-Select ways in which mitosis is used in multicellular organisms. In multicellular organisms, the process of mitosis increases the number of cells as a young organism grows to its adult size. Multicellular organisms use mitosis as part of an immune system response to cancer. Multicellular organisms use mitosis to replace damaged cells. 40-All of the following events occur during prophase except: the nucleolus disappears the nuclear membrane disintegrates the chromosomes arrive at the poles of the cell and begin to decondense the spindle apparatus begins to form between the poles 41-The stage of the cell cycle during which the cell's nucleus and nuclear material divide is interphase. cytokinesis. mitosis. 42-Select the events that occur during prophase. The cell’s chromatin condenses into chromosomes. The nuclear membrane disintegrates. The sister chromatids are pulled toward the center of the cell. Spindle fibers form in the cytoplasm. The sister chromatids separate into two identical chromosomes. The nucleolus disappears. 43-Which structure is made of spindle fibers, centrioles, and aster fibers? Spindle apparatus Nuclear envelope Sister chromatids 45-Which are structures that contain identical copies of DNA? Centromeres Spindle apparatuses Sister chromatids 46-Which is the structure at the center of the chromosome where the sister chromatids are attached? Spindle apparatus Centromere Centriole 47-During which stage of mitosis are the chromatids are pulled apart? anaphase prophase telophase metaphase 48-Which stage of mitosis is represented by the illustration? Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 49-During which phase of mitosis are sister chromatids pulled by motor proteins to the cell's equator? Metaphase Prophase Telophase Anaphase 50-Which events occur in a cell during telophase? The chromosomes arrive at the poles of the cell and begin to relax, or decondense. Two new nuclear membranes begin to form and the nucleoli reappear. The microtubules of the spindle apparatus begin to shorten. The sister chromatids are pulled by motor proteins along the spindle apparatus. The spindle apparatus disassembles and some of the microtubules are recycled by the cell to build various parts of the cytoskeleton. V-Short essay questions 1-Relate the structure of a chloroplast to the stages of photosynthesis. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2-Which process does not occur in the mitochondria? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 3-In cellular respiration, where do the electrons in the electron transport chain originate? What is the final destination of the electrons? __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4-Identify how many carbons from one glucose molecule enter one round of the Krebs cycle. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5-Explain the role of mitosis in the processes of growth and repair. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6-Summarize the role of the spindle apparatus during cell division. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7-Summarize the function of each structure in mitosis. A-centromeres: _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ B-microtubules: _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ C-motor proteins: _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8-Summarize the role of cyclins. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9-Explain how the cancer cell cycle is different from a normal cell cycle. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VI-Use your book to define each vocabulary term. + thylakoid/ granum/ stroma /pigments / NADP /Calvin cycle/rubisco VII-Read the definitions below and write the correct vocabulary term in the blank. anaerobic process/ glycolysis/ aerobic process/ Krebs cycle/ fermentation/ aerobic respiration Compare light-dependent and light-independent reactions by putting each phrase into the correct part of the Venn diagram. light-dependent BOTH light-independent Compare two alternative photosynthesis pathways. Identify plants that use each pathway. Pathway: C4 pathway Pathway: CAM pathway Compare and summarize the three stages of cellular respiration. Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Model the stages of mitosis. Draw and label a cell in each stage, name each stage, and describe what is happening.