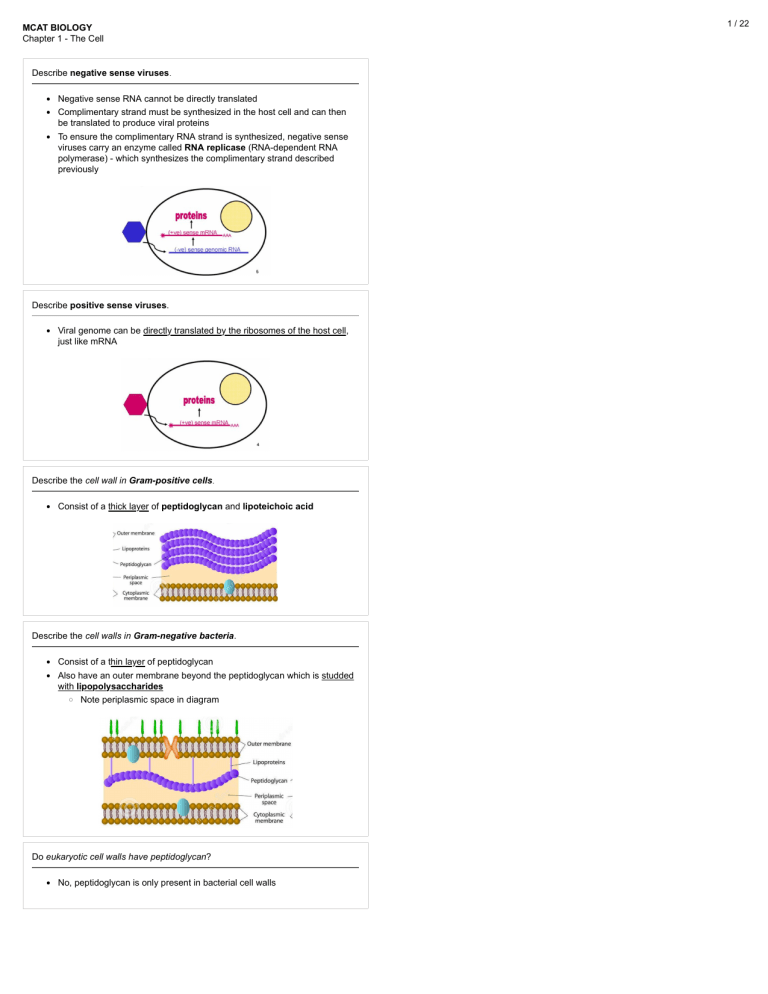
MCAT BIOLOGY Chapter 1 - The Cell Describe negative sense viruses. !" Negative sense RNA cannot be directly translated !" Complimentary strand must be synthesized in the host cell and can then be translated to produce viral proteins !" To ensure the complimentary RNA strand is synthesized, negative sense viruses carry an enzyme called RNA replicase (RNA-dependent RNA polymerase) - which synthesizes the complimentary strand described previously Describe positive sense viruses. !" Viral genome can be directly translated by the ribosomes of the host cell, just like mRNA Describe the cell wall in Gram-positive cells. !" Consist of a thick layer of peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid Describe the cell walls in Gram-negative bacteria. !" Consist of a thin layer of peptidoglycan !" Also have an outer membrane beyond the peptidoglycan which is studded with lipopolysaccharides #" Note periplasmic space in diagram Do eukaryotic cell walls have peptidoglycan? !" No, peptidoglycan is only present in bacterial cell walls 1 / 22 2 / 22 Do prokaryotes contain a cytoskeleton? !" Yes, a primitive simple one Do prokaryotic cells have organelles? !" Yes, just not membrane-bound organelles !" Have ribosomes How are viral progeny released? !" Through cell death, lysis, or extrusion How do bacteria carryout the electron transport chain without mitochondria? !" Use their own cell membrane to house the ETC enzymes How do bacteria get so much genetic variability? !" Transformation, transduction, and conjugation !" Note: Not binary fission How do prokaryotic ribosomes contrast with eukaryotic ribosomes? !" Prokaryotic ribosomes are made of a 30S and a 50S subunit !" Eukaryotic ribosomes are made of a 40S and a 60S subunit How do the concentration of organelles in different cell types vary? !" Concentration of organelles is different from cell type to cell type !" Differences are functional !" Ex. cells that need a lot of energy have a lot of mitochondria, cells that secrete a lot have high RER and golgi apparatus 3 / 22 How do viruses infect cells? !" Attach specific receptors !" Enter the cell by: #" Fusing with the plasma membrane #" Being brought in by endocytosis #" Injecting their genome into the cell How does a lysosome digest material? !" Lysosomes must interact with a membrane-bound carrier of some sort (usually something ending in -some) & fuse with vesicles to exert their effects! !" Fuses its membrane with the carrier !" Injects its hydrolytic enzymes into the new macrostructure !" Digests material inside carrier How does a prion commonly function? !" Causes conversion of α-helix to β-sheet in other proteins !" Decreases the solubility of the protein and increases the cell's ability to degrade the protein !" Leads to aggregates that kill you How does the environment in the nucleus compare to the environment of the rest of the cell? !" Environment in the nucleus is separate and distinct from the environment in the rest of the cell !" Because the nuclear membrane is selectively permeable How is the DNA of prokaryotic cells stored? !" Prokaryotic DNA exists as a single, circular molecule - which floats in a region of space known as the nucleoid region !" Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus (membrane-bound organelle) In what 3 ways are Archaea similar to Eukarya? 1. Start translation with methionine like Eukarya 2. Contain similar RNA polymerases to Eukarya 3. Associate their DNA with histones like Eukarya In what 3 ways are Archaea similar to bacteria? !" Have a singular circular chromosome !" Divide by binary fission or budding !" Share a similar overall prokaryotic structure to bacteria Infection with one strain of phage generally makes bacteria less susceptible to superinfection. The nuclear envelope permits the separation of these two steps of the central dogma of biology: !" Transcription and Translation 4 / 22 What are cristae? !" Infoldings of the inner mitochondrial membrane !" Foldings increase the surface area available for electron transport chain enzymes What are high frequency of recombination (Hfr) cells? !" Sex factor plasmid that has integrated into host chromosomal DNA through process like transformation !" When sex factor plasmid gets incorporated into bacterial genome, it will attempt to replicate and transfer entire genome during conjugation, but bridge usually breaks before it can What are lysosomes? !" Membrane-bound structures containing hydrolytic enzymes !" Found floating in the cell's cytoplasm What are nuclear pores? !" Allow selective two-way exchange of material between the cytoplasm and the nucleus !" Doors into and out of the nucleus What are plasmids? !" Small pieces of circular DNA, usually acquired from the environment !" Don't carry critical genetic information, but can sometimes carry genes that provide the bacterium an evolutionary advantage #" Ex. antibiotic resistance What are some examples of connective tissues? !" Bone !" Cartilage !" Tendons !" Ligaments !" Fat tissue !" Blood What are tail fibers? !" Extensions of a bacteriophage that allow it to recognize and connect to target cells What are the 2 microtubule organizing centers of the cell? !" Centrosome !" Basal body of flagellum or cilia 5 / 22 What are the 2 types of bacterial cell wall? 1. Gram Positive 2. Gram Negative What are the 2 types of single-stranded RNA viruses? 1. Positive Sense 2. Negative Sense What are the 3 components of bacterial flagella? 1. Filament 2. Basal Body (Apparatus) 3. The Hook What are the 3 domains of life? 1. Archaea 2. Bacteria 3. Eukarya What are the 3 forms of genetic recombination seen in bacteria? 1. Transformation 2. Conjugation 3. Transduction What are the 3 functions of the peroxisome? 1. Important in the breakdown of long chain fatty acids (β-Oxidation), because of their hydrogen peroxide 2. Participate in the synthesis of phospholipids 3. Contain some enzymes for the Pentose Phosphate Pathway What are the 3 shapes of bacteria? 1. Cocci 2. Bacilli 3. Spirilli What are the 3 shapes of epithelium? 1. Squamous 2. Cuboidal 3. Columnar 6 / 22 What are the 3 structural components of the cytoskeleton? 1. Microfilaments 2. Microtubules 3. Intermediate Filaments What are the 3 types of anaerobes? 1. Obligate anearobe 2. Facultative anaerobe 3. Aerotolerant anaerobe What are the 3 types of layering found in epithelial cells? 1. Simple 2. Stratified 3. Pseudostratified What are the 4 stages of bacterial growth? 1. 2. 3. 4. Lag Phase Log Phase Stationary Phase Death Phase What are the 4 steps of a Gram stain? !" Stain the bacterium with crystal violet !" Add iodide, which binds the crystal violet and traps it in the cell !" Add ethanol to disrupt the membrane and wash the crystal violet out #" In Gram-positive cells, the thick layer of peptidoglycan will withstand the ethanol and keep the violet in #" In Gram-negative cells, the thin layer of peptidoglycan will be washed away (along with the violet color) !" Bacterium is counterstained with Safranin (pink) What are the 4 tissue types? 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Connective Tissue Muscle Tissue Nervous Tissue 7 / 22 What are the 9 key differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? Prokaryotes 1 Eukaryotes DNA bound to protein (histones) 2 Circular DNA Linear DNA 3 ~ No Introns ~ Has Introns 4 ø Nucleus Has Nucleus 5 ø MembraneBound Membrane-Bound 6 30S, 50S Ribosomes 40S, 60 S Ribosomes 7 Binary Fission Mitosis, Meiosis 8 Single Chromosome (Haploid) Paired Chromosomes (Diploid/etc.) 9 Smaller (~1-5 µm) Larger (~10-100 µm) What are the characteristics and 3 roles of intermediate filaments? !" Intermediate filaments - diverse group of filament proteins #" Ex. keratin, desmin, vimentin, and lamin 1. Able to withstand a lot of tension, which makes the cell structure more rigid and is important in the overal maintenance of the cytoskeleton 2. Anchor organelles to certain locations in the cell 3. Important in cell-cell adhesion. What are the characteristics and 3 roles of microfilaments? !" Microfilaments - solid polymerized rods of actin 1. When organized into bundles and networks, actin filaments provide resistance to compression and fracture for the cell 2. Actin filaments can also generate force for movement by interacting with myosin 3. Actin Filaments are important for the formation of the cleavage furrow in mitosis/meiosis (cytokinesis) #" Accomplished by an actin ring which forms at the site of division between cells #" Ring contracts #" Cell gets pinched into two 8 / 22 What are the characteristics and 3 roles of microtubules? !" Microtubules - hollow polymers of tubulin proteins 1. Radiate throughout the cell, providing pathways along which vesicles can travel #" Accomplished by motor proteins like kinesin and dynein, which travel along the microtubules and drag vesicles with them 2. Important in the structures of cilia and flagella 3. Centrioles are composed of microtubules and use them to exert their effects during mitosis What are the characteristics of Archaea? !" Single-celled organisms that look like bacteria, but have genes and metabolic pathways that are more similar to eukaryotes !" Historically considered extremophiles (high temperature, high salinity, no light) !" Notable for their ability to employ chemosynthesis, an ability to generate energy from inorganic compounds like sulfur and nitrogen What are the components of viruses? !" Genetic material !" Protein coat, also known as capsid !" ~ Lipid-containing envelope What are the four tenets of cell theory? 1. 2. 3. 4. All Living things are composed of cells. The cell is the basic functional unit of life. Cells arise only from preexisting cells. Cells carry genetic information in the form of DNA. This genetic material is passed on from parent to daughter cell. What are the functions of the centriole? !" Organizing center for the microtubules within a cell !" Play an important role in the separation of chromosomes during mitosis #" Responsible for the correct division of DNA #" In prophase, centrioles migrate to opposide poles of the cell and begin to form spindle fibers What are the functions of the epithelial tissues? !" Cover the body and line its cavities !" Being exterior tissues, provide protection against infection and dessication (drying out) !" In some tissues, epithelial cells are also involved in absorption, secretion, and sensation 9 / 22 What are the three places an endosome can transport material to? 1. To-from plasma membrane 2. To lysosomes 3. To trans-golgi What are the two functions of the mitochondria? 1. Produce chemical energy in the form of ATP through the Citric Acid Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain 2. Can induce apoptosis by releasing Electron Transport Chain enzymes into cytoplasm What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum? !" Rough ER and Smooth ER What are virions? !" Viral progeny after replication What are viroids? How do they function? !" Contain a very short, circular single-stranded RNA that usually infects plants !" Bind to RNA sequences or the genes themselves to silence genes #" Result in metabolic and structural changes or cell death !" Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is an example of a human viroid that needs the hepatitis B virus (HBV) to exert its silencing effect What color do Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterium appear after Gram staining? !" Positive - Purple !" Negative - Pink What does it mean for a bacterium to be bacilli? !" Bacilli bacteria are shaped like rods 10 / 22 What does it mean for a bacterium to be cocci? !" Cocci bacteria are shaped like small spheres What does it mean for a bacterium to be spirilli? !" Spirilli bacteria are shaped like long spirals What does it mean that mitochondrion are semi-autonomous? !" Semi-Autonomous - can do a couple of functions on their own, independent from the cell !" Mitochondria: 1. contain some of their own genes (in the form of circular DNA strands) and have their own ribosomes (similar in size to prokaryotic ribosomes) 2. can divide independently of the cell as a whole (by performing binary fission) What does it mean to be a male/donor bacterium? !" F+ cell !" Possess F (fertility) factor/sex factor (plasmid) !" Can construct a conjugation bridge and share genetic information What does it mean to be an female/recipient bacterium? !" F- cell !" Does not possess F (fertility) factor/sex factor (plasmid) !" Can accept genetic information from donor cell via a conjugation bridge What does it mean to be columnar epithelium? !" Composed of long, thin, column shaped cells What does it mean to be cuboidal epithelium? !" Composed of cube shaped cells 11 / 22 What does it mean to be pseudostratified epithelium? !" Cells appear to be stratified, but are actually all attached to a basement membrane like simple epithelium cells What does it mean to be simple epithelium? !" Consists of a single layer What does it mean to be squamous epithelium? !" Flat, scale like epithelial cells What does it mean to be stratified epithelium? !" Consists of multiple layers What does it mean when we say epithelial cells are polarized? !" One side of an epithelial cell will be attached to underlying structural cells and the other side will be exposed to the lumen of an organ or the outside world, because epithelial cells cover the body and line its organs !" Two sides of the epithelial cell are different, because of these dramatically different environments #" Call this phenomenon polarization !" Transport across a cell is possible because the membrane has transport systems on one side that are different from the other side #" Means that epithelial cells are polarized What happens if a lysosome releases its enzymes? !" Enzymes will begin to break the cell down from the inside out in a process known as autolysis 12 / 22 What is a bacteriophage? !" Viruses that specifically target bacteria What is a capsid? !" Protein coat in a virus What is a centriole? !" Hollow structure composed of nine triplets of microtubules !" Involved in microtubule organization in the mitotic spindle What is a centrosome? !" Region of the cell where the centrioles are found What is a chromosome? !" DNA molecule with some or all of the genetic information of a cell What is a cilia? !" Projections from a cell that are involved in movement of materials along the cell's surface !" Ex. cilia in the respiratory tract will undulate in order to move mucus. What is a eukaryotic cell? !" Cells that have nuclei and membrane-bound organelles What is a facultative anaerobe? !" Bacteria that can switch between anaerobic and aerobic metabolism depending on the environment 13 / 22 What is a flagella? !" Structures involved in the movement of the cell itself !" Achieve this by spinning and flailing, generating force for movement What is a histone? !" Protein in the nucleus around which eukaryotic DNA winds !" Helps organize the DNA What is a lumen? !" Inside space of any hollow tubular structure What is a mitochondrion? !" Double-membraned organelle !" Contains inner and outer membrane !" Inner membrane - contains molecules enzymes for the e- transport chain used for ATP generation !" Outer membrane - serves as a selective barrier between the cytosol and the inner environment of the mitochondrion What is a peroxisome? !" Single membrane bound organelle containing hydrogen peroxide !" Hydrogen peroxide is generated with the help of a crystalline core What is a prokaryotic cell? !" Cells that have no nuclei What is a provirus or prophage? !" Latent piece of viral genome that has been integrated into the host's genome 14 / 22 What is a retrovirus? !" Enveloped single-stranded RNA viruses that carry an enzyme called reverse transcriptase #" Reverse transcriptase enzyme synthesizes DNA from RNA, which gets integrated into the host genome #" DNA can then be integrated into genome !" HIV is the most famous retrovirus. What is a sex factor? !" Plasmid that allows bacterium to form sex pili with which they can conjugate to other bacteria What is a sex pilus? !" Appendages that F+ bacterium use to form conjugation bridge What is a tail sheath? !" Long, thin part of a bacteriophage !" Can act like a syringe, injecting the genetic info into the bacterium What is a transposon? !" Genetic elements that are capable of inserting and removing themselves from the host genome What is a vesicle? !" Umbrella term for small membrane bound sacs !" Lysosomes, endosomes, exosomes, etc. are all examples of vesicles What is a virulence factor? !" Plasmid that specifically makes the bacterium more pathogenic 15 / 22 What is an aerotolerant anaerobe? !" Bacteria that cannot use oxygen in metabolism, but are not harmed by the presence oxygen in the environment What is an anaerobe? !" Any bacterium that doesn't need oxygen to survive What is an endosome? !" Endocytic vesicle that pinches off from the membrane during endocytosis What is an episome? !" Plasmid that can integrate itself into the host bacterium's genome What is an obligate aerobe? !" Bacterium that requires oxygen to survive What is an obligate anaerobe? !" Bacterium that dies in the presence of oxygen and therefore needs a nonoxygen environment to survive What is an organelle? !" Any specific sub unit within the cell that has a specialized function !" Functions range from generating energy, protecting the cell, digesting things, transporting material, etc. What is apoptosis? !" Intentional/programmed cell death !" Cell dies because it was told to die and it listened, not because it was randomly killed !" May occur via apoptotic signals or preprogramming What is bacterial conjugation? !" Bacterium forms a conjugation bridge with another bacterium and shares genetic information (including the sex factor) !" Sex factor is shared either through a plasmid (from F+ cell) or a portion of the donor's genome (from Hfr cell) !" With sex factor, recipient can then form a bridge with other bacteria 16 / 22 What is bacterial transduction? !" Virus accidentally traps the genetic information of one bacterium in itself and then incorporates that genetic information into the genome of another bacterium What is bacterial transformation? !" Bacterium picks up foreign genetic material and integrates it into its own genome What is binary fission? !" Simple form of asexual reproduction seen in prokaryotes !" Prokaryote copies its genetic information and then splits into two What is chemotaxis? !" Ability of a cell to detect and move towards (chemoattract) or away (chemorepellent) from chemical stimuli What is cytoplasmic/extranucleur inheritence? !" Transmission of genetic material independent of the nucleus #" Mitochondria 17 / 22 What is exocytosis? !" Material is packaged into a secretory vesicle !" Secretory vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane !" Contents of the secretory vesicle are released outside of the cell What is parenchyma and of which tissue type is it usually comprised? !" Functional parts of an organ #" Ex. nephrons in the kidney or acid producing cells in the stomach !" Usually made up of epithelial cells What is rough ER? What is its function? !" Rough ER - ER studded with ribosomes !" Ribosomes take in ingredients from the cytosol, but secrete their proteins directly into the lumen of the rough ER !" Ability to make proteins that are protected from the cytosol is useful !" Rough ER proteins - usually sent to smooth ER, where they are packaged and sent to the Golgi apparatus What is smooth ER? What are its 3 functions? !" ER that takes on a tubular form !" Has no ribosomes in its membrane 1. Where lipids are synthesized (ex. the phospholipids in bilayers and steroids) 2. Detoxifies certain drugs and poisons 3. Proteins that were synthesized into the rough ER travel to the smooth ER so they can be packaged and transported to the Golgi apparatus What is superinfection? !" Simultaneous infections What is the Golgi apparatus' function? !" To receive materials from the ER and modify these materials by adding various functional groups !" Functional groups serve to both modify the function of the materials and to direct them to certain locations in the cell !" Once the material has been modified and has a location-determining functional group, the material will leave the golgi apparatus in an appropriate vesicle and travel to its intended location !" Intended location can be inside the cell, outside the cell, or back to the ER What is the Golgi apparatus? !" Series of stacked membrane bound sacs inside of the cell 18 / 22 What is the bacterial flagellum filament? !" Long hollow, helical structure composed of flagellin What is the basal body? !" Complex structure that anchors the flagellum to the membrane and provides the motor force necessary to activate the flagellum What is the basement membrane? !" Underlying layer of connective tissue to which groups of epithelial cells will be attached !" This is so the epithelial cells stay close together and can remain a cohesive unit What is the cell envelope? !" Name for all of the layers of the cell from the membrane and extending outward !" Ex. #" In bacteria with a cell wall and a capsule, the envelope would be the membrane, the cell wall, and the capsule #" In bacteria without a capsule, the envelope refers just to the membrane and the cell wall. What is the cell wall? What organisms have them? !" Rigid structure that forms the outer barrier of the cell !" Found in almost all prokaryotes and in certain eukaryotes (plants, algae, fungi) What is the cytoskeleton? !" Large network of 3 structural components that provides shape and structure to the cell !" Structural components also serve as paths by which things can be transported to various locations in the cell 19 / 22 What is the death phase? !" Bacteria have completely consumed nearby resources and begin to quickly die out due to starvation What is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)? !" Series of interconnected membranes that are contiguous with the nuclear envelope. What is the extracellular matrix? !" Vast collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provide structural and biochemical support to the individual cells within a tissue !" Allows cells to associate and communicate with one another without being directly attached What is the function of connective tissue? !" Support the body and provide a framework for the epithelial cells to carry out their function !" Secrete the various molecules that make up the extracellular matrix, such as collagen and elastin What is the function of lysosomes? !" To digest both foreign material (ingested by endocytosis) that has been brought into the cell and damaged/uneeded organelles !" Also degrades misfolded proteins What is the function of the cytosol? !" Suspends the organelles !" Allows diffusion of molecules throughout the cell 20 / 22 What is the hook? !" Connects the filament and the basal body in order to facilitate the motion in the filament, which propels the bacterium forward What is the intermembrane space? !" Space between the outer and inner membrane of the mitochondrion What is the lag phase? !" Bacteria are adapting to the environmental conditions What is the log phase? !" Bacteria have adapted to the environment and start to grow exponentially What is the lysogenic cycle? !" 1 of 2 possible life cycles of a bacteriophage (way it can spread) !" In the lysogenic cycle, the bacteriophage incorporates itself into the host genome as a provirus or prophage #" Virus will be replicated as bacterium reproduces $" Each daughter cell will carry the information to make viruses #" Provirus can: $" Remain in genome indefinitely or $" Leave the genome in response to a stimulus and enter the lytic cycle What is the lytic cycle? !" 1 of 2 possible life cycles of a bacteriophage (way it can spread) !" In the lytic cycle, the cell's machinery is hijacked to produce new viruses #" Viruses accumulate #" Once host cell is swollen, cell lyses #" Other bacteria can be infected !" Viruses in this cycle are said to be virulent What is the mitochondrial matrix? !" Space inside the mitochondrion's inner membrane 21 / 22 What is the nuclear membrane? What does it contain? !" Double membrane the surrounds the nucleus !" Contains nuclear pores !" Also called the nuclear envelope What is the nucleolus? !" Structure in the nucleus that synthesizes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) !" Appears as a large dark spot in the nucleus What is the nucleus? !" Control center of the cell !" Surrounded by a double-membrane envelope !" Houses all of our genetic information and machinery What is the order of taxonomy from most general to most specific? !" Domain > Kingdom > Phylum > Class > Order > Family > Genus > Species #" Mnemonic: Kids Play Cod On Fuzzy Green Sofas) What is the restriction on bacterial conjugation? !" F+ Bacteria can only conjugate to F- Bacteria !" F+ Bacteria cannot conjugate with other F+ Bacteria What is the shared structure of flagella and cilia in eukaryotic cells? !" 9 + 2 structure - 9 doublets of microtubules surrounding a central doublet. What is the stationary phase in bacterial growth? !" Bacteria have reduced resources to the point where they are starting to run out and can no longer grow as quickly What is the stroma and of which tissue type is it usually composed? !" Support structure of an organ upon which the parenchyma depends !" Made of connective tissue 22 / 22 What is viral extrusion? !" Virus leaves a cell by exocytosis, instead of just killing the cell !" Keeps the host cell alive and allows for the continued use of the host cell by the virus #" Virus in this state are said to be in the productive cycle What is viral lysis? !" Virus kills the host cell !" Host cell spills out its contents, including the virus, which goes off to infect new cells !" Disadvantagous because cell can't make any more virions What kind of genetic information can viruses carry? !" Basically any kind !" Genetic info in viruses can be linear or circular, DNA or RNA, and singlestranded or double-stranded What kinds of proteins are usually found in the rough ER? !" Proteins that are destined for secretion !" Proteins that are destined for integration into a membrane Which bacterial recombination process is the only one that requires a vector? !" Transduction