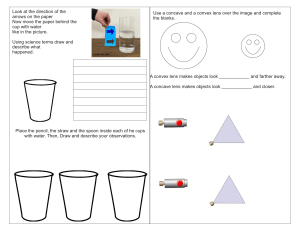
LENSES LEARNING OBJECTIVE • To draw and use ray diagrams for the formation of a real image by a converging lens. • To describe the characteristics of an image. KEY WORDS A real image A virtual image Inverted Diminished STARTER What are the Factors that affect the image formed by a lens? Type of lens The Distance between the object and the lens CONVERGING LENS - REAL IMAGE • Lenses can be used to form images of objects placed in front of them • The location (and nature) of the image can be found by drawing a ray diagram: THREE KEY RULES FOR CONVEX RAY DIAGRAMS • Light passing through the centre of a lens continues through in a straight line. • Light travelling parallel to the principal axis is refracted by the lens so that is passes through the principal focus on the other side. • Light passing through the focus into the lens comes out travelling parallel to the principal axis. • The image forms where the rays cross. • If the object is far away, the image formed is much closer to the lens, smaller, inverted and real (the rays do cross over) • If the object is much closer to the lens, the image formed is very different. CASE-1 : Object at “infinity” Infinity simply means “far away”. No image Object NOTE Since the object is at “infinity”, all rays arrive parallel. No image formed (All rays pass through F) Click Note-2 A ray that goes through the Centre goes right through. CASE-2 : Object Object just beyond NOTE In order to establish 2F’ an image point, all we need are two Note-1 intersecting rays. A ray that comes parallel is refracted through F. Note-3 Image A ray that goes through F’ is refracted parallel. Image is real (formed by refracted rays) Inverted (upside down) Reduced (smaller than object) Located between F and 2F Nearer to the lens than the object This ray is extra in locating the image. Click CASE-3 : Object at 2F’ Object Again: In order to establish an image point, all we need are two intersecting rays. Image Image is real (formed by refracted rays) Inverted (upside down) Same size as object Located at 2F This ray is extra. Click CASE-4 : Object between 2F’ and F’ Object Image is real (formed by refracted rays) Inverted (upside down) Magnified (larger than object) Located beyond 2F Image Click CASE-5 : Object at F’ Object No image No image is formed (rays refract parallel) Click CASE-6 : Object is within focal length Image Image is virtual Object (formed by extended rays) Upright Magnified Located on same side as object Click PLENARY Question-1 A lens that is thicker in the middle than at the ends is known as: A Convex lens or a Converging lens. Click Question-2 A lens that is thicker at the ends than in the middle is known as: A Concave lens or a Diverging lens. Click Question-3 For each case below, draw the appropriate lens that will produce the indicated rays. a) Concave (diverging) b) Convex (converging) Click Question-4 How is the image formed by a mirror different from the image formed by a lens? A mirror forms an image by reflection whereas a lens forms a an image by refraction. Click Question-5 For each convex lens illustrated below, draw the image. b) Image Image is real, inverted, same size object and located at 2F. Click