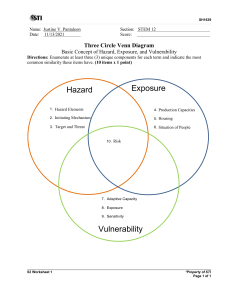
NSTP Notes e. 2. Chapter 1 National Service Training Program (NSTP) Civic Welfare Training Service (CWTS) Literacy Training Service (LTS) NSTP - 3. Required course mandated by law Prepares and trains you to respond to present-day and future challenges - Preparation and opportunity to improve yourself to be of service to others - Chance to be socially involved “The youth is the hope of the motherland” – Jose Rizal History of NSTP Year Significant Happening 1912 Philippine Constabulary started Military Training in UP 1922 1st ROTC Unit in UP 1936 1939 Commonwealth Act 1 (National Defense Act Pres. Quezon; Exec. Order #207 1944 ROTC grads in WWII 1980 Pres. Marcos; PD #1706, National Service Law: Civic Welfare Service, Law Enforcement Service, Military Service Pres. Aquino; Memo Order #11; suspending NSL Expanded ROTC; not required anymore Anomalies, reports on hazing, clamor for abolition of ROTC Mark Welson “Baron” Chua, exposed irregularities in the program; National Service Training Program Law of 2001 or Republic Act 9164 Passage of NSTP Law 1986 1996 Late 1990s 2001 2002 The Good Citizenship Values Filipino Values in the Preamble 1. Pagkamaka-Diyos 2. Pagkamaka-Tao 3. Pagkamaka-Bayan 4. Pagkamaka-Kalikasan 4. Concerns for the family any future generations Pagkamaka-Tao a. Love b. Freedom c. Peace d. Truth e. Justice Pagkamaka-Bayan a. Unity b. Equality c. Respect for Law and Government d. Patriotism e. Common Good Pagkamaka-Kalikasan a. Concern for the Environment Chapter 2 Me as human, unique, and special Humans - Possess dignity Human dignity - Gift only human beings have - Gives worth to our human life - You have worth as a person Selfie to Selfless God created us as unique, special, and rational We are interdependent Selflessness - Caring more about other people’s needs and interest than your own The Thomasian St. Dominic - Born is Calereuga, Spain - Dominican motto “Veritas” which means truth St. Thomas Aquinas - Patron saint of the university - Author of “Summa Theologica SEAL of UST S Servant Leader Specific Categories 1. Pagkamaka-Diyos a. Faith in the Almighty God b. Respect for Life c. Order d. Work E Effective Communicator and Collaborator Show leadership abilities, implement relevant projects, show respect for people Express myself clearly, correctly, and confidently, work productively A L Analytical and Creative Thinker Lifelong Learner with individuals or groups, show profound respect for individual differences Show judiciousness and resourcefulness, engage in research and undertakings, express personal and professional insights Engage in reflective practice, exhibit preparedness and interest, manifest fidelity to the teachings of Christ Thomasian Three Core Values Competence Compassion Commitment Chapter 3 Health-Related Issues in the Philippines Mental Health - Philippine Mental Health Law or RA 11036 HIV and Filipino Youth - 5,000 people newly infected - 2,800 died from AIDs - 66% decline infection among children - Philippine HIV and AIDS Policy Act of 2018 Drug Abuse - Opioids; most harmful drug type - Underage drug abuse is prevalent globally - Common examples o Inhalants o Opiates/Narcotics o Methamphetamine HCl o Marijuana o Ecstasy o Cocaine Current Governance Issues Social Justice - Extra Judicial Killings; deliberate killing Environmental Justice - Reaching 50 degrees Celsius Chapter 4 Disaster Risk Reduction Management (DRRM) - RA 10121 or Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act of 2010 - Disaster = Hazard*Vulnerability*Exposure/ Capacity Types of Hazard 1. Natural Hazard a. Geological or geophysical b. Hydrometeorological c. Biological 2. Anthropogenic hazard a. Technological b. Societal 3. Socionatural hazard Vulnerability - Economic, physical, environmental, material, social, and cultural characteristics Economic/Personal - Lack of biodiversity resources - Lack of control over assets - Limited skills and formal education - Low income - Poor public and mental health - Poverty and inequality Physical/Environment - Decline of risk al regulationg ecosystem services - Overconsumptio n of natural resources - Physically living in an unsafe location - Poor environment management - Unprotected building and infrastructure Social and - Conflicts Organizational between individual and groups - Political divisions Capacity - Combination of all the strengths, attributes and resources available within a family, community, society or organization Economic/Human - Access to Resources essential social services - Adequate income - Healthy population - Literacy and numeracy programs Natural/Physical - Biodiversity Resources resources - Food sustainability - Hazard resistant crops - Safe houses and infrastructure Political/Social - Inclusive Resources leadership - Presence of community organization - Presence of solidarity and social networks - Good kinship ties Exposure - Situation of people, infrastructure, housing, production capacities and other tangible human assets located in hazardprone areas. Disaster Risk - Probability that negative consequences may arise when hazards interact with vulnerable people, property and localities Disaster risk is high if: - The probability of a hazard occurring is high - The vulnerability of the community is high - The exposure of the community to the hazard is high - The capacity of the community is low