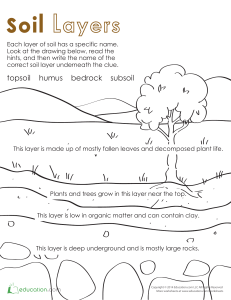
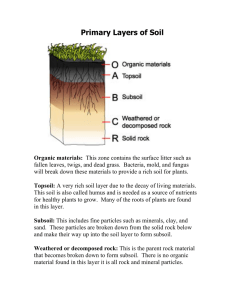
Layers of soil Teacher Jessica López Mejía Goal Identify the layers of the soil and their composition Bedrock • Hard, solid rock beneath surface materials such as soil and gravel • Underlies sand and other sediments on the ocean floor. • Consolidated rock, meaning it is solid and tightly bound Bedrock Weathered parent material • No organic matter here at all. We’re out of reach of all living and dead organisms down here. • It’s all rock particles that are full of minerals. Subsoil • Tree roots and earthworms live here. • Mix of mineral particles and some humus near the top. • Very low in organic matter compared to the topsoil. Subsoil • A lot of soil nutrients are found in this layer. • Deep plant roots come here looking for water. Topsoil • Organic layer. In this layer, plants grow and animals live on top of the soil. The plants keep the soil cool and from drying out. • It has decomposers that recycle the dead plants and animals. • Consists fine textured mineral particles and organic material known as humus. Topsoil Organic layer • Where the plants and animals grow and live. This layer helps keep the soil healthy. • The plants help keep the soil cool and moist. Decomposers such as bugs, bacteria, and fungi break down dead plants and animals. Organic layer What did we learn? • Layers of the soil (organic layer, top soil, subsoil, weathering parent rock, bedrock) • Composition of each layer changes