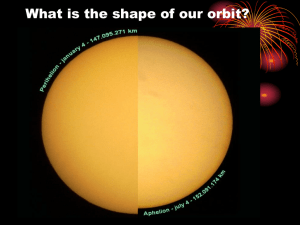
Orbital Mechanics Jeremy Bajado Kepler’s Law Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, in astronomy and classical physics, laws describing the motions of the planets in the solar system. They were derived by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler, whose analysis of the observations of the 16th-century Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe enabled him to announce his first two laws in the year 1609 and a third law nearly a decade later, in 1618. Kepler himself never numbered these laws or specially distinguished them from his other discoveries. Source: https://www.britannica.com/science/Keplers-laws-of-planetary-motion Kepler’s Law (1) planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun as a focus, (2) a planet covers the same area of space in the same amount of time no matter where it is in its orbit, and (3) a planet’s orbital period is proportional to the size of its orbit (its semimajor axis). Source: NASA Solar System Exploration Kepler’s Law Orbital Parameters Calculating the Velocity of a Circular Orbit Calculating the Orbital Period of the Satellite Calculating the Orbital Height of the Satellite Geosynchronous and Geostationary Orbit Circular Orbit Sample Problems