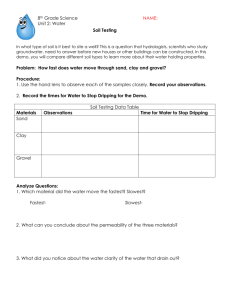
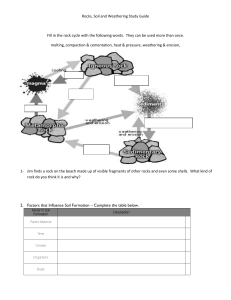
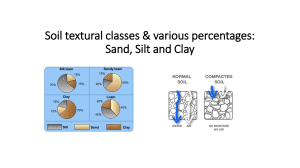
TYPES OF FOUNDATION BEDS - ROCK – undisturbed rock masses DECAYED ROCK – sand and clays resulted from disintegration. LOOSE ROCK – rock masses detached from the ledge. GRAVEL – intermediate; between sand particles and boulders BOULDERS – larger than gravel; transported by water. SAND – non-coherent; smaller than ¼” CLAY – plastic material that resulted from decomposition. HARD-PAN – strong coherent mixture of clay and other cementing material with sand, gravel, and boulders. SILT – deposited from running water (only). MUD – containing vegetable matter and deposited from slow water. MOULD – large proportion of humus LOAM – vegetable matter (only). PEAT – partially carbonized vegetable matter. FILLED GROUND – all artificial fill and some natural fill. SITE INVESTIGATION - Gathering of data to determine the character of materials to be used. METHODS OF EXPLORATION - TEST PITS – for shallow works - TEST BORINGS – for excavations no deeper than the proposed level - LOADING TEST – loading tests of materials forming foundation bed. SOIL MECHANICS - COURSE-GRAINED SOIL – large; visible to the naked eye - FINE-GRAINED SOIL – small particles (ex. silt & clay) STABILITY & STENGTH OF SOIL BED - ALLOWABLE BEARING CAPACITY – max. unit pressure of foundation - DENSITY – bearing capacity of granular soils. (a) SPT – density; (b) MDD – heated. - SHEARING STRENGTH – ability to resist displacement. - WATER TABLE – level beneath with groundwater - NEEDLING & UNDERPINNING – girders are used. (a) NEEDLE – short beam; (b) DEAD SHORE – upright timber EXCAVATION & EARTHWORKING - EXCAVATING – digging the earth LEVELING & GRADING – change land elevation. STABILIZING THE SOIL – compacting soil PROTECTION OF ADJOINING STRUCTURE – law SHORING – process of transferring a portion of load. DEWATERING – lowering of water table. EXCAVATION & EARTHWORKING (members) - SHEET PILES – timbers/ steel is driven side by side. - WALES/ CONTINUOUS HORIZTONTAL BEAMS – sheet piles in place - SOLDIER PILES – steel H-sections driven vertically. - LAGGING – heavy timber planks joined together. - CROSSBRACING OR RAKERS – diagonals that support wales and soldier piles. - TIEBACKS – secured to rock or soil anchors. SITE DRAINAGE - to prevent erosion and collection of excess surface water - SURFACE WATER – rainfall on surface - GROUNDWATER – passes through the subsoil. BASIC TYPES OF SITE DRAINAGE - SUBSURFACE DRAINAGE – underground network of piping (a) CATCH BASINS – retains heavy sediment before it can pass into an underground drainpipe. (b) CULVERTS – channels passing under the road/ walkway. (c) FOUNDATION DRAINAGE TILE – collection and dispersion of septic tank effluent. (d) DRAINAGE TILE – laid end to end as piping in soil to drain. - SURFACE DRAINAGE – grading and surfacing of a site. (a) SHALLOW DEPRESSION – intersection of 2 ground slope (b) DRY WELLS – drainage pits lined with gravel; aka. Absorbing Well (c) ABSORPTION FIELD/ DISPOSAL FIELD – coarse aggregates & distribution pipes through septic tank effluent may seep. (d) ABSORPTION TRENCH – through which septic-tank effluent may flow. SLOPE PROTECTION AND RETAINING STRUCTURES - BINDERS – plant materials that prevent erosion. - RIPRAP – irregularly sized stones placed on the slope of embankment. - CRIBBING – cellular framework of squared steel. - BIN WALL – gravity retaining wall formed by stacking modular. - GABIONS – galvanized or PVC coated wire baskets filled with stones. RETAINING STRUCTURES - Holds the mass of the earth on the uphill side. - GRAVITY RETAINING WALL – resists overturning and sliding. - T-TYPE CANTILEVERED WALL– limited to a height of 20’ (6M) (a) BATTER – backward sloping face of a wall; face leaning forward. - COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL – triangular- shaped cross walls. PAVEMENT - Wearing surface for pedestrians or vehicular traffic in the landscape. - FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT – unit pavers of concrete, brick, or stone laid on sand. - RIGID PAVEMENT – reinforced concrete slabs or mortared paving units TYPES OF PAVERS BRICK PAVER GRID OR TURF BLOCK II. WOOD & LIGHT CONSTRUCTION TYPES OF WOOD FRAMING - BALLOON FRAME – lightest - COMBINATION FRAME – modification of old frame - BRACED FRAME – frames instability (a) GIRT – supports the end of the ceiling joists. - GRAVEL – intermediate; between sand particles and boulders - BOULDERS – larger than gravel; transported by water. - SAND – non-coherent; smaller than ¼” - CLAY – plastic material that resulted from decomposition. - HARD-PAN – strong coherent mixture of clay and other cementing material with sand, gravel, and boulders. - SILT – deposited from running water (only). - MUD – containing vegetable matter and deposited from slow water. - MOULD – large proportion of humus - LOAM – vegetable matter (only). - PEAT – partially carbonized vegetable matter. - FILLED GROUND – all artificial fill and some natural fill.