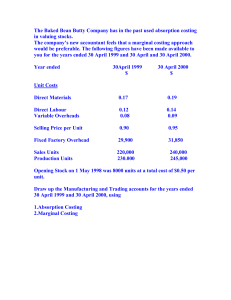
STAR FINANCIAL CONSULTANTS CPA REVIEW CLASSSES MARGINAL AND ABSORPTION COSTING Income statement may be prepared by two methods: Marginal Costing Method Absorption Costing Method MARGINAL COSTING PRINCIPLES Under this method or principle Inventory cost is determined as a sum or total of variable production costs. The variable non-production costs such as (selling costs and commission) plus fixed production and nonproduction are not included in valuation and thus deducted as periodic costs. - Total variable production cost per unit is calculated as follows: Direct material cost per unit XXX Add: Direct labour cost per unit XXX Add: Variable production overhead XXX TVPCU XXX INCOME STATEMENT BY USING MARGINAL COSTING PRINCIPLES (FORMAT) Sales Revenue (Units sold× SPU) XXX Less: Cost of Goods Sold: Opening Stock (Units ×TVPCU) XXX Add: Production Cost (Units produced × TVPCU) XXX Less: Closing Stock (Units ×TVPCU) (XXX) (XXX) Gross Profit XXX Less: Variable Non Production Costs: Selling Cost (XXX) Commission (XXX) XXX Less: Fixed Costs: Production Cost (Budgeted Units ×FOAR) (XXX) Non-Production Cost (marketing and administration cost ) (XXX) NET PROFIT XXX Note: FOAR = Budgeted Fixed Production Cost Budgeted / Normal Production (Units) ABSORPTION COSTING PRINCIPLES Under this method or principle, the cost of inventory is determined as a sum or total of all production costs (both variable and fixed costs). The variable and fixed non-production costs are deducted or treated as periodic costs - The total production cost is calculated as follows: Direct material cost per unit XXX Add: Direct labour cost per unit XXX Add: Variable production overhead XXX Fixed production cost XXX Total production cost per unit (TPCU) XXX STAR FINANCIAL CONSULTANTS CPA REVIEW CLASSSES INCOME STATEMENT BY USING ABSORPTION COSTING PRINCIPLES (FORMAT) Sales Revenue (Units sold× SPU) XXX Less: Cost of Goods Sold: Opening Stock (Units ×TPCU) XXX Add: Production Cost (Units produced × TPCU) XXX Less: Closing Stock (Units ×TPCU) (XXX) (XXX) Gross Profit XXX Under / Over absorption XXX / (XXX) XXX Less: Variable Non Production Costs: Selling Cost (XXX) Commission (XXX) XXX Less: Fixed non production Costs: (marketing and administration cost ) (XXX) NET PROFIT XXX HOW TO DETERMINE / CALCULATE THE OVER OR UNDER ABSORPTION Compare: Budgeted production FOH (Budgeted Production Units × FOAR) Actual production FOH (Actual Units Produced × FOAR) Over / Under Absorption XXX XXX XXX When budgeted production FOH is more than actual production FOH = Over absorption When budgeted production FOH is less than actual production FOH = Under absorption Reconciliation of the Net Profit (By Marginal Costing) and Net Profit (By Absorption Costing) CHANGE in PROFIT = CHANGE in STOCK × FOAR (Absorption Profit – Marginal Profit) = (Closing Stock – Opening Stock) × FOAR Reconciliation of Absorption Profits for Different Periods Absorption Profit 2 – Absorption Profit 1 = (Change in Production) × FOAR + (Change in Sales) × unit profit STAR FINANCIAL CONSULTANTS CPA REVIEW CLASSSES PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON MARGINAL & ABSORPTION COSTIONG QUESTION 1 Laik Company produces a single product which is bottled and sold in cases. Data for the last financial year were as follows. Production 40,000 cases Sales 32,000 cases Selling price per case TZS 600 Costs: Production costs per case: Direct materials: TZS140 Direct labour: TZS120 Variable overhead TZS80 Fixed overhead (budgeted & incurred) TZS 2,160,000 Selling and administration costs: Fixed TZS500,000 Variable 15% of sales revenue There were no opening stock of finished goods and he work in process stock may be assumed to be the same at the end of the year as it was at the beginning of the year. Required: (a) From above information given, prepare income statements for the year under: (i) Absorption costing method (ii) Marginal costing method. (b) Prepare a statement to reconcile the net income or loss obtained under (i) above. QUESTION 2 Tumbi motors limited assembles and sells motor vehicles. It uses an actual costing system, in which unit costs are calculated on a monthly basis. Data relating to the months of March. 2004 is as given below. Particulars Opening inventory 150 Units Production 400 Units Sales 520 Units Selling price per motor vehicle TZS 24,000 Variable cost data: Manufacturing costs per unit produced TZS10,000 Distribution costs per unit sold TZS 3,000 Fixed cost data Manufacturing costs TZS 2,000,000 Marketing costs TZS 600,000 Required (a) Prepare an income statement for Tumbi Limited under (i) Variable costing and (ii) Absorption costing (b) Clearly reconcile the differences between a (i) and (ii) above for the month march STAR FINANCIAL CONSULTANTS CPA REVIEW CLASSSES QUESTION 3 A company sells a single product at a price of TZS. 14 per unit. Variable manufacturing costs per units of the product are TZS6.4. Fixed manufacturing overheads absorbed into the cost of production at a unit rate (based on the normal activity of 20,000 units per period) are TZS92,000 per period. Any over or under absorbed fixed manufacturing overhead balances are transferred to the profit or loss account at the end of each period, in order to establish the manufacturing profit. Sales and production (in units) for the months of March and April 2011 were as follows March April Sales 15,000 22,000 Production 18,000 21,000 Manufacturing profit in March 2011 was reported TZS 35,800 Required: (a) Prepare absorption costing profit statement for April 2011 (b) Prepare marginal costing profit statement for April 2011 (c) Explain, with supporting calculations the reasons for change in profits between March and April where absorption costing is used in each period and reconcile the difference. QUESTION 4 The following data has been extracted from the budget and the standard costing profit statement of Abacus ltd. A company which manufactures and sells a single product. TZS (per unit) Selling price 45,000 Direct material cost 10,000 Direct Wages cost 4,000 Variable production overhand cost 2,500 Budget selling and distribution costs are follows: Variable cost per unit TZS 1,500 Fixed TZS 80,000,000 per annum Budgeted administration costs are TZS 120,000,000 per annum Fixed production overhead costs are budgeted at TZS 400,000,000 per annum. Budgeted normal production is 320,000 units per annum. The following Patten of sales and production is expected during the first six months of year 2010. 1st Quarter January – march 2nd Quarter April – June Sales in units 60,000 90,000 Production in units 70,000 100,000 There is no stock on 1st January 2010 Required: (a) Prepare profit statements for each of the two quarters using. (i) Marginal costing (ii) Absorption costing (b) Reconcile the profits for each of the quarters in (a) above STAR FINANCIAL CONSULTANTS CPA REVIEW CLASSSES QUESTION 5 Keypuzzle limited manufactures a novelty keyring which it sells to conference and event organisers. The keyring comprises a basic metal ring to attach keys and a wooden puzzle which was invented by the managing director and founder of the company, Paul Crean. Having successfully developed and patented the prototype of the keyring, the company commenced production in ennis five years ago. The manufacturing facility has a maximum production capacity of 500,000 keyrings, which is well in excess of current sales. The production director has advised Paul that “it doesn’t make sense not to use the available capacity to produce more keyrings as they will be sold over the coming years”. Consequently, over the past four years the company has produced more key rings than it has sold and has built up a substantial inventory. For its management accounts the company uses variable (marginal) costing and Paul has raised concerns with the management accountant regarding the declining profit levels. It was agreed that the management accountant would prepare the management accounts for the current year and prior year using absorption costing, highlighting the differences compared to variable costing. Unfortunately, the management accountant is ill and has not completed the absorption and variable cost comparison. Information that had been compiled relating to the comparison is shown below. 31 March 2016 31 March 2015 Budgeted annual fixed production overhead TZS105,625 TZS105,625 Sales (units) 350,000 319,500 Opening inventory (units) 19,500 18,000 Closing inventory (units) 22,000 19,500 Direct material (per unit): - Steel ring @ TZS 0.08 - Varnished beech @ TZS 0.12 Direct labour : 4 mins per unit @ TZS 9 per hour Variable overhead : 10% of direct labour cost The Keyring sells for TZS1.95. Direct material and direct labour costs have not increased over the two year period. Fixed production overheads are absorbed based on units of production assuming that the company is operating at 65% of its maximum capacity. The company’s actual annual fixed production overhead is equal to the budgeted amount. Required (a) Show the product cost for one keyring under variable (marginal) costing and absorption costing (b) Prepare management accounts for the year ending 31 March 2016 and 2015 showing profit calculated using: (i) Variable (marginal) costing (ii) Absorption costing (c) Reconcile the profit calculated at (b) (i) and (ii) above. (d) From the perspective of Keypuzzle limited, outline TWO benefits and TWO limitations of using absorption costing. STAR FINANCIAL CONSULTANTS CPA REVIEW CLASSSES QUESTION 6 Dubh DAC is based in Tanzania and manufactures one product, a storage unit made from recycled plastic which sells for TZS58 per unit. Production and sales data for each of the first three months of 2019 are as follows: January February March Sales in units (actual) 4,800 5,000 7,600 Production in units (actual) 5,400 4,800 8,000 Budgeted cost information for each month Product cost: Direct materials: 2 square metres @ TZS4.20 per square metre. Direct labour: 2 hours @ TZS10.25 per hour. Variable production overheads: 50% of direct labour. Actual cost information for each month Fixed production overheads: TZS12,000. Fixed selling overheads: TZS22,500. Sales commission: 10% of sales value. There was no opening inventory at 1 January 2019. Fixed production overheads are budgeted at TZS120,000 per annum and are absorbed into products based on budgeted normal output of 60,000 units per annum. REQUIREMENT: (a) Prepare a profit statement for each of the three months using absorption costing principles. (6 marks) (b) Prepare a profit statement for each of the three months using variable (marginal) costing principles. (8 marks) (c) Present a reconciliation of the profit or loss figures given in your answer to (a) and (b) together with an explanation of the reason for the difference. (3 marks) (d) The managing director of Dubh DAC wants to use variable (marginal) costing principles as the basis for both management accounts and the company’s financial statements. Outline TWO reasons against this course of action. (3 marks) [Total: 20 Marks]