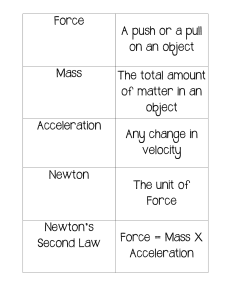
Newton’s Laws A fun way to explore the 3 laws! NAME: _______________________________________________________________ Newton’s Laws Webquest What are Newton’s Three Laws of Motion? Visit the following website: https://www.thoughtco.com/what-are-newtons-laws-of-motion-608324 OR https://tinyurl.com/yb4q3okf First Law: An object ____ ______________ tends to ____________ in motion UNLESS an __________________ _____________________________ acts upon it. In addition, if an object is at _____________ , it will ________________ at rest UNLESS an ______________________ _____________________ acts upon it. This is also known as the Law of __________________. Second Law: When a ______________ acts on an object, it was cause the object to ______________________. The formula is ___________ = ___________ x ______________________________ Third Law: For every ____________________, there is an ____________________ and _____________________ reaction. EXPLORING NEWTON’S FIRST LAW Find out what happens to a roller coaster if forces that we are used to (gravity and friction) are no longer there! http://www.funderstanding.com/educators/coaster/ OR https://tinyurl.com/lo4ompx 1) Without changing any of the settings, click play and watch the roller coaster. What happened to it? __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2) Now change the settings so that there is no gravity- move the indicator all the way to the left. Click play and watch the roller coaster. What happened to it? Why? _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3) Click the “reset” button. Change the settings so that there is no friction and click play. What happened to the roller coaster? Why? ____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4) Click the “reset” button. Change the initial hill so that it is as high as possible and click play. What happened? Why? ________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5) Keeping the hill as high as possible, change the other settings until the roller coaster works. What did you do to be successful? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6) Is there any way to keep the roller coaster on the track if there is no gravity? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ EXPLORING NEWTON’S SECOND LAW How fast will a mass accelerate with different masses, forces, and friction? Click on the ACCELERATION simulation. (The last box) https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/forces-and-motion-basics/latest/forces-and-motion-basics_en.html OR https://tinyurl.com/kdrfxmb Before beginning each simulation, check the boxes next to Forces, Sum of Forces, Values, Masses, Speed, and Acceleration. You can drag the masses on or off the road (a crate will already be there) and set the Friction button. To change the Applied Force, click on the arrows left or right. Double arrows change the force by 50 N; single arrows change the force by 1 N. Find the value of the BLANK box after changing all the other settings. Total Mass Being Pushed Applied Force (N) 50 kg crate 150 N Friction: None, Low, Medium, or Lots Medium 50 kg crate 150 N None 200 kg Fridge 150 N None 100 kg bucket Medium Acceleration m/s2 1.12 m/s2 Choose your own combinations of mass, applied force, and friction for three different situations. Fill in the accelerations. Total Mass Being Pushed Applied Force (N) Friction: None, Low, Medium, or Lots Acceleration m/s2 What happens to the accelerations when the friction is smaller? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Find the same acceleration using different forces and masses. (Example: 2.0 m/s2) Mass Applied Force (N) Friction- None, Acceleration What happens to an object’s acceleration if a force is increased but the mass of the object stays the same? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ EXPLORING NEWTON’S THIRD LAW How can Newton’s cradle demonstrate Newton’s third law? http://www.walter-fendt.de/html5/phen/newtoncradle_en.htm OR https://tinyurl.com/y8qmqyh3 Pull back one ball and let it swing. What happens? _______________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Click “reset”. This time pull back two balls. What happens? _______________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Click “reset.” Now pull back three balls. What happens? ___________________________________________________ Video: Newton’s Third Law of Motion Demonstrated in Space https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZkVU-bj9bDk or https://tinyurl.com/yyhyksxz What was one of the examples given for Newton’s Third Law, or a “force pair,” on Earth or in space? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ In space, what happens to a smaller object (mass 1) when a larger object (mass 2) applies a force to it? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ What happens when two objects of about the same mass apply a force to each other? ___________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ NAME: _____ KEY_______________________________________________________ Newton’s Laws Webquest What are Newton’s Three Laws of Motion? Visit the following website: https://www.thoughtco.com/what-are-newtons-laws-of-motion-608324 OR https://tinyurl.com/yb4q3okf First Law: An object _in_ _motion_____ tends to __stay_____ in motion UNLESS an __external______ _____force____________ acts upon it. An addition, an object at __rest______ will _____remain____ at rest UNLESS an ___unbalanced________ ____force___________ acts upon it. This is also known as the Law of __Inertia_______. Second Law: When a ___force___ acts on an object, it was cause the object to __accelerate_____________. The formula is _force (F)____ = _mass (m)____ x __acceleration (a)_____________ Third Law: For every __action________, there is an ___equal _________ and ___opposite_______ reaction. EXPLORING NEWTON’S FIRST LAW Find out what happens to a roller coaster if forces that we are used to (gravity and friction) are no longer there! http://www.funderstanding.com/educators/coaster/ OR https://tinyurl.com/lo4ompx 1) Without changing any of the settings, click play and watch the roller coaster. What happened to it? The coaster didn’t make it up the second hill. It went backwards down it, and fell going forward through the loop. 2) Now change the settings so that there is no gravity- move the indicator all the way to the left. Click play and watch the roller coaster. What happened to it? Why? The coaster just floats in the air, going left to right. There is no force to pull it down or hold it to the track (no gravity.) 3) Click the “reset” button. Change the settings so that there is no friction and click play. What happened to the roller coaster? Why? The coaster makes it all the way through the loop and over the last hill. It does not lose energy due to the force of friction so it can go further._______________ 4) Click the “reset” button. Change the initial hill so that it is as high as possible and click play. What happened? Why? The coaster flies off the last hill. It had too much kinetic energy, at least enough to overcome the force of gravity at the top of the hill. 5) Keeping the hill as high as possible, change the other settings until the roller coaster works. What did you do to be successful? One way is to increase the loop size and final hill, and increase the amount of friction. 6) Is there any way to keep the roller coaster on the track if there is no gravity? Explain. The only way is to make a new track that is flat. The coaster will only go straight- nothing can push it down if there is no gravity. Even then, if a hill is added, the coaster will fly off. It will make it around a loop though. EXPLORING NEWTON’S SECOND LAW How fast will a mass accelerate with different masses, forces, and friction? Click on the ACCELERATION simulation. (The last box) https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/forces-and-motion-basics/latest/forces-and-motion-basics_en.html OR https://tinyurl.com/kdrfxmb Before beginning each simulation, check the boxes next to Forces, Sum of Forces, Values, Masses, Speed, and Acceleration. You can drag the masses on or off the road (a crate will already be there) and set the Friction button. To change the Applied Force, click on the arrows left or right. Double arrows change the force by 50 N; single arrows change the force by 1 N. Find the value of the BLANK box after changing all the other settings. Total Mass Being Pushed Applied Force (N) 150 N Friction: None, Low, Medium, or Lots Medium Acceleration m/s2 1.12 50 kg crate 50 kg crate 150 N None 3.00 200 kg Fridge 150 N None 0.75 100 kg bucket 300 N Medium 1.12 m/s2 Choose your own combinations of mass, applied force, and friction for three different situations. Fill in the accelerations. Total Mass Being Pushed Applied Force (N) Friction: None, Low, Medium, or Lots Acceleration m/s2 Answers will vary What happens to the accelerations when the friction is smaller? ____Acceleration is faster/higher if friction is lower.____________________________________________________________________________________ Find the same acceleration using different forces and masses. (Example: 2.0 m/s2) (Sample answer) Mass Applied Force (N) 50 kg 100 N Friction- None, Low, Med, Lots None 80 kg 310 N Medium Acceleration 2.0 m/s 2.0 m/s What happens to an object’s acceleration if a force is increased but the mass of the object stays the same? ___The acceleration is a LOT faster. _____________________________________________ EXPLORING NEWTON’S THIRD LAW How can Newton’s cradle demonstrate Newton’s third law? http://www.walter-fendt.de/html5/phen/newtoncradle_en.htm OR https://tinyurl.com/y8qmqyh3 Pull back one ball and let it swing. What happens? ______One ball on the other side will be knocked and swing. The three balls in the middle don’t move._________________________________________________________ Click “reset”. This time pull back two balls. What happens? _______________________________________________ _____This time two balls from the other end will be knocked and swing. The middle ball doesn’t move.________ Click “reset.” Now pull back three balls. What happens? __Same thing, three balls will swing off the other end. The middle ball is always swinging._________________________________________________ Video: Newton’s Third Law of Motion Demonstrated in Space https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZkVU-bj9bDk or https://tinyurl.com/yyhyksxz What was one of the examples given for Newton’s Third Law, or a “force pair,” on Earth or in space? feet push ground/ ground pushes feet, tires push back/ ground pushes forward, ball pushes down/racket pushes up, legs push backwards/wall pushes forward during a flip kick in the pool, thrusters expel air one way/ vehicle steered other way. In space, what happens to a smaller object (mass 1) when a larger object (mass 2) applies a force to it? The smaller object (ball) accelerated away faster; the larger mass barely moved. What happens when two objects of about the same mass apply a force to each other? Both objects accelerated away from each other at about the same speed.