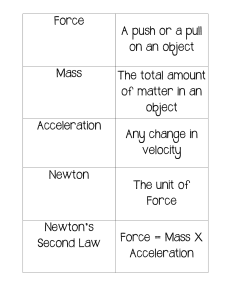
8 Science 8 Quarter 1 – Module 1: Newton’s First and Second Law of Motion (Week 1/Day 1-5) Subject Area – Grade 8 Science Self-Learning Module (SLM) Quarter 1 – Module 1: Newton’s First and Second Laws First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Development Team of the Module Writer:Lalaine M. Biboso, EdD. Editors:Geraldine C. Toledo, Rosalie P.Gillesania, Samuel D. Rosal, Yolka A. Barbecho, Cherilene A. Suscano Reviewers: Sally A. Palomo, Nerissa A. Alfafara Illustrator: Remus Angelo E. Moscoso Layout Artist:Geraldine C. Toledo Cover Art Designer: Reggie D. Galindez Management Team: Allan G. Farnazo, CESO IV – Regional Director Fiel Y. Almendra, CESO V – Assistant Regional Director Romelito G. Flores, CESO V - Schools Division Superintendent Mario M. Bermudez, CESO VI –Assistant Schools Division Superintendent Gilbert B. Barrera – Chief, CLMD Arturo D. Tingson Jr. – REPS, LRMS Peter Van C. Ang-ug – REPS, ADM Peter Van C. Ang-ug – REPS, Science Juliet F. Lastimosa - CID Chief Sally A. Palomo - Division EPS In- Charge of LRMS Gregorio O. Ruales - Division ADM Coordinator Nerissa A. Alfafara – EPS, Science , Edilbert A. Reyes, Ph.D.- Division Science Coordinator Printed in the Philippines by Department of Education – SOCCSKSARGENRegion Office Address: Regional Center, Brgy. Carpenter Hill, City of Koronadal Telefax: (083) 2288825/ (083) 2281893 E-mail Address: region12@deped.gov.ph 8 Subject 8 Quarter 1 – Module 1: NEWTON’S FIRST AND SECOND LAW OF MOTION (Week 1/Day 1-5) Introductory Message For the facilitator: Welcome to the Grade 8 Science Self-Learning Module (SLM) on Newton’s First and Second Law! This module was collaboratively designed, developed and reviewed by educators both from public and private institutions to assist you, the teacher or facilitator in helping the learners meet the standards set by the K to 12 Curriculum while overcoming their personal, social, and economic constraints in schooling. This learning resource hopes to engage the learners into guided and independent learning activities at their own pace and time. Furthermore, this also aims to help learners acquire the needed 21st century skills while taking into consideration their needs and circumstances. In addition to the material in the main text, you will also see this box in the body of the module: Notes to the Teacher This contains helpful tips or strategies that will help you in guiding the learners. As a facilitator you are expected to orient the learners on how to use this module. You also need to keep track of the learners' progress while allowing them to manage their own learning. Furthermore, you are expected to encourage and assist the learners as they do the tasks included in the module. 2 For the learner: Welcome to the Grade 8 Science Self-Learning Module (SLM) on Newton’s First and Second Laws! The hand is one of the most symbolized part of the human body. It is often used to depict skill, action and purpose. Through our hands we may learn, create and accomplish. Hence, the hand in this learning resource signifies that you as a learner is capable and empowered to successfully achieve the relevant competencies and skills at your own pace and time. Your academic success lies in your own hands! This module was designed to provide you with fun and meaningful opportunities for guided and independent learning at your own pace and time. You will be enabled to process the contents of the learning resource while being an active learner. This module has the following parts and corresponding icons: What I Need to Know This will give you an idea of the skills or competencies you are expected to learn in the module. What I Know This part includes an activity that aims to check what you already know about the lesson to take. If you get all the answers correct (100%), you may decide to skip this module. What’s In This is a brief drill or review to help you link the current lesson with the previous one. What’s New In this portion, the new lesson will be introduced to you in various ways such as a story, a song, a poem, a problem opener, an activity or a situation. What is It This section provides a brief discussion of the lesson. This aims to help you discover and understand new concepts and skills. What’s More This comprises activities for independent practice to solidify your understanding and skills of the topic. You may check the answers to the exercises using the Answer Key at the end of the module. What I Have Learned This includes questions or blank sentence/paragraph to be filled in to process what you learned from the lesson. 3 What I Can Do This section provides an activity which will help you transfer your new knowledge or skill into real life situations or concerns. Assessment This is a task which aims to evaluate your level of mastery in achieving the learning competency. Additional Activities In this portion, another activity will be given to you to enrich your knowledge or skill of the lesson learned. This also tends retention of learned concepts. Answer Key This contains answers to all activities in the module. At the end of this module you will also find: References This is a list of all sources used in developing this module. The following are some reminders in using this module: 1. Use the module with care. Do not put unnecessary mark/s on any part of the module. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises. 2. Don’t forget to answer What I Know before moving on to the other activities included in the module. 3. Read the instruction carefully before doing each task. 4. Observe honesty and integrity in doing the tasks and checking your answers. 5. Finish the task at hand before proceeding to the next. 6. Return this module to your teacher/facilitator once you are through with it. If you encounter any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Always bear in mind that you are not alone. We hope that through this material, you will experience meaningful learning and gain deep understanding of the relevant competencies. You can do it! 4 What I Need to Know On February 29, 2020 Philstar reported about 31 students and a driver who were hurt when a jeepney plunged into a 40 – foot ravine in Barangay Olympog in General Santos City. According to the police investigator, the students were on their way home from a trip at the Sanchez Peak. Three of the injured students were confined in the hospital while the others were immediately discharged after receiving first aid (John Unson, Philstar, Feb.29, 2020.) Why did this happen? Who is to be blamed? What should passengers do inside the vehicle? How can we prevent accidents on the road? This module will help you answer these questions. This module was designed and written with you in mind. It is here to help you master the Newton’s First and Second Law. The scope of this module permits it to be used in many different learning situations. The language used recognizes the diverse vocabulary level of students. The lessons are arranged to follow the standard sequence of the course. But the order in which you read them can be changed to correspond with the textbook you are now using. After going through this module, you are expected to: Investigate the relationship between the amount of force applied and the mass of the object to the amount of change in the object’s motion. (S8FE-1a-15) And, specifically you are to: 1. 2. 3. 4. differentiate balanced and unbalanced forces; investigate the effects of force and mass to the motion of the object; relate first law of Newton to the second law; and cite situations in life where Newton’s laws are applied. 5 What I Know Are you excited to learn a new topic today? Before that, you need to answer the pre-test to measure how much you know about the lesson. Directions: Encircle the letter of the correct answer. 1. 2. Which chair will require the most amount of force to get it moved or accelerated? A. a plastic chair with a mass of 2 kg. B. a rattan chair with a mass of 3 kg. C. a wooden chair with a mass of 5 kg. D. a steel chair with a mass of 6 kg. Look at the boys playing tug of war. Assuming that each of the boys can exert a 50N force, who will win the game? A. only one boy B. the two boys 3. C. no movement D. cannot be determined Below are four shoppers. Which of the shoppers require more force to push the cart? A. C. B. D. 6 4. If the force is constant, what will happen to the motion or acceleration of the object if the mass is increased? A. decreased B. increased C. the same D. zero 5. A bus moves along national highway from Koronadal City to General Santos City. A passenger has noticed that over time, he passes the kilometer markers in shorter periods of time. Which statement best describes the motion of the bus? A. the bus is keeping the same direction B. the bus is increasing its speed C. the bus is changing its direction D. the bus is maintaining the same speed 6. What is A. B. C. D. 7. If Josh exerts a force of 3N, and Jun is 6N, what is the net force? A. B. C. D. the net force on girl who is sitting on the chair? 0 1 2 3 6N, 3N, 3N, 9N, left left right left 8. Which of the following could be done to accelerate a moving object? A. apply inertia B. apply a balanced force C. apply an unbalanced force D. apply both balanced and unbalanced forces 9. Which of the following vehicles will come to a complete stop FIRST when the drivers apply brake at the same time? A. the fully loaded ten-wheeler truck B. the van loaded with passengers C. the empty dump trucks D. the small car 7 10. If a van driver suddenly makes a sharp turn, which of the following will likely to happen due to inertia? A. Passengers will slide back and forth. B. Passengers will move backward. C. Passengers will move forward. D. Passengers will slide to the side of the van. 11. Two objects A and B were applied with the same net force. It is observed that the acceleration of object A is two times greater than B. Which of the following is correct? A. Object A has a mass two times greater than B. B. Object has a mass ½ of the mass of object B. C. Object A has a less streamlined shape than object B. D. Object A has more friction than object B. 12. 13. Which of the following indicates that an object is accelerating? A. speeding up B. slowing down C. changing direction D. any of the above Based on the figure below, if the boy number 1 will be able to push the boy number 2 away from him, who exerts greater force? A. boy number 1 B. boy number 2 C. they have the same force D. cannot be determined 14. What Newton’s law is illustrated in the picture below? A. B. C. D. First law only Second law only First and Second laws Third Law only 15. Why should we wear seatbelts in riding a vehicle? A. We should wear seatbelts to maintain our inertia. B. We should wear seatbelts so that our body will not move if we meet an accident or a force is applied to the brake. C. We should wear seatbelts so that we can sleep while travelling. D. We should wear seatbelts so if we are in an accident our body doesn’t keep moving at the same speed and in the same direction that the car was going. 8 Lesson 1 Physics: Newton’s First and Second Laws You are now introduced to your new lesson. This has something to do with your daily activities like household chores, exercises, playing and marketing. The amount of force applied in doing these is a factor to make our motion fast or slow. Example, in arranging your furniture you usually push or pull it. Techniques are important to overcome friction and inertia for a fast movement. In helping drivers pushing their vehicle out of sticky mud or engines stop working, playing tug of war, baseball and soccer games are only few of the many applications of Newton’s first and second law. Before going further, you need to recall first your previous lessons to connect to your new lesson. What’s In You have learned in your previous lessons that the layman’s understanding of a force is that it is a push or a pull which refers to a very specific action. Force acts on an object. This implies that, when we pull or push, there is an object that receives it. The force exerted on the objects has a magnitude and direction. This is called vector quantity. Newton is the unit for force. You also learned about net force which refers to the sum of the forces acting on an object, capable of changing the object’s state of motion. Examples: 1. This ball is acted by forces with different directions. Its net force is equal to 2N, right. The direction of the net force follows the direction of the force of the greater magnitude. 5N 3N ● Net Force = 2N, right. Can you explain why? Answer: The direction of forces is opposite. A 5N force is pointing to the right and the other force is pointing to the left so you need to make one positive and the other negative. 9 2. The second ball is acted by forces of the same directions. The net force is; equal to 8N, left. 3N 5N Net Force =8N, left In this example, both the directions and the magnitudes are combined when adding vectors. Another important concepts you need to be refreshed are the following: When a string, rope or wire pulls on an object, it exerts a contact force which we call Tension Force. MOTION PUSHING FORCE Friction force is the opposing or resisting force between two solid surfaces. FRICTION FORCE The force exerted by a surface (the agent) against an object that is pressing against the surface is called as the Normal Force. 10 These are common forces which you will encounter as you study this module. Now please proceed to your engagement activity. There are four pictures to analyze. The first two pictures are about the competition of strong men showing their amazing strength in pulling the truck. The second set is a scenario at the mall. Please use your observation skills to do what is asked. Activity 1 Force is the key Study the pictures. Give your observations regarding the force exerted by the contestants in pulling the truck and grocery goers in pushing the cart. How did you find the activity? This activity shows that magnitude of force matters in pushing or pulling to move the object. Object with greater mass needs greater force to move it. 11 What’s New The next activity is a game for survival. Technique, cooperation, and unity are needed to win the game. Still force, matters. Find out! Activity 2 Making the balanced, unbalanced I. II. III. Objectives: 1. Differentiate balanced force from unbalanced force 2. Find out the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces when applied to objects at rest or in motion Materials: Colored pencil Bond paper Pentel pen Procedure: 1. The Team A and the Team B are to pull the cart full of groceries to be used during the Enhanced Community Quarantine due to COVID-19. After the final round, the winner will take the groceries home. Study the series of illustrations and be able to determine what makes the winner, win the game. 2. Summarize your observations in table form. Summary of observations Round Total Amount of force exerted by the team Team A (wearing BLUE T-shirt) Team B (wearing RED T-shirt) Round 1 Round 2 Round 3 Round 4 12 Is the force equal? (Yes/No) Will the cart move? (Yes/No) To what direction? THE TEAMS! Team A(Blue Team) – wearing BLUE T-shirt Team B(Red Team)– wearing RED T-shirt Team A/Blue Team versus Team A/Red Team Note: The final round is the basis in determining the winner. FIRST ROUND! 50 N Remember, you need to record the data in the table. 13 SECOND ROUND! 200 NN 200 200NN 200 150 150NN 100NN 100 THIRD ROUND! 14 FOURTH ROUND!- FINAL ROUND, WINNER TAKES ALL! 200 N 250NN 250 Questions: 1. Who wins the game? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______ 2. What strategy did they use to win the game? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _________ 3. What force did the team exert to win the game? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Did you enjoy the activity? Did your chosen team win? In the activity, it shows that balanced forces do not move the object at rest but it is the unbalanced forces cause the motion. Are you excited to do the next activity?. This will give you idea about inertia. In this activity, you will observe the coin falling into the glass without touching it. 15 Activity 3 Investigating Inertia 1. Objectives: 1. Demonstrate Newton’s first law of motion. 2. State Newton’s First law. 2. Materials: empty glass cardboard 1-peso coins (5 pcs or more) plastic ruler 3. Procedure Coin Drop 1. Lay the cardboard on top of the glass. Have one edge of the cardboard a little beyond the rim so you can give that edge a good flick without smacking your fingertip on the glass. Coin moves away Coin 2. Place a coin on top of the cardboard so it’s centered over the glass. 3. Use a finger to flick an edge of the cardboard. You will not flick the cardboard directly from the side. (Do not flick it downwards or upwards by hitting from above or below the cardboard.) Coin falls into glass Figure 1 4. Watch the coin drop straight into the glass! (Refer to the figure 1.) Questions: 1. What happens when you flipped the cardboard? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is Newton’s first law? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 16 How many trials did you make until you succeed in the activity? This was about Newton’s first law introduced by Sir Isaac Newton who is an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author. The activity proves that inertia is the factor to make the object at rest unless acted by an unbalanced force. You found out in the activity that the motion of the object is related to the amount of force applied. In the next activity you will discover what kind of relationship is existing on these variables. This is about Newton’s second law. So, please do it. Activity 4 Simulation of Newton’s Second Law I. Objectives: 1. Determine the relationship of acceleration to the following: a. Mass and acceleration at constant force b. Mass and acceleration at increasing force c. Force and acceleration at constant mass d. Force and acceleration at increasing mass 2. State Newton’s Second Law base on the activity II. Materials: Activity Sheets Calculator III.Procedure: 1. The series of drawings/figures are of 2 sets, Set A and Set B. 2. Fill in the table below for easy analysis of each figure. Table 1. Summary table of the objects’ mass, acceleration, speed, and force Picture number Mass Force applied 1 2 3 4 5 6 17 Speed Acceleration The following illustrations are for your references in doing the activity. Illustrations for analysis Set A Picture 1 The man is pushing the box. The arrows indicate the direction and magnitude of the force applied and the friction. Record the mass, speed, and acceleration in the table. Speed = 35.1m/s Acceleration 8.12 m/s2 FRICTION FORCE APPLIED FORCE 500 N 94 N 50 kg Picture 2 Compare this picture with picture 1. Observe what is added and the force applied. Take a look at the speed and acceleration. Are there any changes? Record the data in the table. Force exerted by the man in pushing = 500N Mass of the man on top of the box= 80kgs Speed = 33 m/s Acceleration 1.97 m/s2 80kg Mass of the box = 50 kg APPLIED FORCE 244 N FRICTION FORCE 50 kg 18 500 N Picture 3 What is the difference of this picture with the previous two pictures? What is increased and what made constant. What happened to the speed and acceleration? Force exerted by the man in pushing = 500N Mass of the man on top of the box= 80kgs 80 kg Speed = 13.9 m/s Mass of the box = 50 kg Acceleration 0.90 m/s2 APPLIED FORCE FRICTION FORCE 50 kg 338 N 500 N 50 kg Picture 4 Illustrations for analysis Set B Set B illustrations have different scenarios compared to set A. Try to spot the difference. Record the mass, acceleration speed and the force applied in pushing the box. Speed = 6.0 m/s FRICTION FORCE 181 N Acceleration 1.74 m/s2 APPLIED FORCE Force exerted by the man in pushing the box = 181N Mass of the box = 50 kg 50 kg 19 Picture 5 What is the difference of this picture to that of # 4? What is increased in this picture? Is the mass the same? Speed = 15.0 m/s Acceleration 2.14 m/s2 FRICTION FORCE 201 N 94N APPLIED FORCE Force exerted by the man in pushing the box = 201N 50 kg Mass of the box = 50 kg Picture 6 Is the man pushing the same object? Is the force increased? As a result, what happened to its speed and acceleration? Speed =36.6 m/s Acceleration 3.32 m/s2 FRICTION FORCE 260 N 94N 50 kg APPLIED FORCE Force exerted by the man in pushing the box = 260N Mass of the box = 50 kg Questions: 1. What is constant in set A and B illustrations? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. If the force is constant and the mass is increased, what happened to its acceleration? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. If mass is constant, and the force is increased, what is its effect to acceleration? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is Newton’s second law? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 20 What is It Newton’s first and second laws can be understood by mastering the concept of balanced and unbalanced forces. The table below can help you to differentiate these forces from each other. Bases comparison for Balanced Forces Unbalanced forces Magnitude and direction of forces equal size but in opposite direction, Unequal and opposite or may the same in direction Effect to object in Motion The object continues to move in the speed The moving object changes its speed and direction Effect to object at rest Object stays at rest Object moves in the direction of greater force Net force Zero Non-zero Newton’s first law is also known as the law of inertia. It states that: An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion will continue to move at constant speed and direction unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Let us use a ball as an example. A ball if it is at rest, will continue in the same state of rest. If an unbalanced force is applied, say, by kicking the ball, it will be in motion. If the ball is in motion, say with an eastward velocity of 3m/s, the ball will continue in motion unless acted by an unbalanced force. This is shown in the illustration below. How about Newton’s Second law? Newton’s second law states that: Acceleration is directly related to force and inversely related to mass. Consider the situations given. 21 Situation 1.The man is pushing the cart with a box inside. Observe on the change in acceleration of the cart by comparing the two pictures. As you can see in the illustrations, at constant mass if force is increased, acceleration increases. This means that acceleration is directly related to force. Situation 2. Here is another situation. The same man is pushing the cart. Observe the load, force and acceleration. Can you spot the difference between the two situations? In the second, it shows that at constant force acceleration decreases when mass is increased. This implies that the mass is inversely related to acceleration. 22 What’s More You have learned Newton’s first and second laws through different activities. The proceeding activity needs your reflection on the things that you can see in the environment and maybe you have done before. Again, study the picture and be able to answer the questions. Activity 5 Too risky In most of our actions/activities and decisions in doing something Newton’s first and second laws are not considered therefore, risks assessment is overlooked. I. Objectives: 1. Relate the situations to Newton’s first and second law. 2. Reflect about the situation and give comments in terms of: a. Mass b. Acceleration c. Force 3. Determine the risks in every situation. II. Material: Pictures III. Procedure: Study the pictures reflecting how Newton’s first and second law are applied. Answer the questions in every situation. Situation 1 1. In this picture, can the little boy move the cart? Yes/No. Why? _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 2. What law is applicable to this situation? ________________________________________ ________________________________________ 3. What are the risks? _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 23 Situation 2 4. What can you say about the acceleration of the bicycle? _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 5. What Newton’s law is applicable? _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 6. What are the risks? _______________________________________ _______________________________________ Did you appreciate the activity? This activity implies that force play an important role to make our tasks easy and fast. However, risks in every action we take need to be considered. Example, in pushing or lifting heavy objects, proper positioning of the body is important to prevent injury. While in riding in any type of transportation, safety of every passenger must be the concern of everyone. Let us see if you are the most experienced passenger by doing this another activity. Try to recall your experiences in riding vehicles so that you can relate to the activity. Are you ready? What I Have Learned Activity 6 It’s in the law Determine if the scenarios stated are related to Newton’s first or second laws. Mark a check ( ✔ ) that corresponds to the law. Scenarios 1. The bus driver suddenly starts his engine when he realized that it is already his time to go. The passengers sitting or standing in the bus tend to fall backward. 2. The player hits a baseball ball harder so it goes faster and longer. 3. The driver suddenly stops the car and his passengers strain against the seatbelt. 4. The bus decelerates when it approaches the checkpoint for inspection. 5. The visitors were amazed when the waiter pulls the tablecloth out from under the table full of dishes. 24 First law Second law Do you know now which of your actions or experiences are related to Newton’s laws? This implies that most of our experiences are applications of Newton’s laws. Do you have the most unforgettable experience being a passenger? What was your reaction? How did you protect yourself? Strange questions? Find out in the next activity. What I Can Do Common experiences in riding a multicab/ vehicle Did you experience these? Mark a check (✔) What did you do? 1. Body moved to the right when the driver stepped on the brake. 2. Felt on the floor due to a sudden application on the brake by the driver. 3. The vehicle bumped to another vehicle. 4. No seatbelt available in the vehicle. 5. Thrown forward when the vehicle abruptly decelerates and eventually stopped. Tell which of the following you experienced in riding our local transportation. The activity allows us to recall our instant reactions in time that our lives are in danger. This tells us that precautions and alertness in riding vehicles must be practice. Do not sleep if you are travelling. Did you enjoy all the activities? Did you learn? Let us find out by answering the assessment portion of the module. 25 Assessment Answer the following questions by underlining the letter of the correct answer. 1. 2. Which chair will require the most amount of force to get it moved or accelerated? A. a plastic chair with a mass of 2 kg B. a rattan chair with a mass of 3 kg. C. a wooden chair with a mass of 5 kg. D. a steel chair with a mass of 6 kg. Look at the boys playing tug of war. Assuming that each of the boys can exert a 50N force, who will win the game? A. only one boy B. the two boys 3. C. no movement D. cannot be determined Below are four shoppers. Which of the shoppers require more force to push the cart? A. 4. C. B. D. If the force is constant, what will happen to the motion or acceleration of the object if the mass is increased? A. decreased C. the same B. increased D. zero 26 5. A bus moves along national highway from Koronadal City to General Santos City. A passenger has noticed that over time, he passes the kilometer markers in shorter periods of time. Which statement best describes the motion of the bus? A. the bus is keeping the same direction B. the bus is increasing its speed C. the bus is changing its direction D. the bus is maintaining the same speed 6. What is A. B. C. D. 7. If Josh exerts a force of 3N, and Jun is 6N, what is the net force? A. B. C. D. the net force on girl who is sitting on the chair? 0 1 2 3 6N, 3N, 3N, 9N, left left right left 8. Which of the following could be done to accelerate a moving object? A. apply inertia B. apply a balanced force C. apply an unbalanced force D. apply both balanced and unbalanced forces 9. Which of the following vehicles will come to a complete stop FIRST when the drivers apply brake at the same time? A. the fully loaded ten-wheeler truck B. the van loaded with passengers C. the empty dump trucks D. the small car 10. If a van driver suddenly makes a sharp turn, which of the following will likely to happen due to inertia? A. Passengers will slide back and forth. B. Passengers will move backward. C. Passengers will move forward. D. Passengers will slide to the side of the van. 27 11. Two objects A and B were applied with the same net force. It is observed that the acceleration of object A is two times greater than B. Which of the following is correct? A. Object A has a mass two times greater than B. B. Object has a mass ½ of the mass of object B. C. Object A has a less streamlined shape than object B. D. Object A has more friction than object B. 12. 13. Which of the following indicates that an object is accelerating? A. speeding up B. slowing down C. changing direction D. any of the above Based on the figure below, if the boy number 1 will be able to push the boy number 2 away from him, who exerts greater force? A. boy number 1 B. boy number 2 C. they have the same force D. cannot be determined 14. What Newton’s law is illustrated in the picture below? A. B. C. D. First Law only Second Law only First and Second Laws Third Law only 15. Why should we wear seatbelts in riding a vehicle? A. We should wear seatbelts to maintain our inertia. B. We should wear seatbelts so that our body will not move if we meet an accident or a force is applied to the brake. C. We should wear seatbelts so that we can sleep while travelling. D. We should wear seatbelts so if we are in an accident our body doesn’t keep moving at the same speed and in the same direction that the car was going. 28 Additional Activities Answer this critically. A big truck ban stuck on a muddy road. The driver challenged the by standers to push the truck ban out of the mud because he is going to give a prize. Would you join? Explain your decision in relation to Newton’s first and second laws. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 29 Answer Key 30 31 32 References Books Grade 8 Science Learner’s Material Grade 8 Science Teacher’s Guide 33 DISCLAIMER This Self-learning Module (SLM) was developed by DepEd SOCCSKSARGEN with the primary objective of preparing for and addressing the new normal. Contents of this module were based on DepEd’s Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELC). This is a supplementary material to be used by all learners of Region XII in all public schools beginning SY 2020-2021. The process of LR development was observed in the production of this module. This is version 1.0. We highly encourage feedback, comments, and recommendations. 34 35