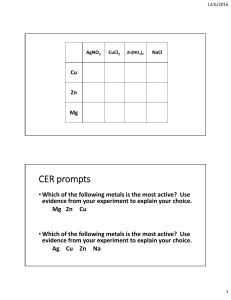
TOPIC: TRANSITION METALS/ ELEMENTS • Between groups 2 and 3 • They are: • • • • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m0Uj7mSC6HU Harder Denser Stronger Have higher melting points than group 1 metals • They are good conductors of heat and electricity • They are less reactive than group 1 metals • Mercury (Hg) is an exception. It has a low melting point. It’s the only metal that is a liquid at room temperature. Extension: Draw a mind map for the properties of transition elements. How does this data show that sodium is a typical group 1 metal and chromium is a typical transition metal? What do we know about the density of transition metals compared to group 1 metals? What do we know about the melting point of transition metals compared to group 1 metals? Do Na and Cr follow these patterns? How can you demonstrate that, using the data? Group 1 metals react readily with oxygen, at room temperature, whereas transition metals react with oxygen either very slowly, or only with heat. Transition metals do not react with water, unlike the alkali metals – which react vigorously with water! Transition metals can also react with halogens, to form metal halides. 3 1 2 4 What product would be formed in each of these reactions? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Iron + Chlorine Sodium + Bromine Manganese + Iodine Chromium + Chlorine Lithium + Fluorine HINT: When they react, halogens change their endings from –ine to –ide Challenge: Which of these reactions will be the most vigorous? Which pair or pairs are the most reactive? Transition metals form positive ions like all metals However, each transition metal can form positive ions with different charges. • E.g. copper can form Cu+ and Cu2+. • E.g. chromium can form Cr2+ and Cr3+. • E.g. iron can form Fe2+ and Fe3+ In transition metal compounds we use roman numerals to show the charge E.g. iron (III) oxide tells you the iron is a 3+ ion copper (II) oxide tells you the copper is a 2+ ion Write a balanced symbol equations for each of these reactions Copper + oxygen → copper (II) oxide Iron + oxygen Iron (III) oxide HINT: The number in brackets tells you the charge on the metal ion. So, Nickel (II) oxide shows that the Ni ion has a +2 charge. Remember that the oxide ion has a -2 charge. The overall compound should be neutral – the charges should balance. Chromium + oxygen Chromium (III) oxide Manganese + oxygen Manganese(II) oxide Challenge: Try writing the symbol equation for the reactions of the +2 and +3 ions for each metal How does that affect the compound and the balancing of the equations? Transition metals form coloured compounds. You will probably have seen (or made) copper sulphate crystals – which are bright blue. Not only do different transition elements make different coloured compounds, but the same elements can make different coloured compounds depending on the charge of their ion. Carry out some research to find the names of the transition metal compounds that are the catalysts in the following reactions: 1. Haber process (making ammonia) 2. Contact process (making sulphuric acid) 3. Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide Extension Question: In 1973 aluminum wire was found to be dangerous by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission and is not advised for electrical wiring any longer. Why were Al wires replaced with Cu ? Aluminum is susceptible to oxidation. This occurs when it comes into contact with moisture and dissimilar metals. The oxidization increases resistance in this connection. With too much built up resistance the wire can heat up possibly melt surrounding insulation which could trigger a fire. For further Refrence : https://www.bryantelectricservice.com/aluminum-vs-copper-wiring/ 1A B C 1B 1C