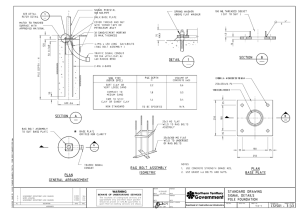
Process Specification Installation of Close-tolerance Bolts (Hi-Lite, Veri-Lite) CONTENT 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Scope and Application Related Documents Prerequisites Materials and Equipment Process Quality Assurance Safety and Health Process Flow Chart 80-T-34-5817 Issue: 01/2017 Page 1 of 30 All directives are originally compiled, checked and approved in the German language. In case of discrepancies which could result from possible translation errors or wrong interpretation of the English text, the German version of these directives shall always be binding. Data Sheet 1: Data Sheet 2: Data Sheet 3: Data Sheet 4: A320 Family Program - Final Assembly Line A320 Program Not applicable A380 Program - GLARE ® and GLARE® / AL Combinations Annex 1: Adjustment procedure Previous issue: 01/2017 The reproduction, distribution and utilization of this document as well as the communication of its contents to others without explicit authorization is prohibited. Offenders will be held liable for the payment of damages. All rights reserved in the event of the grant of a patent, utility model or design. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 2 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 1 SCOPE AND APPLICATION This process specification describes the installation of metric and inch-type close-tolerance bolts. The riveted connection consists of a close-tolerance bolt and a collar. Close-tolerance bolts per JN, HSTMJ and VLM have a metric thread. Hi-Lite close-tolerance bolts per ABS, EN, HST, VL have an inch thread. Form of close-tolerance bolts: Close-tolerance bolts have a cylindrical shank with a thread end. They differ according to material, surface protection, shape of the head, and thread. The face of the bolt shank has a hexagon socket. When a collar is screwed onto a close-tolerance bolt installed with clearance or transition fit, the bolt is prevented from rotating by positioning a socket head wrench onto this hexagon socket. Fig. 1: Close-tolerance bolt with universal head Fig. 2: Close-tolerance bolt with countersunk head Collar shape Collars differ according to material, surface protection, preload, tightening torque, (tear-off torque of the hexagonal part) and thread. a) Collar, not self-aligning (e.g. ASNA2528, ASNA2536) The self-locking collar has an undercut which ensures the clearance of the fastener shank in the collar within the grip length range of the close-tolerance bolt. When the collar is installed, the hexagonal part of the collar shears off when reaching the specified preload or torque. Fig. 3: Collar, not self-aligning Collars which are not self–aligning can be used when the angular deviation of the hole with reference to the component surface amounts to ≤ 2° on the side of the collar. Allowance must be made for the fact that an angular deviation of ± 1° and ± 0,5° from dia. 8 mm onwards with reference to the component surface is permitted during production (see 80-T-30-9910). DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 3 b) 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Collar, self-aligning (e.g. ASNA2537, ASNA2538) If the component surface on the collar side has an inclination of > 2° ≤ 7° to the hole, a selfaligning collar is used. The spherical washer on the collar has a self-aligning effect. Fig. 4: Self–aligning collar, hexagon sheared off One special variant of the collar is the collar with ”double hexagon”, see Fig. 5. When the collar is initially fitted, the tool must grip on the break-off hexagon. As soon as the tightening torque is reached, the hexagon shears off (see also Fig. 4) but can still be loosened or torqued further on the remaining wrench surfaces. Break-off hexagon Fig. 5: Collar which can be re-tightened Nuts for screwed connections (self-locking): Metric and inch-type close-tolerance bolts can be provided with self-locking nuts (e.g. ASNA2527, ASNA2531) if such a combination is specified in the manufacturing documents. Self-aligning nuts (e.g. ASNA2532) must be used for angular deviations > 2° between hole and component surface. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 4 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 2 RELATED DOCUMENTS A2406.1 80-T-30-0032 80-T-30-9910 80-T-34-0185 80-T-34-5803 80-T-34-9600 80-T-35-9023 ABS0873 ASNA2528 ASNA2531 ASNA2532 ASNA2536 ASNA2537 ASNA2538 EN6114 EN6115 NAS1149 Manage NonConformity Notification Machining of FRP Components Drilling, Reaming and Countersinking of Rivet and Screw Holes Installation of ACRES Oversize Sleeves Wet Installation of Fasteners Application of Sealing Compounds Preservation of Rivet Rows Bolt – Close tolerance, 130° countersunk head, Short thread Nut – Hexagonal, Self-Locking, Bihex, Shear Type Nut, hexagonal, self-locking Nut, self-locking, with a spherical joint and a self-alignment washer (slope 5° max.) Nut-hexagonal, self-locking, bihex, shear type Nut – Hexagonal, Self-Locking, Ball, Bihex, Shear Type, Aluminium Alloy Nut – Hexagonal, self-locking, ball, bihex, shear type, CRES Aerospace series, Bolt – Countersunk head, Short thread, Inch series Aerospace series, Bolt – Protruding head, Short thread, Inch series Washer, Flat 3 PREREQUISITES 3.1 Personnel Personnel must be familiar with the special aspects and requirements concerning the preparation of holes and installation of close-tolerance bolts. 3.2 Manufacturing documents The manufacturing documents must specify the standard designation of the close-tolerance bolt and collar. If self-locking nuts are used, the tightening torque must additionally be stated. 3.2.1 Design note Close-tolerance bolts can only be used in areas where there is sufficient space for drilling and installation. 3.2.2 Fastener designation in the manufacturing documents 3.2.2.1 Designation of close-tolerance bolts Example of designation in the manufacturing documents: DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 5 a) JN0011MJ 6 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 16 Grip length Nominal dia. code Standard b) EN6114 V 4 - 8 Grip length Nominal dia. code PT Standard 3.2.2.2 Designation of collars Example of designation in the manufacturing documents: a) JN0042MJ 6 Nominal dia. code Manufacturer's serial no. b) ASNA2536 - 3 Nominal dia. code PT Standard 4 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT 4.1 Bolts 4.1.1 Identification of bolts Manufacturer’s identification and diameter code are recessed (example, see Fig. 6). 114 K N6 4 E Note: The manufacturer's identification may deviate from the standard designation. EN6114 K 4 VS V S Fig. 6: Example of identification of an inch-type bolt DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Bolt standard PT / material code Diameter code no. Manufacturer's identification according to TR 3198 (example) Page 6 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 4.1.2 Identification of collars Manufacturer’s identification in cylindrical area in form of code letter. Manufacturer's identification is embossed in the collar Fig. 7: Identification of collars 4.2 Tools It is only permitted to use drilling and reaming tools which assure compliance with the requirements laid down in this process specification. For drilling machines see 80-T-30-9910. Special installation tools are required for the installation of collars. The same applies to their removal. -1 The speed of the screwdriver must not exceed n = 275 min during the installation process. The special tools must be serviced at least once per year. In special cases (areas where access is difficult) it is also permitted to use manual tools such as ring, open-end and possibly hexagon socket wrenches or special tools. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 7 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 5 PROCESS 5.1 Drilling of hole The hole dimensions for Hi-Lite bolts are given in Tables 2 and 3 and in the program-specific data sheets of this process specification. Holes in metal and FRP must be drilled in accordance with 80-T-30-9910 and 80-T-30-0032. In aluminum, holes with a tolerance H11 are drilled with a step drill with spiropoint or cross cut (with diameter tolerance h6) with manual feed and holes with a tolerance H10 with automatic feed. Hole tolerances Unless specified otherwise in the manufacturing documents, holes for close-tolerance bolts are to be prepared in accordance with this process specification. Hole tolerances differ depending on component thickness (grip length) and material (see Tables 2 to 5). Regarding hole tolerances, the following requirements generally apply to Al components and Ti bolts: a) Grip length of bolt ≤ 3 d Diameter sizes -2, -3 and -3A Transition fit with slight clearance, tolerance field size IT 11 Diameter sizes -4 and -5 Interference fit, tolerance field size IT 10 Diameter sizes -6 and -7 Transition fit with slight clearance, tolerance field size IT 10 b) Grip length of bolt ≤ 3 d All diameter sizes Transition fit, tolerance field size IT 9 DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 8 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Contrary to these regulations, the following can apply to nominal bolt diameters of 5,6 mm: a) With variations in component thickness around 3d it is permissible to use the tolerance H11 and also > 3d in a mixed field. it is permissible to use the tolerance of ≤ 3d as well as > 3d in a mixed field for bolt diameter 5,6 mm (see Diagram 1). Advantage: Drilling tool does not have to be changed. b) If difficulties occur when the bolt is forced into the structure, it is permissible to use the tolerance of ≤ 3d as well as > 3d in a mixed field (see Diagram 1). Advantage: Selection of interference fit in allowable range to facilitate installation. Bolt dia. min. 5,530 max. 5,542 Drilled hole/bolt dia. [mm] 5,540 5,535 A lH9 5,510 Al H11 5,46 0 > 3d 3≤ d 1 5 9 1 3 1 7 2 1 Mixed area (selection between H11 and H9) 2 5 2 9 L [grip length] [mm] Diagram 1: Allowable hole tolerances for Hi-Lite fasteners of nominal dia. 5,6 mm, diameter code 3A DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 9 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) For holes with a tolerance H9 in aluminum, grip length > 3d, as well as holes in steel, titanium and FRP, the hole quality is achieved by reaming. In order to make sure that the hole is drilled at right angles to the workpiece when using hand drills, the following procedures are permissible: 1. Use of stop holders in connection with supports which can be positioned safely on the component. Fig. 8: Example of a stop holder 2. Use of drilling blocks for areas which are not easily accessible and areas with considerable loft curvature. The drilling blocks are adapted to the component and must be seated firmly. For guidance, the drilling sleeve used must be 2 mm higher than the pre-drill step of the step drill to center the pre-drill step in the drilling sleeve (see Fig. 10). Drilling block Step drill 2 mm Drilling sleeve Component Fig. 9: Drilling block Fig. 10: Drilling sleeve 3. Other procedures are only permitted in areas where access is difficult. The required tolerances for the hole diameter and angularity must be observed. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 10 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) X = 90 ± 1° X = 90 ± 0,5° Fig. 11: Angular deviations during drilling DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed (for dia. < 8 mm) (for dia. ≥ 8 mm) DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed EN6114B3E EN6115B3E EN6114B3AE EN6115B3AE EN6114B4E EN6115B4E EN6114B5 EN6115B5 EN6114B6 EN6115B6 EN6114B7 EN6115B7 EN6114B8 EN6115B8 EN6114T3 EN6115T3 EN6114T3A EN6115T3A EN6114T4 EN6115T4 EN6114T5 EN6115T5 EN6114T6 EN6115T6 EN6114T7 EN6115T7 EN6114T8 EN6115T8 4,8 5,6 6,4 7,9 9,5 11,1 12,7 EN6114C2E EN6115C2E L1 ≙ grip length EN6114C8 EN6115C8 EN6114C7 EN6115C7 EN6114C6 EN6115C6 EN6114C5 EN6115C5 EN6114C4E EN6115C4E EN6114C3AE EN6115C3AE EN6114C3E EN6115C3E 12,674 12,687 11,087 11,100 9,500 9,512 7,911 7,925 6,324 6,337 5,529 5,542 4,800 4,813 4,140 4,153 - 0,008 0,062 - 0,013 0,070 9,450 3) 9,508 11,030 3) 11,100 6) Larger tolerances from dia. 12,7 mm. 5) Holes to be produced by reaming. - 11,080 11,126 9,490 9,526 7,900 7,936 6,310 6,346 5,510 5,540 4,780 4,810 4,120 4,150 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - - 0,036 0,020 - 0,026 0,022 - 0,025 0,025 - 0,022 0,027 - 0,011 0,032 - 0,010 0,033 - 0,010 0,033 + Interference - Clearance Fit Tolerance H9 Al (L1 ≤ 3d) ** d ≙ bolt diameter 0,003 0,075 7,850 3) 7,908 - 0,006 0,077 6,260 3) 6,318 - - 0,006 0,082 - 0,005 0,083 - 0,015 0,073 + Interference 4) In component areas where subsequent reaming of titanium parts is possible Al (column 1 or 2) may be used. 3) With automatic feed (tolerance H10). 2) Exception: AIRBUS titanium crack stopper; hole like in Al (L1 ≤ 3d). Fit - Clearance 5,460 5,535 4,730 4,805 4,080 4,155 1) For dia. 4,2 mm to dia. 5,6 mm: tolerance = H11. For dia. 6,4 mm to dia. 11,1 mm: Tolerance = H10. Dimension in mm EN6114B2E EN6115B2E EN6114T2 EN6115T2 4,2 d max dia. max nominal d min dia. min Drilled hole Tolerance 1) Al (L1 ≤ 3d) Diameter Standard designation Titanium Hi-Lite bolts (material code T, B and C) Bolt dia. - 0,040 0,000 - 0,074 - 0,005 12,692 6) 12,748 - 0,032 0,002 - 0,041 - 0,005 - 0,038 - 0,003 - 0,031 0,002 - 0,028 0,003 - 0,028 0,003 + Interference - Clearance Fit 11,100 11,127 9,510 9,532 7,930 7,952 6,340 6,362 5,540 5,560 4,810 4,828 4,150 4,168 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole 12,692 12,802 11,100 11,190 9,510 9,600 7,930 8,020 6,340 6,430 5,540 5,615 4,810 4,885 4,150 4,225 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - 0,128 - 0,005 - 0,103 0,000 - 0,100 0,002 - 0,109 - 0,005 - 0,106 - 0,003 - 0,086 0,002 - 0,085 0,003 - 0,085 0,003 + Interference - Clearance Fit Tolerance H11 combinations with Ti, St, Al Tolerance H8 Ti 2) and St 4) 5) FRP and combin. Page 11 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Table 1: Drilled hole tolerances for inch-type close-tolerance bolts (Material code T, B and C) DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed EN6114B3E EN6115B3E EN6114B3AE EN6115B3AE EN6114B4E EN6115B4E EN6114B5 EN6115B5 EN6114B6 EN6115B6 EN6114B7 EN6115B7 EN6114B8 EN6115B8 EN6114T3 EN6115T3 EN6114T3A EN6115T3A EN6114T4 EN6115T4 EN6114T5 EN6115T5 EN6114T6 EN6115T6 EN6114T7 EN6115T7 EN6114T8 EN6115T8 5,2 6,0 6,8 8,3 9,9 11,5 13,1 L1 ≙ grip length EN6114C8 EN6115C8 EN6114C7 EN6115C7 EN6114C6 EN6115C6 EN6114C5 EN6115C5 EN6114C4E EN6115C4E EN6114C3AE EN6115C3AE EN6114C3E EN6115C3E EN6114C2E EN6115C2E d min 13,072 13,084 11,484 11,496 9,897 9,909 8,309 8,321 6,722 6,734 5,924 5,939 5,134 5,146 4,800 4,813 d max - 0,011 0,081 - 0,001 0,069 - 0,006 0,076 8,240 3) 8,298 9,840 3) 9,898 11,420 3) 11,490 d ≙ bolt diameter - - 0,004 0,074 6,660 3) 6,718 - - 0,003 0,082 - 0,001 0,086 - 0,005 0,083 + Interferenc e - Clearance Fit 5,857 5,930 5,060 5,135 4,730 4,805 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole 6) Larger tolerances from dia. 12,7 mm. 5) Holes to be produced by reaming. - 11,470 11,513 9,880 9,916 8,300 8,336 6,710 6,746 5,907 5,937 5,110 5,140 4,780 4,810 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - - 0,029 0,026 - 0,019 0,029 - 0,027 0,021 - 0,024 0,024 - 0,010 0,032 - 0,006 0,036 - 0,010 0,033 + Interferenc e - Clearance Fit Tolerance H9 Al (L1 ≤ 3d) ** 4) In component areas where subsequent reaming of titanium parts is possible Al (column 1 or 2) may be used. 3) With automatic feed (tolerance H10). 2) Exception: AIRBUS titanium crack stopper; hole like in Al (L1 ≤ 3d). 1) For dia. 4,2 mm to dia. 5,6 mm: tolerance = H11. For dia. 6,4 mm to dia. 11,1 mm: tolerance = H10. Dimensions in mm EN6114B2E EN6115B2E EN6114T2 EN6115T2 4,8 1st repair stage Standard designation Tolerance 1) Al (L1 ≤ 3d) - 0,043 - 0,004 - 0,073 - 0,005 13,089 6) 13,145 - 0,035 - 0,001 - 0,033 0,001 - 0,030 0,004 - 0,030 - 0,001 - 0,034 - 0,004 - 0,028 0,003 + Interferenc e - Clearance Fit 11,500 11,527 9,910 9,932 8,320 8,342 6,730 6,752 5,940 5,957 5,150 5,168 4,810 4,828 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole 13,089 13,199 11,500 11,610 9,910 10,000 8,320 8,410 6,730 6,820 5,937 6,010 5,150 5,225 4,810 4,885 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - 0,127 - 0,005 - 0,126 - 0,004 - 0,103 - 0,001 - 0,101 0,001 - 0,098 0,004 - 0,083 0,002 - 0,091 - 0,004 - 0,085 0,003 + Interferenc e - Clearance Fit Tolerance H11 combinations with Ti, St, Al Tolerance H8 Ti 2) and St 4) 5) FRP and combin. Table 2: Diameter Titanium Hi-Lite bolts (material code T, B and C) dia. Bolt Page 12 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 1st repair stage – hole tolerances (material code T, B and C) DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed EN6114B3E EN6115B3E EN6114B3AE EN6115B3AE EN6114B4E EN6115B4E EN6114B5 EN6115B5 EN6114B6 EN6115B6 EN6114B7 EN6115B7 EN6114B8 EN6115B8 EN6114T3 EN6115T3 EN6114T3A EN6115T3A EN6114T4 EN6115T4 EN6114T5 EN6115T5 EN6114T6 EN6115T6 EN6114T7 EN6115T7 EN6114T8 EN6115T8 5,6 6,4 7,1 8,7 10,4 11,9 13,5 L1 ≙ grip length EN6114C8 EN6115C8 EN6114C7 EN6115C7 EN6114C6 EN6115C6 EN6114C5 EN6115C5 EN6114C4E EN6115C4E EN6114C3AE EN6115C3AE EN6114C3E EN6115C3E EN6114C2E EN6115C2E 13,468 13,480 11,880 11,892 10,293 10,305 8,705 8,717 7,118 7,130 6,324 6,337 5,529 5,542 5,134 5,146 d max d min - 0,003 0,067 - 0,017 0,065 - 0,020 0,062 8,650 3) 8,708 10,240 3) 10,310 11,830 3) 11,900 6) Larger tolerances from dia. 12,7 mm. 5) Holes to be produced by reaming. 4) In component areas where subsequent reaming of titanium parts is possible Al (column 1 or 2) may be used. 3) With automatic feed (tolerance H10). 2) Exception: AIRBUS titanium crack stopper; hole like in Al (L1 ≤ 3d). - 11,870 11,913 10,280 10,323 8,690 8,726 7,100 7,136 6,310 6,346 5,510 5,540 5,110 5,140 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - - 0,033 0,022 - 0,030 0,025 - 0,021 0,027 - 0,018 0,030 - 0,022 0,027 - 0,011 0,032 - 0,006 0,036 + Interferenc e - Clearance Fit Tolerance H9 Al (L1 ≤ 3d) ** d ≙ bolt diameter - - 0,000 0,070 7,060 3) 7,118 - - 0,006 0,077 - 0,006 0,082 - 0,001 0,086 + Interferenc e - Clearance Fit 6,260 6,318 5,460 5,535 5,060 5,135 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole 1) For dia. 4,2 mm to dia. 5,6 mm: tolerance = H11. For dia. 6,4 mm to dia. 11,1 mm: tolerance = H10. Dimensions in mm EN6114B2E EN6115B2E EN6114T2 EN6115T2 5,2 2nd repair stage Standard designation Tolerance 1) Al (L1 ≤ 3d) - 0,047 - 0,008 - 0,073 - 0,005 13,485 6) 13,541 - 0,044 - 0,005 - 0,039 - 0,003 - 0,034 0,000 - 0,038 - 0,003 - 0,039 0,002 - 0,034 - 0,004 + Interferenc e - Clearance Fit 11,900 11,927 10,310 10,337 8,720 8,744 7,130 7,152 6,340 6,362 5,550 5,568 5,150 5,168 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole Tolerance H8 with Ti, St, Al FRP and combin. 13,485 13,595 11,900 12,000 10,310 10,420 8,720 8,810 7,130 7,220 6,340 6,430 5,540 5,615 5,150 5,225 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - 0,127 - 0,005 - 0,120 - 0,008 - 0,127 - 0,005 - 0,105 - 0,003 - 0,102 0,000 - 0,106 - 0,003 - 0,086 0,002 - 0,091 - 0,004 + Interferenc e - Clearance Fit Tolerance H11 combinations Ti 2) and St 4) 5) Table 3: Diameter Titanium Hi-Lite bolts (material code T, B and C) dia. Bolt 12,7 11,1 9,5 7,9 6,4 5,6 4,8 4,2 nominal Diameter Page 13 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 2nd repair stage – hole tolerances (material code T, B and C) DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed EN6114F3 EN6115F3 EN6114F3A EN6115F3A EN6114F4 EN6115F4 EN6114F5 EN6115F5 EN6114F6 EN6115F6 EN6114F7 EN6115F7 EN6114F8 EN6115F8 EN6114K3 EN6115K3 EN6114K3A EN6115K3A EN6114K4 EN6115K4 EN6114K5 EN6115K5 EN6114K6 EN6115K6 EN6114K7 EN6115K7 EN6114K8 EN6115K8 - 0,009 0,075 - 0,021 0,062 7,850 3) 7,908 9,450 3) 9,508 - 11,100 3) - - 0,026 0,069 - 0,006 0,077 6,260 3) 6,318 11,030 - 0,018 0,082 - 0,017 0,083 - 0,027 0,073 - 11,080 11,126 9,490 9,526 7,900 7,936 6,310 6,346 5,510 5,540 4,780 4,810 4,120 4,150 6) Larger tolerances from dia. 12,7 mm. 5) Holes to be produced by reaming. 4) In component areas where subsequent reaming of titanium parts is possible Al (column 1 or 2) may be used. 3) With automatic feed (tolerance H10). 2) Exception: AIRBUS titanium crack stopper; hole like in Al (L 1 ≤ 3d). 6) 12,692 11,100 11,127 9,510 9,532 7,930 7,952 6,340 6,362 5,540 5,560 4,810 4,828 4,150 4,168 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - 0,086 - 0,005 - 0,053 - 0,001 - 0,045 0,002 - 0,053 - 0,005 - 0,050 - 0,003 - 0,043 0,002 - 0,040 0,003 - 0,040 0,003 Interference + - Clearance Fit 12,692 12,802 11,100 11,190 9,510 9,600 7,930 8,020 6,340 6,430 5,540 5,615 4,810 4,885 4,150 4,225 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - 0,140 - 0,005 - 0,116 - 0,001 - 0,113 0,002 - 0,121 - 0,005 - 0,118 - 0,003 - 0,098 0,002 - 0,097 0,003 - 0,097 0,003 Interference + - Clearance Fit Tolerance H11 combinations with Ti, St, Al 6) Tolerance H8 Ti 2) and St 4) 5) FRP and combin. 12,748 d ≙ bolt diameter - - 0,049 0,019 - 0,039 0,022 - 0,037 0,025 - 0,034 0,027 - 0,023 0,032 - 0,022 0,033 - 0,022 0,033 Interference Interference - Clearance Fit + dia. max dia. min Drilled hole Tolerance H9 Al (L1 ≤ 3d) ** + - Clearance Fit 5,460 5,535 4,730 4,805 4,080 4,155 dia. max dia. min L 1 ≙ grip length 12,662 12,687 11,074 11,099 9,487 9,512 7,899 7,925 6,312 6,337 5,517 5,542 4,788 4,813 4,128 4,153 d max d min Drilled hole Tolerance 1) Al (L1 ≤ 3d) 1) For dia. 4,2 mm to dia. 5,6 mm: tolerance = H11. For dia. 6,4 mm to dia. 11,1 mm: tolerance = H10. Dimensions in mm EN6114F2 EN6115F2 EN EN6114K2 EN6115K2 EN Standard designation Titanium Hi-Lite bolts (material code F and K) Bolt dia. 12,7 11,1 9,5 7,9 6,4 5,6 4,8 4,2 nominal Diameter Page 14 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Table 4: Drilled hole tolerances for inch-type close-tolerance bolts (Material code F and K) DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed EN6114F3X EN6115F3X EN6114F3AX EN6115F3AX EN6114F4X EN6115F4X EN6114F5X EN6115F5X EN6114F6X EN6115F6X EN6114F7X EN6115F7X EN6114F8X EN6115F8X EN6114K3X EN6115K3X EN6114K3AX EN6115K3AX EN6114K4X EN6115K4X EN6114K5X EN6115K5X EN6114K6X EN6115K6X EN6114K7X EN6115K7X EN6114K8X EN6115K8X - 0,016 0,082 - 0,010 0,074 - 0,002 0,081 - 0,015 0,069 - 0,019 0,076 5,857 5,930 6,660 3) 6,718 8,240 3) 8,298 9,840 3) 9,898 11,420 3) 11,490 - 5,914 5,939 6,708 6,734 8,296 8,321 9,883 9,909 11,471 11,496 13,058 13,084 L1 ≙ grip length - - 0,014 0,086 5,060 5,135 5,121 5,146 - 0,017 0,083 - 11,470 11,513 9,880 9,916 8,300 8,336 6,710 6,746 5,907 5,937 5,110 5,140 4,780 4,810 - - 0,042 0,026 - 0,033 0,029 - 0,040 0,021 - 0,038 0,024 - 0,023 0,032 - 0,019 0,036 - 0,022 0,033 - 0,087 - 0,005 13,089 6) 13,145 d ≙ bolt diameter - 0,056 - 0,004 6) Larger tolerances from dia. 12,7 mm. 5) Holes to be produced by reaming. 4) In component areas where subsequent reaming of titanium parts is possible Al (column 1 or 2) may be used. 3) With automatic feed (tolerance H10). 2) Exception: AIRBUS titanium crack stopper; hole like in Al (L1 ≤ 3d). - 0,049 - 0,001 - 0,046 0,001 - 0,044 0,004 - 0,043 - 0,001 - 0,047 - 0,004 - 0,040 0,003 11,500 11,527 9,910 9,932 8,320 8,342 6,730 6,752 5,940 5,957 5,150 5,168 4,810 4,828 + Interference - Clearance Fit + dia. max dia. min Drilled hole Interference - Clearance Fit + dia. max dia. min Drilled hole 13,089 13,199 11,500 11,610 9,910 10,000 8,320 8,410 6,730 6,820 5,937 6,010 5,150 5,225 4,810 4,885 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - 0,141 - 0,005 - 0,139 - 0,004 - 0,117 - 0,001 - 0,114 0,001 - 0,112 0,004 - 0,096 0,002 - 0,104 - 0,004 - 0,097 0,003 Interference + - Clearance Fit Tolerance H11 combinations with Ti, St, Al 6) Tolerance H8 Ti 2) and St 4) 5) FRP and combin. Interference - Clearance 4,730 4,805 dia. max dia. min 4,788 4,813 d max d min Fit Tolerance H9 Al (L1 ≤ 3d) ** 1) For dia. 4,2 mm to dia. 5,6 mm: tolerance = H11. For dia. 6,4 mm to dia. 11,1 mm: tolerance = H10. Dimensions in mm EN6114F3 EN6115F3 EN EN6114K3 EN6115K3 EN Drilled hole Tolerance 1) Al (L1 ≤ 3d) Table 5: Standard designation Titanium Hi-Lite bolts (material code F and K) dia. Bolt ABS0873K3A ABS0873F3A ABS0873K4 ABS0873F4 - 5,6 6,4 7,9 12,7 11,1 - - - ABS0873K3 ABS0873F3 4,8 9,5 ABS0873K2 ABS0873F2 ABS 4,2 nominal Diameter Page 15 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 1st repair stage - drilling tolerances (material code F and K) 1st repair stage 4,8 5,2 6,0 6,8 8,3 9,9 11,5 13,1 4,2 4,8 5,6 6,4 7,9 9,5 11,1 12,7 Diameter nominal Diameter DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed - - - - ABS0873K4X ABS0873F4X ABS0873K3AX ABS0873F3AX ABS0873K3X ABS0873F3X ABS0873K3 ABS0873F3 ABS Page 16 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed 5,2 5,5 6,4 7,1 8,7 10,4 11,9 13,5 4,2 4,8 5,6 6,4 7,9 9,5 11,1 12,7 EN6114F5Y EN6115F5Y EN6114F6Y EN6115F6Y EN6114F7Y EN6115F7Y EN6114F8Y EN6115F8Y EN6114K4 EN6115K4 EN6114K4Y EN6115K4Y EN6114K5Y EN6115K5Y EN6114K6Y EN6115K6Y EN6114K7Y EN6115K7Y EN6114K8Y EN6115K8Y ABS0873K4 ABS0873F4 ABS0873K4Y ABS0873F4Y - - - - EN6114F4Y EN6115F4Y EN6114K3A EN6115K3A ABS0873K3A ABS0873F3A L1 ≙ grip length EN6114F4 EN6115F4 EN6114F3A EN6115F3A EN6114F3X EN6115F3X EN6114K3X EN6115K3X ABS0873K3X ABS0873F3X EN EN ABS Standard designation - 0,006 0,077 - 0,014 0,070 - 0,016 0,067 - 0,031 0,065 - 0,033 0,062 6,260 6,318 7,060 3) 7,118 8,650 3) 8,708 10,240 3) 10,310 11,830 3) 11,900 - 6,312 6,337 7,104 7,130 8,692 8,717 10,279 10,305 11,867 11,892 13,454 13,480 d ≙ bolt diameter 6) Larger tolerances from dia. 12,7 mm. 5) Holes to be produced by reaming. 4) In component areas where subsequent reaming of titanium parts is possible Al (column 1 or 2) may be used. 3) With automatic feed (tolerance H10). 2) Exception: AIRBUS titanium crack stopper; hole like in Al (L1 ≤ 3d). - - 0,018 0,082 5,460 5,535 5,517 5,542 - 0,014 0,086 - 11,870 11,913 10,280 10,323 8,690 8,726 7,100 7,136 6,310 6,346 5,510 5,540 5,110 5,140 - - 0,046 0,022 - 0,044 0,025 - 0,034 0,027 - 0,032 0,030 - 0,034 0,027 - 0,023 0,032 - 0,019 0,036 Interference Interference - Clearance Fit + dia. max dia. min Drilled hole Tolerance H9 Al (L1 ≤ 3d) ** + - Clearance 5,060 5,135 dia. max dia. min Fit 5,121 5,146 d max d min Drilled hole 1) For dia. 4,2 mm to dia. 5,6 mm: tolerance = H11. For dia. 6,4 mm to dia. 11,1 mm: tolerance = H10. Dimensions in mm 2nd repair stage Diameter Tolerance 1) Al (L1 ≤ 3d) - 0,060 - 0,008 - 0,087 - 0,005 13,485 6) 13,541 - 0,058 - 0,005 - 0,052 - 0,003 - 0,048 0,000 - 0,050 - 0,003 - 0,051 0,008 - 0,047 - 0,004 Interference + - Clearance Fit 11,900 11,927 10,310 10,337 8,720 8,744 7,130 7,152 6,340 6,362 5,550 5,568 5,150 5,168 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole Tolerance H8 with Ti, St, Al 6) FRP and combin. 13,485 13,595 11,900 12,000 10,310 10,420 8,720 8,810 7,130 7,220 6,340 6,430 5,540 5,615 5,150 5,225 dia. max dia. min Drilled hole - 0,141 - 0,005 - 0,133 - 0,008 - 0,141 - 0,005 - 0,118 - 0,003 - 0,116 0,000 - 0,118 - 0,003 - 0,098 0,002 - 0,104 - 0,004 Interference + - Clearance Fit Tolerance H11 combinations Ti 2) and St 4) 5) Table 6: nominal Diameter Titanium Hi-Lite bolts (material code F and K) dia. Bolt Page 17 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 2nd repair stage - drilling tolerances (material code F and K) Page 18 5.2 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Countersinking Holes in metal and FRP must be prepared in accordance with 80-T-30-9910 and 80-T-30-0032. 5.3 Chamfering and deburring To ensure that the universal head is flush and the countersunk head has contact, in case of manual assembly, the component must be provided with a chamfer or a radius on the manufactured head side (see Fig. 12). To obtain the required depth of chamfer/radius, make sure that the stop holder setting is correct. No chamfer is required for sheet thicknesses < 1.0 mm if close-tolerance bolts with a universal head are installed. Instead, a washer with an appropriate chamfer is placed under the universal head. Chamfering (drilling/countersinking) is not required in aluminum components if drilling/countersinking and Hi-Lite installation are performed automatically and with reproducible parameters e.g. with a riveting system and if it is ensured that the Hi-Lite countersunk head sits properly in the countersink without a gap. If a tool is used which provides the holes with an appropriate chamfer during drilling (combined drilling/countersinking tool), subsequent chamfering is not necessary. Alternatively, it is possible to use combined drilling/countersinking tools which show a radius as the countersunk head/shank transition. In a countersunk and chamfered component or a component with a transition radius, the remaining cylindrical part of the hole in the component must not be less than 0,2 mm (see also Fig. 12). For FRP, the cylindrical part of the hole depends on the individual component. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 19 a) for universal head: Chamfer A or radius R 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Table 7: Universal head 90° to 100° °C Nom. bolt dia. [mm] b) A (chamfer) [mm] R (radius) [mm] up to and including 6,4 0,6 - 0,7 0,5 - 0,7 from 7,9 0,7 - 0,8 - for countersunk head: Table 8: Countersunk head 50° to 60° 50° bis 60° Nom. bolt dia. [mm] F (chamfer) [mm] R (radius) [mm] to 6.4 0,4 -0,6 0,5 - 0,7 7,9 0,7 - 0,9 0,8 - 1,0 9,5 0,7 - 0,9 0,8 - 1,0 11,1 0,9 - 1,1 1,1 - 1,3 12,7 0,9 - 1,1 1,1 - 1,3 Transition radius Übergangsradius Übergangsfase Transition chamfer F 0,2 min. 0,2 mind. FF==siehe see Tab. Tab.77 0,2 min. 0,2 mind. R ==siehe see Tab. R Tab. 7 7 Fig. 12: Chamfering of holes Deburring is not necessary on the collar side and between the components if the requirements of 80-T-30-9910 are met. Sample holes in materials of the same type serve to adjust the microstop drill-cage, to check the drill/countersink tools and to check for burrs. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 20 5.4 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Bolt shank length Prior to installation of the close-tolerance bolt, the grip length must be checked at the properly fixed component with the aid of a ruler (see Fig. 13). If the bolt length specified in the manufacturing documents is either too short or too long, a bolt of the next-higher or next-lower grip length must be selected. If the required bolt length is not in stock, it is permitted to place a washer with a minimum thickness of 0,8 mm and a maximum thickness of 1,6 mm under the upset head. The material of the washer must correspond to the collar or spherical disk or nut material including the surface protection of these parts. Washers per NAS1149 are used for adjustment of standard Hi-Lites. It is also possible to use two washers instead of one. However, the total washer height of 1,6 mm max. must not be exceeded. If due to a thickness variation or a component inclination an oversize bolt (too long) was installed, a washer may also be used under the general conditions specified above. However, this applies only to transition/interference fit in metal structures and/or component areas that are difficult to access, where the removal of a bolt may lead to damaging the drilled hole. Grip length L Grip length L 1 Ruler Ruler Fig. 13: Measurement of grip length (in both cases -8) 5.5 Surface protection and wet installation The surface protection of close-tolerance bolts and collars is defined in the purchase order or related standard and is applied by the manufacturer of the close-tolerance bolts. This surface protection must not be removed. For exceptions, refer to the data sheets. The break-off point of the collar and the countersink must be protected against corrosion. This protection must be in accordance with program-specific requirements (standards or manufacturing documents, 80-T-35-9023). Wet installation of the bolts shall be in accordance with 80-T-34-5803. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed 1 Page 21 5.6 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Installation of close-tolerance bolt a) Installation of close-tolerance bolt A close-tolerance bolt is installed as follows: in the case of clearance fits by hand, in case of interference fits, by driving-in (directly with a plastic hammer or a hammer with Al mandrel or a riveting hammer with suitable rivet set) until the manufactured head is positioned correctly. Damage to the manufactured head (see 5.8) or the structure (bulging, deformation) during installation of the bolt is not permitted. In the case of a tight interference fit and small component thicknesses, back-up with a suitable tool. Please note: Under no circumstances should the close-tolerance bolt be pulled in with the aid of the collar. Fig. 14: Installation of close-tolerance bolt b) Screwing on the collar Screw the collar onto the close-tolerance bolt by hand until self-locking starts (this work step is not required if installation tools with automatic collar feed device are used). Fig. 15: Screwing on the collar DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 22 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) c) Positioning the tools with installation tools: with manual tools: The hexagon wrench of the installation tool is introduced into the hexagon socket of the closetolerance bolt. The tool is then pushed onto the hexagon of the collar. The hexagon socket screw wrench is introduced into the hexagon socket of the closetolerance bolt. A wrench (ring or open-end wrench) is then positioned on the hexagon of the collar. Fig. 16: Positioning the installation tool d) Tightening the collar with installation tools: with manual tools: Operate the tool until the hexagon of the collar shears off. Tighten collar with wrench until the hexagon of the collar shears off. The close-tolerance bolt is held with the hexagon socket screw wrench to prevent it from rotating. Fig. 17: Tightening of the collar with the installation tool DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 23 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) e) Installed close-tolerance bolt Pull back the tool; the collar’s hexagon which has sheared off is released. Fig. 18: Installed close-tolerance bolt Visible damaging of the collar or the external thread is not admissible. 5.7 Check of bolt shank protrusion Standard inspection gages should be used to check the protrusion of the bolt shank after installation. If washers have been used, check the protrusion of the shank to the washer surface. If collars with spherical washers have been used, the inspection gage must be positioned centrally on the slant (Fig. 21). If the protrusion of the shank is out of tolerance (see Table 8), replace the close-tolerance bolt (see 5.9). Fig. 19: Standard inspection gages DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 24 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Fig. 20: Check of bolt shank protrusion with a standard inspection gage (limit cases shown) Measuring range α max. 7° Measurement axis Fig. 21: Check of protrusion on component slants Table 9: Shank protrusions for inch-type close-tolerance bolts ”Hi-Lite/Veri-Lite” Bolt shank protrusion Nominal diameter 5.8 Minimum Maximum [mm] [inch] [mm] [inch] [mm] [inch] 4,1 5/32 6,86 .270 8,94 .352 4,8 3/16 7,11 .280 9,19 .362 5,6 7/32 7,49 .295 9,57 .377 6,4 1/4 7,87 .310 9,96 .392 8,0 5/16 9,40 .370 11,48 .452 9,5 3/8 10,41 .410 12,50 .492 11,1 7/16 12,07 .475 14,15 .557 12,7 1/2 13,10 .516 15,20 .598 Non-mating manufactured heads and collars 5.8.1 Measurement procedure 100 % of the head circumference must be checked with a 1/10 mm feeler gage. The feeler gage may penetrate in an area ≤ 25 % of the circumference. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 25 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) If fasteners have been installed wet, make certain that any gap at the head produced by measuring is sealed afterwards. 5.8.2 Universal head A gap on one side is permitted between component and manufactured head of the close-tolerance bolt with universal head provided that this gap is not bigger than 0,1 mm (the feeler gage must just wedge) and does not exceed 25 % of the circumference. Such gaps are admissible at 10 % of the bolts if no two adjacent bolts have the same defect. Fig. 22: Gap at manufactured head 5.8.3 Countersunk head A gap on one side is permitted between component and manufactured head of the close-tolerance bolt with countersunk head provided that this gap is not bigger than 0,1 mm (the feeler gage must just wedge) and does not exceed 25 % of the circumference. Such gaps are admissible at 10 % of the bolts if no two adjacent bolts have the same defect. If, according to the type-specific aerodynamic surface requirements, a countersunk head protrudes excessively, it shall not be further processed. In case of protrusion of the countersunk head, the bolt must be removed and the countersink reworked. If a countersunk head lies too deep, a decision per A2406.1 has to be obtained. Deviating values for head protrusion and heads which are too low are permitted if specified in the manufacturing documents. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 26 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Chamfer Fig. 23: Gap at countersunk head 5.8.4 Collars Collars, which are self-aligning, must not have a gap. Collars, which are not self-aligning: - no gap is permitted in the case of parallel components, - in the case of installation on component slants (≤ 2°), the resulting gap is allowable. The assembled components shall not reveal any gaps when the collars have been tightened. 5.9 Damaged manufactured heads and collars The defects at manufactured heads shown in Figures 24 and 25 are not allowable. Fig. 24: Unacceptable defects at countersunk head Fig. 25: Unacceptable defects at universal head DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 27 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) Any damage to the surface protection of the manufactured head must be repaired in accordance with 5.5. The defects on collars as well as the deformations shown in Fig. 26 are not allowable. Cracks Fig. 26: Inadmissible defects on collar Damage to the surface protection of the nut/collar must be repaired in accordance with 5.5. 5.9.1 Gap between components Arching of the components between the rivets shall not produce a gap of more than 0,2 mm. At the rivet shank, the gap must not exceed 0,05 mm. max. 0,2 mm max. 0,05 mm Fig. 27: Gaps between components DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 28 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 5.10 Repair If power tools are used for removal of the fasteners, it is recommendable to loosen the collar with pliers in order to reduce the pre-tension. In the case of clearance fits, hold the close-tolerance bolt with a wrench while the collar is turned off (see Fig. 28). If Hi–Shear tools are used, the tool cuts into the collar. Fig. 28: Removal The close-tolerance bolts are pushed out of the hole. If necessary, use a ring-shaped tool to provide counter-pressure. If the bolt shanks and threads do not reveal any damage such as scratches, deformations etc., it is permitted to re-use them. The hole must be measured. If the hole dimensions are within the tolerances and if the hole quality conforms to 80-T-30-9910, a bolt with a standard diameter can again be used. Collars may only be used once, even if the hexagon has not been sheared off. For repair purposes, oversize close-tolerance bolts in accordance with Data Sheet 1 are used. For using oversize close-tolerance bolts and oversize sleeves an approval per A2406.1 is required. It is also permitted to use oversize sleeves per 80-T-34-0185 if the oversize sleeves are approved as a repair solution for the model concerned. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 29 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018) 6 QUALITY ASSURANCE Unless otherwise specified in process- or component-specific design, manufacturing or QA documents, the competent segment shall ensure that the following measures are taken. 1. Check tolerance and dimensions of holes/countersinks according to 5.1 and 5.2 and angularity per 80-T-30-9910. 2. Check protrusion of bolt shank according to 5.7. 3. Check seat of head and collar according to 5.8 using a 0,1 mm feeler gage (prior to application of surface protection). 4. Check manufactured head and collar for any damage according to 5.9 (prior to application of surface protection). 5. The scope of the inspections must be defined by the Quality Assurance department. 6. Check thread for damaging. 7 SAFETY AND HEALTH Apply the local safety regulations. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed Page 30 8 PROCESS FLOW CHART Drilling of holes per 5.1 Countersunk head Universal head Countersinking per 5.2 Chamfering and deburring per 5.3 Checking of holes/countersinks per 6 Checking of grip length per 5.4 Surface protection and wet installation per 5.5 Installation of close-tolerance bolt per 5.6 Checking of bolts, bolt shank protrusion, seat of head and nut per 6. Surface protection of break-off groove per 5.5 DocMaster: Uncontrolled copy when printed 80-T-34-5817 (07/2018)