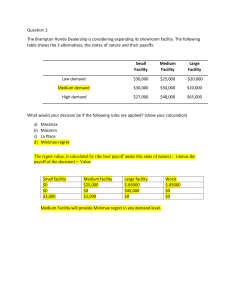
Exam 2 Module 5: Profit Model 1. Possible values for Profit versus revenue (ie which can be negative) 2. Profit model, How calculate profit : From a set of data, calculate Profit, Revenue, Fixed costs, variable costs 3. Profit Calculation Including converting time periods, such as monthly data into daily date. Converting Profit to a different time period. ( day, month, year) 4. Break even; How calculate and what it means 5. Contribution Margin, calculation and what it means ( ie contribute to paying off FC or profit ) The Profit Model The Profit Model and Fixed versus variable Expenses Updated Profit Model when demand and production are not equal: 6. Crossover point: calculation 7. Understand negative crossover Calculating the crossover point When Cross over is negative ( at bottom of story) The Profit Model and Calculating the crossover point Updated Profit Model when demand and production are not equal: 8. Profit and quantity at crossover 9. How demand being greater or less than production influences Profit calculation Break Even, when profit = 0 Contribution Margin Module 6: Simulation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 4 Video Why do we use simulations: Purpose, benefits and Why we use simulation;…Video limitations of simulation Understand probability in percent terms and ranges. Review: Probability in decimal versus percent form Decimal versus percent form Variable to use simulation for. Why we use simulation;…Video Discrete versus continuous variable, deterministic Why we use simulation;…Video versus probabilistic How to simulate a discrete variable? Coin Flip Sim Apply to a business situation and interpret results Video: Donut Simulation Convert frequency data into a probability 1. Calculate probabilities Convert frequency data into cumulative probability 2 Cumulative Probabilities Converting a random number to a value 3_Ranges for different outcomes Using Rand and Vlookup to create a simulation in 4_Put into Vlookup Excel. Given a Vlookup table, understand what value will be returned. Vlookup, how it works Module 1 Excel Vlookup Module 7: Decision Making under Ignornace 1. States of Nature, Decision Alternatives, Outcomes or Payoff, Know what these are, what they represent and where they go on payoff table. Decision making under Certainty, Ignorance, and Risk. Know how they are the same and different and how to solve for each of them. 2. Decision Making under Certainty, what is it? Video States of Nature, Decision Alternatives, Outcomes or Payoff, Decision Making under Certainty 3. Decision Making under Ignorance a. Maximax , what type of person chooses this method and how to use b. Maximin, what type of person chooses this method and how to use c. LaPlace, what type of person chooses this method and how to use d. Opportunity Loss Table (Regret Table), and Minimax Regret method. Always check if I have given you the Regret table or not. 4. Any Excel functions used in class exercises, a. Min, Max, If, Module 8 : Decision Making under Risk Decision Making under Risk : What all the following abbreviations mean and how to solve for them a. EV , Expected Return b. EOL c. EVUII, d. EVUPI, e. EVPI, 5. Decision Trees, How they compare to the payoff tables and how to solve a decision tree Being able to solve all values on a decision tree 6. Other expected value calculations , when using to determine an amount of something 7. Combining probabilities and Expected values to determine an amount Excel Functions 1. Count 2. What adding the if and ifs to a function allows you to do 3. Now/today 4. Freezing top pain 5. Sumifs, countifs, maxifs, minifs, averageifs Module 9: Bayes Theorem and Histograms 1. Meaning of |, P, ∩ 2. Recognize Bayes’ Theorem and definition 3. What do probabilities of all states of nature add to? 4. What do probabilities for all possibilities in a given condition add to? 5. Difference between a histogram and a bar chart 6. How Spam filters work 7. How Market Research uses Bayes Theorem Decision Making under Ignorance Decision Making under Ignorance: maximax, maximin. laplace Decision Making under Ignorance: maximax, maximin. laplace Decision Making under Ignorance: maximax, maximin. laplace Regret Table and Minimax regret Using Excel to create Maximax, Maximin, Laplace, using Excel Funcations Min, Max and IF Decision Making under Risk : EV, EVUPI Decision Making under Risk : EOL Decision Making under Risk : EVUII Decision Making under Risk : EV, EVUPI Decision Making under Risk : EVPI Decision Tree Other examples of using Expected Value Calculation Videos at end of module 8 Videos at end of module 8 Videos at end of module 8 Videos at end of module 8 Videos at end of module 8 Bayes Theorem Bayes Theorem Bayes Theorem, Horse Racing Bayes Theorem, Horse Racing Creating Histograms on Excel Spam Filter Market research the