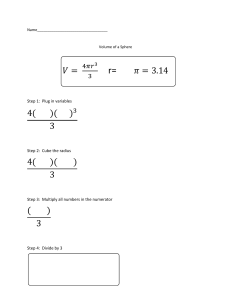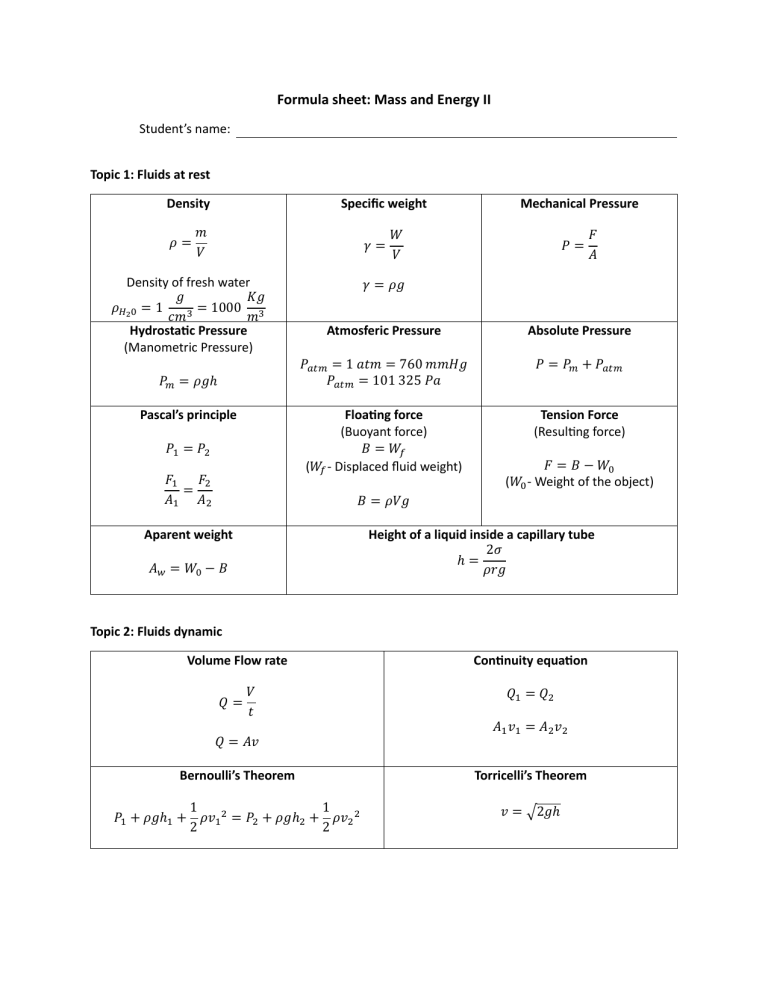
Formula sheet: Mass and Energy II Student’s name: Topic 1: Fluids at rest Density 𝜌= Specific weight 𝑚 𝑉 𝛾= Density of fresh water 𝑔 𝐾𝑔 𝜌𝐻2 0 = 1 = 1000 3 3 𝑐𝑚 𝑚 Hydrostatic Pressure (Manometric Pressure) 𝑃𝑚 = 𝜌𝑔ℎ Pascal’s principle 𝑃1 = 𝑃2 𝐹1 𝐹2 = 𝐴1 𝐴2 Mechanical Pressure 𝑊 𝑉 𝑃= 𝐹 𝐴 𝛾 = 𝜌𝑔 Atmosferic Pressure Absolute Pressure 𝑃𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 760 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 𝑃𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 101 325 𝑃𝑎 𝑃 = 𝑃𝑚 + 𝑃𝑎𝑡𝑚 Floating force (Buoyant force) 𝐵 = 𝑊𝑓 (𝑊𝑓 - Displaced fluid weight) Tension Force (Resulting force) 𝐹 = 𝐵 − 𝑊0 (𝑊0 - Weight of the object) 𝐵 = 𝜌𝑉𝑔 Aparent weight Height of a liquid inside a capillary tube 2𝜎 ℎ= 𝜌𝑟𝑔 𝐴𝑤 = 𝑊0 − 𝐵 Topic 2: Fluids dynamic Volume Flow rate 𝑄= 𝑉 𝑡 𝑄 = 𝐴𝑣 Continuity equation 𝑄1 = 𝑄2 𝐴1 𝑣1 = 𝐴2 𝑣2 Bernoulli’s Theorem Torricelli’s Theorem 1 1 𝑃1 + 𝜌𝑔ℎ1 + 𝜌𝑣1 2 = 𝑃2 + 𝜌𝑔ℎ2 + 𝜌𝑣2 2 2 2 𝑣 = √2𝑔ℎ Tema 3: Vibración Frecuency Period 𝑓= 𝑛 𝑡 𝑇= 𝑡 𝑛 𝑓= 1 𝑇 𝑇= 1 𝑓 Angular frequency 𝜔= Angular displacement 𝜃 𝑡 𝜃 = 𝜔𝑡 𝜔 = 2𝜋𝑓 𝜔= 2𝜋 𝑡 Position (Linear displacement) Velocity 𝑣 = −𝐴𝜔 ∙ 𝑠𝑒𝑛(𝜔𝑡) 𝑥 = 𝐴 ∙ 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝜔𝑡) Acceleration Maximum speed 𝛼 = −𝐴𝜔2 ∙ 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝜔𝑡) 𝑣𝑀𝑎𝑥 = 𝐴𝜔 𝑣𝑀𝑎𝑥 = 2𝜋𝐴𝑓 Frecuency (In function of 𝑥 and 𝑎) 𝑓= 1 𝑎 √ 2𝜋 𝑥 𝑥 𝑎 𝑇 = 2𝜋√ Mass-spring system Frecuency Period Restoring force (Hooke’s Law) Acceleration (In function of 𝑘 and 𝑚) 𝐹 = −𝑘𝑥 𝑓= Maximum speed 𝑣𝑓𝑀𝑎𝑥 Period (In function of 𝑥 and 𝑎) 1 𝑘 √ 2𝜋 𝑚 𝑚 𝑘 𝑇 = 2𝜋√ Elastic Potential Energy 1 𝑈 = 𝑘𝑥 2 2 𝑘𝑥0 2 =√ 𝑚 𝑎= Law of Conservation of Energy (In relation with the elastic forces) 1 1 1 1 𝑘𝑥0 2 + 𝑚𝑣0 2 = 𝑘𝑥𝑓 2 + 𝑚𝑣𝑓 2 2 2 2 2 Simple Pendulum Frecuency 𝑓= 1 𝑔 √ 2𝜋 𝐿 𝑘𝑥 𝑚 Period 𝐿 𝑇 = 2𝜋√ 𝑔 Topic 4: Waves Propagation speed of a wave 𝑣 = 𝜆𝑓 Linear density of a string 𝜇= 𝑚 𝐿 𝜆 𝑣= 𝑇 Speed of a wave on a string under tension 𝐹 𝑣=√ 𝜇 𝐹𝐿 𝑣=√ 𝑚 Wave lenght of the 𝒏 harmonic 𝜆𝑛 = 2𝐿 𝑛 Harmonics on a string Resonant Frecuencies for the 𝒏 harmonic 𝑓𝑛 = 𝑛𝑣 2𝐿 𝑛 = 1, 2, 3, … Resonant Frecuencies for the 𝒏 harmonic in function of 𝑭 𝑓𝑛 = 𝑛 𝐹 √ 2𝐿 𝜇 𝑛 = 1, 2, 3, … 𝑛 = 1, 2, 3, … Energy in a wave: Intensity 𝐼 = 2𝜋 2 𝑣𝜌𝑓 2 𝐴2 Topic 5: Sound Sound speed through the air at a specific temperature 𝑣 = (331 Sound speed through a liquid Sound speed through a solid (Bar) 𝐵 𝑣=√ 𝜌 𝑚 𝑇 )√ 𝑠 273°𝐾 𝑌 𝑣=√ 𝜌 Absolute temperature 𝑇 = °𝐶 + 273.15 Sound speed through an extended solid (Body) Sound speed through a gas Sound speed through an ideal gas 𝛾𝑃 𝑣=√ 𝜌 4 𝐵 + 3𝑆 √ 𝑣= 𝜌 𝛾𝑅𝑇 𝑣=√ 𝑀 Harmonic frecuencies through open pipes Wave lenght of the 𝒏 harmonic Frecuencies of the 𝒏 harmonic 𝜆𝑛 = 2𝐿 𝑛 𝑓𝑛 = 𝑛𝑣 2𝐿 𝑛 = 1, 2, 3, … 𝑛 = 1, 2, 3, … Harmonic frecuencies through closed pipes Wave lenght of the 𝒏 harmonic Frecuencies of the 𝒏 harmonic 𝜆𝑛 = 4𝐿 2𝑛 + 1 𝑓𝑛 = 𝑛 = 1, 2, 3, … Sound intensity 𝐼= 𝑃 𝐴 𝐹𝑜𝑟 𝑛 = 1, 𝑚 = 0 𝐹𝑜𝑟 𝑛 = 2, 𝑚 = 1 𝐹𝑜𝑟 𝑛 = 3, 𝑚 = 2 Sound level (dB) 𝐼 𝛽 = 10𝑙𝑜𝑔 ( ) 𝐼0 𝐼0 = 1 × 10−12 (2𝑚 + 1) 𝑣 4 𝐿 𝑊 𝑚2 Doppler effect (Approaching) 𝑓𝐿 = 𝑓𝑠 ( 𝑣 + 𝑣𝐿 ) 𝑣 − 𝑣𝑠 𝑣 = 343 𝑚 𝑠 Doppler effect (Moving away) 𝑓𝐿 = 𝑓𝑠 ( 𝑣 − 𝑣𝐿 ) 𝑣 + 𝑣𝑠 𝑣 = 343 𝑚 𝑠 Topic 6: The charge and its interactions Coulomb’s Law (Electrostatic force) 𝐹=𝐾 |𝑞1 𝑞2 | 𝑟2 Electrostatic constant 𝐾 = 9 × 109 𝑁𝑚2 𝐶2 Scientific notation 1 𝜇𝐶 = 1 × 10−6 𝐶 1 𝑛𝐶 = 1 × 10−9 𝐶 1 𝐾𝑁 = 1 × 103 𝑁 Topic 7: Electric field Electric field 𝐹 𝐸= 𝑞 𝐸=𝐾 One electron charge 𝑞 = 1.6 × 10−19 𝐶 |𝑞| 𝑟2 Topic 8: Gauss’ Law Electric flow Gauss’ Law Φ𝐸 = 𝐸𝐴𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 Φ𝐸 = 𝑞𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝜀0 𝜀0 = 8.854 × 10−12 Linear charge density 𝜆= 𝑞 𝐿 Surface charge density 𝜎= 𝑞 𝐴 𝐶2 𝑁𝑚 Volumetric charge density 𝜎= 𝑞 𝑉 Electric field for different charge distributions Charge distribution Electric field point Electric field magnitude 1 𝑞 Single point charge Distance 𝑟 from 𝑞 𝐸=( ) 2 4𝜋𝜀0 𝑟 1 𝑞 Outside the sphere, 𝑟 > 𝑅 𝐸=( ) Charge 𝑞 in a conductor sphere 4𝜋𝜀0 𝑟 2 surface of radius 𝑅 Inside the sphere, 𝑟 < 𝑅 𝐸=0 1 𝜆 Infinite wire, charge per unit Distance 𝑟 from the wire 𝐸=( ) lenght 𝜆 2𝜋𝜀0 𝑟 1 𝜆 Infinite conductor cylinder with Outside the cylinder, 𝑟 > 𝑅 𝐸=( ) radius 𝑅, charge per unit lenght 2𝜋𝜀0 𝑟 𝜆 Inside the cylinder, 𝑟 < 𝑅 𝐸=0 1 𝑄 Solid insulated sphere with Outside the sphere, 𝑟 > 𝑅 𝐸=( ) 2 radius 𝑅, with charge 𝑄 4𝜋𝜀0 𝑟 1 𝑄𝑟 distributed uniformly through Inside the sphere, 𝑟 < 𝑅 𝐸=( ) all volume 4𝜋𝜀0 𝑅 3 𝜎 Infinite charged plate with 𝐸= Any point 2𝜀0 uniform charge per unit area 𝜎 Two conductor plates with 𝜎 𝐸= opposite charges uniformly At any point between plates 𝜀0 distributed +𝜎 and −𝜎 Topic 9: Electric potential energy Electric Potential Energy Electric Work 𝑈 = 𝑞0 𝐸𝑟 𝑊 = 𝑞𝐸𝑑 Electric Potential Energy due to two-point charges 𝑈=𝐾 𝑞1 𝑞2 𝑟 Electric Potential Energy in a system with three-point charges 𝑈 = 𝐾[ 𝑞1 𝑞2 𝑞1 𝑞3 𝑞2 𝑞3 + + ] 𝑟12 𝑟13 𝑟23 Electric Potential 𝑉= Electric Potential in the point B 𝑈 𝑞 𝑉𝐵 = 𝑊𝐴𝐵 𝑞 Topic 10: Electric Potential Electric Potential 𝑉=𝐾 𝑛 𝑞 𝑟 Δ𝑉 = 𝑉𝐵 − 𝑉𝐴 𝑞𝑖 𝑞1𝑃 𝑞2𝑃 𝑉𝑃 = 𝐾 ∑ = 𝐾 +𝐾 +⋯ 𝑟𝑖 𝑟1𝑃 𝑟2𝑃 𝑖=1 Potential Difference 𝑊𝐴𝐵 = 𝑉𝐵 − 𝑉𝐴 𝑞0 Potential difference between two charged plates with opposite charges and the same magnitude 𝑉𝐵 − 𝑉𝐴 = 𝐸𝑑 Δ𝑈 = 𝑉𝐵 − 𝑉𝐴 𝑞0 Conservation of Energy Law in Electrostatics (Applied to the movement of one charge between two parallel charged plates) 𝑈1 + 𝐾1 + 𝑊 = 𝑈2 + 𝐾2 Electron-Volt 1 𝑒𝑉 = 1.6 × 10−19 𝐽 Topic 11: Electric current 1 Electric Current 𝐼= Current Density 𝑄 𝑡 𝐽= 𝐼 𝐴 Electric Current (Drift velocity) 𝐼 = 𝑛𝑞𝑣𝑑 𝐴 𝐽 = 𝑛𝑞𝑣𝑑 Electric Resistance 𝑅=𝜌 Temperature Coefficient 𝐿 𝐴 𝛼= 𝛼= Δ𝑅 Ohm’s Law 𝑉 = 𝐼𝑅 𝑅𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 ∙ Δ𝑇 𝑅𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 − 𝑅𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 ∙ [𝑇𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 − 𝑇𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 ] Electric Power 𝑃 = 𝑉𝐼 𝑃= 𝑉2 𝑅 Ohm´s Law and Electric Power 𝑃 = 𝐼2 𝑅 Topic 12: Electric Current 2 Series connection 𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑅1 + 𝑅2 + ⋯ + 𝑅𝑛 𝐼𝑇 = 𝐼1 = 𝐼2 = ⋯ = 𝐼𝑛 𝑉𝐵𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑦 = 𝑉1 + 𝑉2 + ⋯ + 𝑉𝑛 Parallel connection 𝑅𝑒𝑞 = [ 1 1 1 −1 + + ⋯+ ] 𝑅1 𝑅2 𝑅𝑛 𝐼𝑇 = 𝐼1 + 𝐼2 + ⋯ + 𝐼𝑛 𝑉𝐵𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑦 = 𝑉1 = 𝑉2 = ⋯ = 𝑉𝑛 Kirchhoff’s Laws Currents Law Voltages Law ∑ 𝐼𝐸𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑛𝑔 = ∑ 𝐼𝐿𝑒𝑎𝑣𝑖𝑛𝑔 ∑𝑉 =0 Topic 13: Introduction to Magnetism Magnetic Force Magnetic force on a moving charge Magnetic force on a conductor carrying a current ⃗⃗ 𝐹⃗ = 𝑞𝑣⃗ × 𝐵 ⃗⃗ 𝐹⃗ = 𝐼⃗𝐿 × 𝐵 𝐹 = 𝑞𝑣𝐵𝑠𝑒𝑛𝜃 𝐹 = 𝐼𝐿𝐵𝑠𝑒𝑛𝜃 Topic 14: Magnetism Current distribution Long and straight conductor Point in the magnetic field Distance 𝑟 from the conductor At the center of the coil Circular coil of radius 𝑎 On the coil axis Inside the conductor, 𝑟 < 𝑅 Long cylindric conductor of radius 𝑅 Outside the conductor, 𝑟 > 𝑅 Magnitude of magnetic field 𝜇0 𝐼 𝐵= 2𝜋𝑟 𝜇0 𝐼 𝐵= 2𝑎 𝜇0 𝐼𝑎2 𝐵= 3 2(𝑥 2 + 𝑎2 )2 𝜇0 𝐼 𝑟 𝐵= 2𝜋 𝑅 2 𝜇0 𝐼 𝐵= 2𝜋𝑟 𝜇0 𝑁𝐼 𝐵= 𝐿 𝐵≈0 Inside the solenoid, near the center Outside the solenoid Inside the space enclosed by the 𝜇0 𝑁𝐼 coil, at a distance 𝑟 of the axis of 𝐵= Toroidal solenoid (toroid) with 2𝜋𝑟 symmetry compact coil and 𝑁 turns Outside the space enclosed by 𝐵=0 the coil Permeability Constant in vacuum Absolut Permeability Long solenoid, with compact coil and 𝑁 turns per lenght 𝐿 𝜇0 = 4𝜋 × 10−7 𝑇 𝑚 𝐴 𝜇0 = 1.2567 × 10−6 𝑇 𝜇 = 𝜇𝑅 𝜇0 𝑚 𝐴 Topic 15: Introduction to Modern Physiscs Lorentz Transformations 𝑥 ′ = 𝛾(𝑥 − 𝑣𝑡) Gamma Factor 𝛾= 𝑦′ = 𝑦 1 Speed of light 𝑐 = 3 × 108 2 √1 − 𝑣 2 𝑐 𝑚 𝑠 𝑧′ = 𝑧 𝑡 ′ = 𝛾 (𝑡 − 𝑣𝑥 ) 𝑐2 Time Dilation Lenght Contraction Δ𝑇 = 𝛾Δ𝑇0 Δ𝑇 = Δ𝐿 = Δ𝑇0 𝐸 = 𝑚𝑐 2 Δ𝐿0 𝛾 2 √1 − 𝑣2 𝑐 Mass-energy Relation Δ𝐿 = Δ𝐿0 √1 − 𝑣2 𝑐2 Electromagnetic Energy Planck’s constant 𝐸 = ℎ𝑓 ℎ = 6.63 × 10−34 𝐽𝑠 DeBroglie’s equation (Wave lenght) Frecuency 𝜆= ℎ 𝑚𝑣 𝑓= 𝑐 𝜆 Supporting formulas Theorem of Pitagoras Trigonometric functions 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 = ̅̅̅̅ 𝑂𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡 𝐿𝑒𝑔 𝐵𝐶 = 𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 = 𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐿𝑒𝑔 ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐶 = ̅̅̅̅ 𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝐴𝐵 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃 = ̅̅̅̅ 𝑂𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡 𝐿𝑒𝑔 𝐵𝐶 = ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐿𝑒𝑔 𝐴𝐶 Areas Circle Volumes Cube 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟 2 1 𝐴 = 𝜋𝐷 2 4 Square 𝐴 = 𝑙2 Rectangle 𝑉 = 𝑙3 Prism/Cylinder 𝑉 = 𝐴𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒 ℎ Sphere 4 𝑉 = 𝜋𝑟 3 3 𝐴 = 𝑏ℎ Venturi tube 𝑃1 − 𝑃2 = 𝜌𝑔ℎ 1 1 𝑃1 − 𝑃2 = 𝜌𝑣2 2 − 𝜌𝑣1 2 2 2 2(𝑃1 − 𝑃2 ) 𝑣1 = 𝐴2 √ 𝜌(𝐴1 2 − 𝐴2 2 )