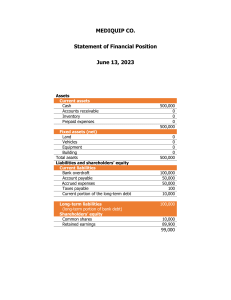
FINANCE FOR NON-FINANCIAL STAFF DEFINITIONS BALANCE SHEET A financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company's financial position at a specific point in time. It presents a summary of a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. The balance sheet follows the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity. PROFIT AND LOSS A financial statement that summarizes a company's revenues, expenses, gains, and losses over a specific period, usually a fiscal quarter or year. It shows the company's net income or net loss by subtracting expenses and losses from revenues and gains. CASH FLOWS Cash flow refers to the movement of money into and out of a business over a specific period. Positive cash flow means more money is coming in than going out, while negative cash flow indicates more money is being spent than earned. Balance sheet 2022 2023 Change Intangible assets Tangible assets Other investments and assets Non-current assets 100 300 100 500 200 400 150 750 100 100 50 250 Inventories Account Receivable Other current assets Cash Current assets 200 450 100 175 925 300 500 150 1,290 2,240 100 50 50 1,115 1,315 $ $ Total assets 1,425 2,990 Equity 500 1,790 1,565 0 1,290 Long term financial debt Other long term liabilities Long term fin. liabilities 250 250 500 250 250 500 0 0 0 Trade payables Financial liabilities Other liabilities Current liabilities 100 200 125 425 350 200 150 700 250 0 25 275 1,425 2,990 1,565 Total Equity and liabilities 3 PROFITABILITY Profitability refers to the ability of a business or investment to generate profits or financial gains. It measures the extent to which a company's revenues exceed its expenses and costs, resulting in a positive net income. Revenue COGS variable COGS fixed COGS 2023 Change 10,000 6,000 200 6,200 11,000 6,600 200 6,800 1,000 600 0 600 3,800 4,200 Gross profit 1,000 1,000 2,000 1,100 1,100 2,200 50 120 10 10 190 50 90 10 10 160 400 0 100 100 200 0 0 (30) 0 0 (30) EBITDA / Operating profit Depreciation and amortization 1,610 100 1,840 100 230 0 EBIT 1,510 1,740 230 Interest and financial expenses Financial income EBT Tax Net income 50 10 1,470 280 1,190 50 10 1,700 310 1,390 0 0 230 30 200 Overhead - variable Overhead - fixed Overhead costs Gains from sale of non-current assets Losses from sale of non-current assets Impairment of receivables Impairment of inventories Other Cash flow statement 2022 2023 1,190 1,390 Depreciation and amortization Impairment of receivables Impairment of inventories Losses (gains) from sale of non-current assets, net 100 10 10 100 10 10 70 40 (Incerease) or decrease of other current assets (100) (60) (Incerease) or decrease in account receivables (Incerease) or decrease in inventories Increase (decrease) in trade payables Increase (decrease) in other liabilities CF from operating activities (250) (120) (120) (100) 690 (60) (100) 250 25 1,605 Sales of non-current assets Purchase of non-current assets CF from investing activities 200 650 (450) 125 515 (390) 0 (70) (45) (115) 125 50 175 100 0 (200) (100) 1,115 175 1,290 $ Net income Increase of share capital Increase (decrease) in financial liabilities Dividends paid CF from financing activities Total cash flow Cash at the beginning of period Cash at the end of period PROFIT AND LOSS BALANCE SHEET FIXED ASSETS EQUITY REVENUES RETAINED EARNING EXPENSES CURRENT ASSETS LONG-TERM LIABILITIES CASH SHORT-TERM LIABILITIES GROSS MARGIN BY NEVENA MISKOVIC 2022 NET PROFIT + DEPRECIATION EBITDA stands for "Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization." It is a financial metric that measures a company's operating performance and profitability by excluding certain non-operating expenses and non-cash items. EBITDA provides a clearer picture of a company's core operating profitability and cash flow generation. CURRENT ASSETS Assets that is expected to be converted in cash in period less than 1 year, such as account receivable, inventories. EQUITY Equity is calculated by subtracting a company's total liabilities from its total assets LIABILITIES LIQUIDITY Ability of company, to convert assets into cash quickly and without significant loss in value and pay its current liabilities in time KPIs Key Performance Indicators, are quantifiable metrics used to measure and evaluate the performance and progress of an organization or specific activities within it. KPIs are used to assess how effectively an organization is achieving its goals and objectives CAPEX Funds invested by a business to acquire, upgrade, or maintain long-term assets that are expected to generate benefits or revenue over an extended period. OPEX Ongoing expenses that a business incurs to operate and maintain its day-to-day activities. It represents the costs necessary to keep a business functioning on a regular basis, excluding any investments or capital expenditures ROI It is a financial metric used to measure the profitability and efficiency of an investment. ROI is calculated by dividing the net profit from an investment by the initial cost of the investment and expressing it as a percentage. QUICK RATIO (Current assets – inventoris) / current liabilities CASH BALANCE NET PROFIT DSO Average Account receivable / Revenues * 365 DIO Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) measures the average number of days it takes for a company to sell its inventory. DPO ACCOUNTING CONTROLING TREASURY Policy and audit Risk Financial accounitng, bookkeeping, tax, preparation FS Financial planning, analysis, budget, resource planning Financial operations, cash management, collection Preparaton of procedures, internal audit conducting Financial risk management VERTICAL FINANCIAL ANALYSIS Vertical analysis 2024 2025 2026 2027 CASH BASIS Cash basis accounting recognizes revenues and expenses when cash is received or paid. Revenue is recorded when cash is received from customers, and expenses are recorded when cash is paid to suppliers or vendors. Revenues COGS variable COGS fixed COGS 100% 60% 2% 62% 100% 60% 2% 62% 100% 60% 2% 62% 100% 60% 2% 62% 100% 60% 2% 62% Gross profit 38% 38% 38% 38% 38% Overhead - variable Overhead - fixed Overhead costs 9% 10% 19% 12% 10% 22% 12% 10% 22% 12% 10% 22% 12% 10% 22% DEBIT Debits are recorded on the left side of an account. vs vs ACCURAL BASIS Recognizes revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid. Under this method, revenue is recorded when goods or services are delivered or completed, and expenses are recognized when they are incurred, irrespective of cash flow CREDIT Credits are recorded on the right side of an account. EBITDA / Operating profit 18% 15% 14% 15% 16% Depreciation and amortization Interest and financial expenses Financial income EBT 2% 0% 0% 16% 3% 0% 0% 12% 3% 0% 0% 11% 3% 0% 0% 12% 3% 0% 0% 13% They increase asset accounts and decrease liability and equity accounts. They increase liability and equity accounts and decrease asset accounts. 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% Debits are used to record increases in expenses and losses. Credits are used to record increases in revenue, income, and gains. 14% 10% 9% 10% 11% In general, debits represent the flow of value into an account. In general, credits represent the flow of value out of an account. Net income DISCOUNTING EFFICIENCY Discounting is process of determining the present value of future cash flows or a future sum of money by adjusting it for the time value of money. The time value of money recognizes that a dollar received in the future is worth less than a dollar received today due to factors such as inflation, opportunity cost, and risk. Efficiency refers to the ability to accomplish a task, process, or activity in the most optimal and resource-efficient manner. It focuses on minimizing waste, reducing costs, and maximizing output or results while utilizing the least amount of resources, such as time, money, or materials Discounted Cash Flows 2024 2025 2026 2027 2028 CASH FLOW Net income 1,055 1,086 1,088 1,167 1,159 235 235 275 275 275 (106) (570) 613 1.1342 (7) 0 1,314 1.2864 (8) (200) 1,155 1.4590 (8) 0 1,434 1.6548 (9) 0 1,424 1.8768 Cash flow is concerned with the movement of actual cash in and out of the company. ash flow provides a more direct measure of a company's ability to generate and manage cash 541 1,021 792 866 759 Depreciation and amortization Net Working capital adjustments CAPEX adjustments Free Cash Flow Discount factor DCF EBITDA Multiple valuation EBITA non-adjusted 1,629 Non operating items One-time items Asset impairments (reversal) GAAP adjustments IC fair prices adjustment Adjustments EBITDA adjusted Valuation Cash on hand Interest bearing debt Net financial position Valuation adjusted NEVENA MISKOVIC 75 20 15 (30) 25 140 1,769 11,499 1,376 450 926 12,425 | CAPEX Capital expenditures in Balance sheet involve significant investments in assets that have a long-term impact on the business SHORT TERM vs EBIT EBIT represents the operating profitability before considering interest and taxes OPEX Recognized in P&L and incurred for day-today operations. Those are regular operating business expenses such as payroll, marketing vs LONG TERM Due in more than 1 year BALANCE SHEET Helps stakeholders assess the financial health, liquidity, and solvency of a company. CCC The Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) represents the time it takes for a company to convert its investments in inventory and other resources into cash flow from sales. DIO+DSO-DPO ASSET TURNOVER Asset turnover measures a company's efficiency in utilizing its assets to generate revenue. Revnue / Assets EBITDA COVERAGE EBITDA to interest coverage ratio evaluates a company's ability to cover its interest expenses with its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization EBITDA / Interest expenses EBITDA MARGIN EBITDA margin represents the percentage of revenue that remains as after deducting all operating expenses, indicating the company's operating profitability. EBITDA / Revenues NET PROFIT RATE Net profit rate (also known as net profit margin or net profitability) measures the percentage of revenue that remains as net profit after deducting all expenses, including taxes and interest, reflecting the company's overall profitability. Net income / Revenues vs Due less than 1 year FOLLOW ON LINKEDIN EFFECTIVENES Relates to the degree of achieving or fulfilling a desired objective, goal, or outcome. It emphasizes the extent to which the desired results or intended targets are met. Effectiveness is about doing the right things and ensuring that the desired outcome or purpose is achieved successfully vs Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) determines the average number of days it takes for a company to pay its suppliers. Average trade payables / COGS *365 TERMS COMPARISON 2028 $ Tax Financial obligations or debts that a company owes to external parties. They represent the company's legal or financial responsibilities that need to be fulfilled in the future Current assets / current liabiiltes CASH FLOW TAX OPERATING PROFIT What company owns like property, plants, equipment, intellectual property, shares in associate companies, etc. The current ratio measures a company's ability to cover its short-term liabilities with its short-term assets Average inventories / COGS * 365 The difference between total revenues and total costs FIXED ASSETS Measures a company's profitability and efficiency in generating profits from the shareholders' equity The quick ratio (also known as the acid-test ratio) evaluates a company's ability to meet short-term obligations using its most liquid assets. CFO NET PROFIT Revenues are defined as the inflows of economic benefits arising from the ordinary Activities of an entity when those inflows result in an increase in equity, other than increases relating to contributions from equity participants ROE (PROFITABILITY) +/- CHANGE IN ASSETS FINANCE DEPARTMENT ORGANIZATION EBITDA REVENUES Financial ratios are quantitative metrics used to analyze and assess the financial performance, health, and stability of a company. These ratios are derived from the financial statements and provide insights into various aspects of a company's operations, profitability, efficiency, liquidity, and solvency. Financial ratios are widely used by investors, analysts, and stakeholders to evaluate the financial position and make informed decisions. Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) calculates the average number of days it takes for a company to collect payment from its customers for sales made on credit. A financial metric that represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It measures how efficiently a company produces its products or services and is a key indicator of its profitability at the most basic level. Financial metric that represents the profit generated from a company's core operations before deducting interest and taxes. DEFINITION CURRENT RATIO CASH FLOWS PROFIT BEFORE TAX FINANCIAL RATIOS Net income / Revenues BASIC FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND THEIR RELATION NET MARGIN Financial ratio that indicates the percentage of revenue that remains as net profit after deducting all expenses, including COGS, operating expenses, interest, taxes, and other non-operating costs. It measures the profitability of a company's operations and reflects how effectively it manages its costs and generates profit. Profit and Loss Account vs PROFIT & LOSS Provides insights into a company's operational performance, profitability, and ability to generate consistent earnings. EQUITY RATIO Equity ratio compares the company's total equity to its total assets, expressing the proportion of assets funded by equity and indicating the company's financial leverage and stability. Equity / total liabilities DEBT RATIO Debt ratio assesses the proportion of a company's total debt relative to its total assets, providing insight into the company's financial risk and dependency on debt financing. Total liabilities / Assets | REPOST