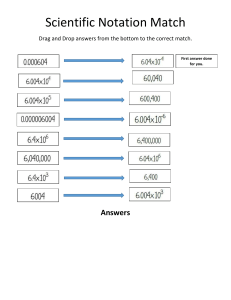
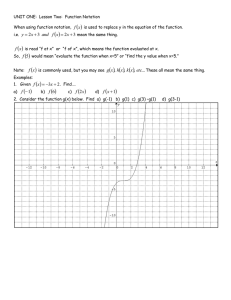
The Absolute Value Function The absolute value function: 𝑓(𝑥) = |𝑥| → On a number line, this function describes the distance or magnitude of the the number x from the origin → 𝑓(𝑥) = |𝑥| is a piecewise function in which 𝑓(𝑥) = � −𝑥, 𝑥 < 0 𝑥, 𝑥 ≥ 0 Example 1: |3| = |−2| = |−3| = Example 2: Find |−2−4|+2 |4| = Example 3: Express using absolute value notation. a) 𝑥 ≤ −2 𝑜𝑟 𝑥 ≥ 2 b) −5 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5 b) |𝑥| ≤ 5 Example 4: Graph on a number line. a) |𝑥| > 4 Example 5: Rewrite using absolute value notation. a) b) Example 6: Graph 𝑓(𝑥) = |𝑥 − 2| Example 7: Graph 𝑓(𝑥) = |𝑥| + 2 Example 8: Graph 𝑓(𝑥) = |3𝑥 − 6|