Digital Communication & Networks: Transmission Media Overview
advertisement

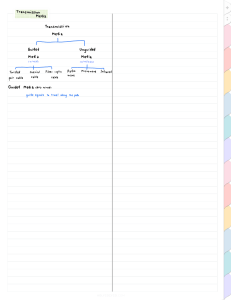
DIGITAL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS Data transmission - is the physical transfer of data over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium either wired or wireless. Data – is a distinct piece of information. Data can exist in a variety of forms such as sound, text, numbers or images. The data is often represented as an electro-magnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage signal, a radio wave or an infra-red signal. Types of Data Transmission Serial Transmission - is a method of data transmission in which the bits of a data character are transmitted sequentially over a single channel. Parallel Transmission - is a method of data transmission in which the bits of a data character are transmitted simultaneously over a number of channels/ports. Transmission Media – refers to any modes or materials which can propagate waves or electrical energy for telecommunications purposes. TRANSMISSION MEDIA The physical path through which computers send and receive these signal is called the transmission medium. Transmission media are divided into two categories: 1. Cable Media (Guided) – transmits signal along a solid medium such as a transmission line. 2. Wireless Media (Unguided) - transmits signal over large distance by using antenna. It employs the higher electromagnetic frequencies, such as radio waves, microwaves and infrared. Types of material use in guided transmission: 1. Twisted pair cable 3. Fiber optics 2. Coaxial cable Three main types of wireless media: Radio wave Microwave Infrared Radio wave - Radio frequencies can be transmitted across electrical cables (twisted pair or coaxial) or by using radio broadcast transmission. Microwave – microwave transmissions are use to communicate between earth stations and satellites. Infrared Media – infrared media use infrared light to transmit signals. Characteristics of Transmission Media: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cost Installation Requirements Bandwidth Band Usage (Baseband or Broadband) Attenuation Immunity from electromagnetic interferences Bandwidth - In computer networking, the term bandwidth refers to the capacity of a medium to transmit data. Bandwidth is measured in: Bps - bits per second Kbps - kilo-bits per second Mbps - mega bits per second Gbps - gigabits per second NOTE: A medium that has a high capacity has a high bandwidth, whereas a medium that has a limited capacity has a low bandwidth. The greater the bandwidth, the more data can be transferred in a given time. Attenuation – is a measure of how much a signal weakness as it travels through a medium. Electromagnetic signals tend to weaken during the transmission. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) – consist of outside electromagnetic noise that distorts the signal in a medium. It affects the signal that is sent through the transmission media making it difficult for the receiving computer to accept or decode the signal. Signaling is the way data is transmitted across the medium. Two forms of signaling: 1. Analog Signaling 2. Digital Signaling Analog Signal - The signal propagated through the medium is continuously varying electromagnetic waves. Digital Signal - Digital signals vary between two discrete values of some physical quantity, one value representing the binary number 0 and the other representing 1. Baseband and Broadband Transmission Baseband – A signaling technology that sends digital signals over a single frequency as discrete electrical pulses. The signal uses the entire bandwidth of a transmission medium. The baseband signal is bidirectional so that a baseband system can transmit and receive signals simultaneously. Broadband – A signaling technology that sends signal over a range of different frequencies as electromagnetic waves. A single transmission medium is divided and shared simultaneously. Broadband signals are unidirectional-traveling in only one direction at a time so a broadband system can generally either transmit or receive but cannot do both simultaneously. TRANSMISSION MEDIUMS Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable Shielded Twisted Pair Cable Coaxial Cable Fiber Optics Cable