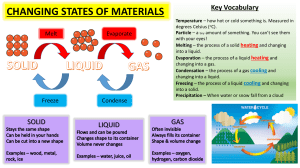
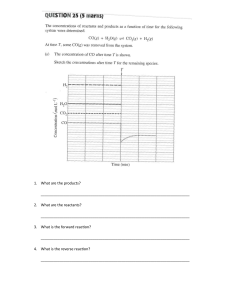
MOCK QUIZ BEE TEAM 2 PHYSICS / CHEMISTRY / THERMODYNAMICS / ECONOMICS EASY ROUND QUESTION 1: means that the goals to be accomplished or the issue to be overcome is ill-defined, that solutions are difficult to determine and that information on results is inaccessible A. Ambiguity C. Risk B. Certainty D. Uncertainty QUESTION 1: means that the goals to be accomplished or the issue to be overcome is ill-defined, that solutions are difficult to determine and that information on results is inaccessible A. Ambiguity C. Risk B. Certainty D. Uncertainty QUESTION 2: How does Joseph John Thompson call his model of the atom A. Orbital Model B. Planetary Model C. Radioactive Model D. Plum-pudding Model QUESTION 2: How does Joseph John Thompson call his model of the atom A. Orbital Model B. Planetary Model C. Radioactive Model D. Plum-pudding Model QUESTION 3: What refers to a negligible body when compared to the distances involved regarding its motion A. Quarks B. Particle C. Atomic Substance D. Element QUESTION 3: What refers to a negligible body when compared to the distances involved regarding its motion A. Quarks B. Particle C. Atomic Substance D. Element QUESTION 3: A pure substance at absolute zero temperature is in perfect order, and its entropy is zero. This is best known as ____________ ANS: The Third Law of Thermodynamics QUESTION 4: ________________What happens to the pressure of a sample of helium gas if the temperature is increased from 200 K to 800 K, with no change in volume? A. P will decrease by a factor of 4 B. P will increase by a factor of 4 C. P will not change D. P will increase by a factor fo 2 QUESTION 4: ________________What happens to the pressure of a sample of helium gas if the temperature is increased from 200 K to 800 K, with no change in volume? A. P will decrease by a factor of 4 B. P will increase by a factor of 4 C. P will not change D. P will increase by a factor fo 2 QUESTION 4: ________________6. Which material is commonly used as a reinforcing phase in fiberreinforced composites? A. Aluminum B. Glass C. Copper D. Carbon fibers QUESTION 5: 1 pound (as a unit for force) is equal to ____ N. A. 2.25 B. 3.33 C. 4.45 D. 1.45 QUESTION 5: 1 pound (as a unit for force) is equal to ____ N. A. 2.25 B. 3.33 C. 4.45 D. 1.45 QUESTION 6: At the surface of the earth, an object of mass m has weight w. If this object is transported to an altitude that’s twice the radius of the earth, then, at the new location, A. its mass is m/2 and its weight is w/2 B. its mass is m/2 and its weight is w/4 C. its mass is m and its weight is w/4 D. its mass is m and its weight is w/9 QUESTION 6: At the surface of the earth, an object of mass m has weight w. If this object is transported to an altitude that’s twice the radius of the earth, then, at the new location, A. its mass is m/2 and its weight is w/2 B. its mass is m/2 and its weight is w/4 C. its mass is m and its weight is w/4 D. its mass is m and its weight is w/9 QUESTION 6: The ratio of quick assets to current liabilities is called _______. A. gross margin ratio B. profit margin ratio C. acid-test ratio D. return of investment QUESTION 7: Defined as the collection of past information and current knowledge to predict the future A. Regression Analysis B. Simulation C. Forecasting D. Sampling Theory QUESTION 7: Defined as the collection of past information and current knowledge to predict the future A. Regression Analysis B. Simulation C. Forecasting D. Sampling Theory QUESTION 8: Which of the following materials is an example of a ferromagnetic material? A. Aluminum (Al) B. Copper (Cu) C. Iron (Fe) D. Silicon (Si) QUESTION 8: Which of the following materials is an example of a ferromagnetic material? A. Aluminum (Al) B. Copper (Cu) C. Iron (Fe) D. Silicon (Si) MODERATE ROUND QUESTION 1: What is the critical cooling rate required to form an amorphous structure in a material? A. Very slow cooling B. Moderate cooling C. Rapid cooling D. Extremely rapid cooling QUESTION 1: What is the critical cooling rate required to form an amorphous structure in a material? A. Very slow cooling B. Moderate cooling C. Rapid cooling D. Extremely rapid cooling QUESTION 2: (3 MINUTES) In how many years is required for P 2,000 to increase by P 3,000 if interest at 12% compounded semiannually? A. 7.86 years B. 7.65 years C. 7.23 years D. 8.12 years QUESTION 2: (3 MINUTES) In how many years is required for P 2,000 to increase by P 3,000 if interest at 12% compounded semiannually? A. 7.86 years B. 7.65 years C. 7.23 years D. 8.12 years QUESTION 3: What is the measure of the outer diameter of the seal of a Professional Electronics Engineer, in accordance with R. A. No. 9292? A. 48 mm B. 46 mm C. 50 mm D. 44 mm QUESTION 3: What is the measure of the outer diameter of the seal of a Professional Electronics Engineer, in accordance with R. A. No. 9292? A. 48 mm B. 46 mm C. 50 mm D. 44 mm QUESTION 4: (3 MINUTES) A block of mass A = 8 kg is moving with velocity v = 6 m/s toward a target block of mass B = 2 kg, which is stationary (v = 0). The objects collide head-on, and immediately after the collision, the speed of block B is twice the speed of block A. What is the speed of block A after the collision? A. 2 m/s C. 3 m/s B. 1 m/s D. 4 m/s QUESTION 4: (3 MINUTES) A block of mass A = 8 kg is moving with velocity v = 6 m/s toward a target block of mass B = 2 kg, which is stationary (v = 0). The objects collide head-on, and immediately after the collision, the speed of block B is twice the speed of block A. What is the speed of block A after the collision? ANS: D. 4 m/s m1v1 + m2v2 = m1v1‘ + m2v2‘ 8(6) + 2(0) = 8(x) + 2(2x) x=4 QUESTION 5: It is the energy change accompanying a mole of electrons being added to a mole of a gaseous atoms or ions. A. Electronic Affinity B. Bingling Energy C. Biochemical Energy D. Fission QUESTION 5: It is the energy change accompanying a mole of electrons being added to a mole of a gaseous atoms or ions. A. Electronic Affinity B. Bingling Energy C. Biochemical Energy D. Fission ANS: A. Electronic Affinity QUESTION 6: (3 MINUTES) 2.5g of glucose is dissolved into 375 ml of water. What is the molarity of the solution? A. 0.012 M B. 0.037 M C. 0.067 M D. 0.081 M QUESTION 6: (3 MINUTES) 2.5g of glucose is dissolved into 375 ml of water. What is the molarity of the solution? A. 0.012 M B. 0.037 M C. 0.067 M D. 0.081 M ANS: B. 0.037 M M= 2.5 g MW 0.375 L QUESTION 7: QUESTION 7: QUESTION 8: QUESTION 8: (3 MINUTES) DIFFICULT ROUND QUESTION 1: A debt of P 10,000 with 10 % interest compounded semi-annually is to be amortized by semi-annual payment over the next 5 years. The first due in 6 months. Determine the semi-annual payment. A. P 1,234.09 B. P 1,255.90 C. P 1,275.68 D. P 1,295.05 QUESTION 1: A debt of P 10,000 with 10 % interest compounded semi-annually is to be amortized by semi-annual payment over the next 5 years. The first due in 6 months. Determine the semi-annual payment. A. P 1,234.09 B. P 1,255.90 C. P 1,275.68 D. P 1,295.05 QUESTION 2: Which of the following polymers is known for its exceptional heat resistance and is commonly used in applications such as cookware, electrical insulation, and aerospace components? A. Polyethylene (PE) B. Polypropylene (PP) C. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) D. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) QUESTION 2: (3 MINUTES) Which of the following polymers is known for its exceptional heat resistance and is commonly used in applications such as cookware, electrical insulation, and aerospace components? A. Polyethylene (PE) B. Polypropylene (PP) C. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) D. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) QUESTION 3: Section 8 (e) of R. A. No. 9292 states that the chairman and members of the Board must be in active practice of the electronics engineering profession for at least ____ years prior to his appointment, either in self-practice, or employment in government service and/or in the private sector. A. 3 B. 5 C. 7 D. 10 QUESTION 3: Section 8 (e) of R. A. No. 9292 states that the chairman and members of the Board must be in active practice of the electronics engineering profession for at least ____ years prior to his appointment, either in self-practice, or employment in government service and/or in the private sector. A. 3 B. 5 C. 7 D. 10 QUESTION 4: The heat of fusion for water is 334 kJ/kg. How much thermal energy is required to completely melt a 100gram ice cube? A. 3.34 kJ B. 33.4 kJ C. 51.1 kJ D. 5.11 kJ QUESTION 4 QUESTION 5: (3 MINUTES) What law states that the rate of effusion of a gas, which is the amount of gas that through the hole in a given amount of time, is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass? A. Henry’s law B. Graham’s law of effusion C. Hund’s law D. Lewis theory QUESTION 5: (3 MINUTES) What law states that the rate of effusion of a gas, which is the amount of gas that through the hole in a given amount of time, is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass? A. Henry’s law B. Graham’s law of effusion C. Hund’s law D. Lewis theory QUESTION 6: Ammonium sulfate has a chemical formula of (NH4)2SO4. Calculate how many percent of this compound is oxygen? A. 48.43% B. 49.43% C. 43.34% D. 42.34% QUESTION 6: QUESTION 7: (3 MINUTES) Two balls roll toward each other. The red ball has a mass of 0.5 kg and a speed of 4 m/s just before impact. The green ball has a mass of 0.3 kg and a speed of 2 m/s. After the headon collision, the red ball continues forward with a speed of 2 m/s. Find the speed of the green ball after the collision. A. + 1.3 m/s B. B. + 2.6 m/s C. – 1.3 m/s D. – 2.6 m/s QUESTION 7: (3 MINUTES) QUESTION 8: These plans are designed primarily to incorporate steps that are fairly new and unlikely to be replicated A. Single Use Plans B. Budget C. Program D. Project QUESTION 8: These plans are designed primarily to incorporate steps that are fairly new and unlikely to be replicated A. Single Use Plans B. Budget C. Program D. Project GOOD NIGHT