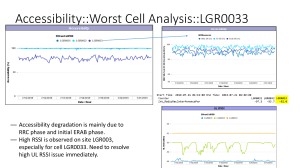
LTE Access Issue Troubleshooting HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Content Poor Accessibility Reasons Checklist of Required Action for Access Problem Access Performance Evaluation Analysis of Tracing Case Study HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 2 Poor Accessibility Reasons Common causes Network Planning and Optimization Incorrect ZC sequence Improper TAC/TAL planning Weak coverage Coverage overlap External interference Failure of resource admission on the air interface CPU overload CAPS overcapacity Insufficient license capacity HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 3 Poor Accessibility Reasons Parameter, RF channel, Interference and Transmission Improper parameter setting Use of non-optimal parameters Improper license sharing policy RF channel fault GPS clock lost and ineffective subframe offset configuration(TDD) Intermodulation interference (FDD) Incorrect transmission IP address SCTP link intermittence Packet loss on or long delay of a transmission link Devices UE’s are faulty Bad access performance of the UE ENodeB fault(Fault alarms, VSWR alarm, board alarm) Sleeping cell EPC fault(abnormal operations, message response timeout, NAS procedure exception) HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 4 Content Poor Accessibility Reasons Checklist of Required Action for Access Problem Access Performance Evaluation Analysis of Tracing Case Study HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 5 Checklist Of Required Actions For Access Problems Action Prerequisite Purpose 1.Determine whether the problem is a top cell problem or network-wide problem. Action 1: performing scope identification, KPI trend analysis, and cause resolution None 2.Analyze the major causes of access failures and come up with priority actions. 3.Submit a sleeping cell problem to R&D for analysis. Action 2: checking operation logs, device faults, alarms, and external events None. Pay attention to this action in the event of sudden deterioration of KPIs. 1.Check operation logs to identify parameter modification and operations that may cause problems. Then, find out why parameters are modified and take measures to restore modified parameters. 2.Check whether there are device faults that result in access problems or whether access-related alarms are reported. 3.Check whether EPC upgrades or network cutover are performed, or the transmission networking changes. Action 3: checking parameters HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR 1.Analyze whether the core access parameters are proper on or consistent between the eNodeB and EPC. None 2.Check whether parameter settings are consistent before and after parameter mapping is finished in a network swapping scenario. Page 6 Checklist Of Required Actions For Access Problems Action Prerequisite Purpose Perform proper actions based on site conditions: Action 4: checking version differences and known issues None 1.Check for version difference on the top sites. 2.Check for known issues. 1.Check whether the access problem is caused by improper configurations of parameters such as TAC, TAL, and subframe configuration. Action 5: checking network planning and optimization Perform this action based on the analysis results provided by action 1. 2.Check whether an access problem is caused directly by resource congestions or indirectly by improper parameter configurations. For details how to analyze a congestion problem caused by the system CAPS overcapacity, see LTE performance-Basic Network Planning and Optimization. 3.Check whether an access failure is caused by weak coverage. For top cell problems, perform this action. Action 6: checking RF channels Perform this action for interference check based on the analysis results provided by action 1. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR 1.Check whether RF channels are normal. 2.Check for uplink interference Page 7 Checklist Of Required Actions For Access Problems Action Action 7: checking top UE types and top users Prerequisite Purpose For top-cell problems, check top users. 1.Check whether access-related KPI deterioration happens on individual user(s). For network-wide problems, check top UE types. 2.Check whether the access problem is caused by a certain type of UEs. 1.Check whether an access failure is caused by the EPC faults. Action 8: checking the EPC Perform this action based on the analysis results provided by action 1. Action 9: checking transmission Perform this action based on cause resolution results. Action 10: repeating a complained problem Perform this action for analyzing a complained problem. For other problems, perform this action when problems needs to be repeated. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR 2.Check whether an access problem is caused by operations on the EPC (for example upgrades and configuration changes). Check whether the access failure is caused by transmission faults. 1.Provide the general principles for analyzing a complained problem. 2.Repeat the problems and collect the related logs. Page 8 Content Poor Accessibility Reasons Checklist of Required Action for Access Problem Access Performance Evaluation Analysis of Tracing Case Study HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 9 Access Performance Evaluation • From performance management › Access successful ratio = RRC setup successful ratio x ERAB setup successful ratio › Random access and NAS failures are not considered in eNodeB performance management, but these factors also impact user experience • From drive test tools (Nemo) › It can identify access failure caused by random access failure and NAS failure HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 10 Accessibility- RRC Setup Success Rate KPI Name RRC Setup Success Ratio Measurement Scope Network Level Measurement Period Network Busy Hour Formula L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ/L.RRC.ConnReq.Att*100% Associated Counters A: L.RRC.ConnReq.Att C: L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ Unit Percentage (%) Target 99% Remark KPI 2.03 RRC Overall RRC Setup HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 11 Accessibility- RRC Setup Success Rate (Service) KPI Name E UTRAN RRC Setup Success Ratio (Service) Measurement Scope Network Level Measurement Period Network Busy Hour Unit (L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ.Emc+L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ.Hig hPri+L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ.Mt+L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ. MoData+L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.DelayTol)/(L.RRC.ConnRe q.Att.Emc+L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.HighPri+L.RRC.ConnRe q.Att.Mt+L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.MoData+L.RRC.ConnReq. Succ.DelayTol)*100% A: (L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.Emc+L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.HighPri +L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.Mt+L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.MoData+ L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.DelayTol)) C: (L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ.Emc+L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ.Hig hPri+L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ.Mt+L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ. MoData+L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ.DelayTol) Percentage (%) Target Monitoring Remark KPI 2.031 RRC Service Formula Associated Counters HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR RRC Setup Page 12 Accessibility- RRC Setup Success Rate (Signaling) KPI Name E UTRAN RRC Setup Success Ratio (Signaling) Measurement Scope Network Level Measurement Period Network Busy Hour Formula L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ.MoSig/L.RRC.ConnReq.Att.M oSig*100% Associated Counters A: L.RRC.ConnReq.Att C: L.RRC.ConnReq.Succ Mosig Unit Percentage (%) Target Monitoring Remark KPI 2.032 RRC Signaling RRC Setup HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 13 Accessibility- S1 SIG Setup Success Rate KPI Name S1 SIG Setup Success Rate Measurement Scope Network Level Measurement Period Network Busy Hour Formula L.S1Sig.ConnEst.Succ / L.S1Sig.ConnEst.Att *100% Associated Counters A: L.S1Sig.ConnEst.Att B: L.S1Sig.ConnEst.Succ Unit Percentage (%) Target 98.5% Remark KPI 2.04 S1 Setup HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 14 Accessibility- eRAB Setup Success Rate KPI Name eRAB Setup Success Rate Measurement Scope Network Level Measurement Period Network Busy Hour Formula L.E-RAB.SuccEst/L.E-RAB.AttEst *100% Associated Counters A: L.E-RAB.AttEst B: L.E-RAB.SuccEst Unit Percentage (%) Target 99% Remark KPI 2.05 HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Initial Context Setup Page 15 eRAB Setup Accessibility- eRAB Setup Success Rate (QCI=i) KPI Name eRAB Setup Success Rate (QCI=i) Measurement Scope Network Level Measurement Period Network Busy Hour Formula L.E-RAB.SuccEst.QCI.i/L.ERAB.AttEst.QCI.i*100% A: L.E-RAB.AttEst.QCI.i B: L.E-RAB.SuccEst.QCI.i (i=1,2,3,…,9) Associated Counters Unit Percentage (%) Target Monitoring Remark KPI 2.051 HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Initial Context Setup Page 16 eRAB Setup General Process • Determine the scale of problem › From the performance statistic, we can determine the scale of the problem, is it global problem, or cell level problem or just some individual UE problem. Then we can select bottom N cell as optimization target › Customer complain is an effective way to locate the individual UE problem • For large scale access failure › Check eNodeB alarm and basic configuration › Check RF channel problem » Once RF channel is abnormal, such as high VSWR, low RSSI Too Low or RSSI is unbalanced, then the access performance should be significantly affected. • For individual UE problem, signaling analysis can be used to locate the detailed cause HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 17 Handle Enodeb Generic Alarm • Tools: M2000 or WebLMT • Procedure › Check the generic hardware fault alarm, such as hardware fault, board unusable , or any other alarms which are related with hardware failure or link failure. » Solution: Replace the faulty component. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 18 Check DL Power Configuration • To ensure the coverage, the DL power parameters should be properly set › RS power = Maximum RRU power/channel – 10lg(total subcarriers ) + 10lg(Pb+1) › PDSCH power = PA + RS power » PA = -10lg(Pb+1) • Related command: › LST PDSCHCFG: check Pb and RS power setting › LST CELLDLPCPDSCHPA: check PA setting HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 19 Check CRPI Rate • If the bandwidth is 10MHz or above, the CPRI rate should be equal or more than 2.5Gbps, otherwise, the cell can’t be setup • If the rate is not correct, change the CPRI module HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 20 Check S1 Interface Status • If SCTP link is faulty, check the SCTP configuration, such as peer IP address, SCTP port number • If S1intrface state is faulty, check the PLMN and operator ID. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 21 Check Cell Barred Status • If cell is barred, use the following command to recover it HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 22 Check RF Channel Problem • Due to the bad feeder quality, incorrect feeder connection or strong interference, it might affect RF channel performance which has impact on UE access. • Relevant problem: › High VSWR: ALM-26529 RF Unit VSWR Threshold Crossed › Low RSSI: ALM-26521 RF Unit RX Channel RSSI Too Low › RSSI unbalance: ALM-26522 RF Unit RX Channel RSSI Unbalanced » RSSI of the main RX channel and the RSSI of the diversity RX channel exceeds 10 dB. › High RSSI: Caused by interference HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 23 Cause Of High VSWR • VSWR: Voltage Standard Wave Ratio, indicate the if feeder impedance is match or not. The normal VSWR range is 1~1.5. If current VSWR is more than a specified threshold, then eNodeB will generate relevant alarm. • Alarm generation: › Cell is activated › RF power is more than 34dBm/channel › VSWR is more than a specified threshold • Possible cause: › Incorrect VSWR alarm threshold › RF unit hardware fault › RRU/RFU wrong connection › Bad feeder quality or nonstandard feeder installation HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 24 Solution For High VSWR • Step 1: Check if the VSWR alarm threshold is correct (default is 2dB). › Note: RRU TX channel will automatic closed if VSWR is extremely high (more than post- processing threshold) Threshold for TX shutdown Threshold VSWR alarm generation • • Step 2: If alarm threshold is correct, then check if relevant feeder installation and RRU connections are meet the standard. Step3: After the feeder tuning, if TX channel is closed, then activate TX channel again › MOD TXBRANCH HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 25 Cause Of Low RSSI • Alarm generation: If RSSI is less than a specified value • Incorrect RX attenuation setting › If no TMA, the attenuation should be 0 › If 12dB TMA is used, the attenuation should be 4 to 11dB › If 24dB TMA is used, the attenuation should be 11 to 22dB • Feeder problem › Due to bad feeder quality, causing additional loss › RRU fault HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 26 Solutions For Low RSSI • Step 1: Check if RRU RX attenuation is correct • Step2: If attenuation is correct, then check the feeder installation and connection HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 27 Cause Of Imbalance Of RSSI Alarm generation: RSSI of the main RX channel and the RSSI of the diversity RX channel exceeds 10 dB. • Possible causes › High interference › RRU cross connections HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 28 Solution of Imbalance of RSSI • UL interference check › From web-LMT: Perform spectrum detection to evaluate UL interference › From M2000 client: Perform interference detect monitoring › Find out interference source • Check RRU connections, avoid cross connections, show as below A N T 1 A N T 2 RRU1 RRU2 HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 29 Classification Of Interference • Passive inter-module interference: › Due to non-linearity of radio component ,the high phase harmonic wave might be generated and inter-modulated by RX signal, thus the new inter-module signal will arrive the receiver causing the interference. • External interference: › Interference from the other system, such as 2G, 3G, CDMA, radio, radar eg. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 30 How To Located Inter-modulated Interference • This kind of interference increases with eNodeB transmit power, so we can simulate the DL load, and check RSSI, if it obviously increases with the DL load incensement, then we can determine the interference • Load simulation: HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 31 How To Located External Interference • If we exclude inter-modulated interference, then it should be external interference › Lower the TX of RRU/RFU, if RSSI is still high, then we can conclude this is external interference HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 32 Analysis Of Radio Network Fault • Possible cause › UU message process failure due to UE capability (UE doesn’t support relevant service) › eNodeB failure during ERAB setup • Solutions: › Check UE capability › Check eNodeB status HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 33 Analysis Of No Radio Resource • Possible cause › Radio admission failure for ERAB • Solution: › Check if admission parameters is correct › Consider to enable load balance algorithm › Consider capacity extension HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 34 Analysis Of Security Mode Failure • Possible cause: › UE security capability is not identical with eNodeB security capability • Solution: › Modify the eNB security algorithm to match it. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 35 Analysis Of EPC Fault • Cause: › S1 message validity check failure, including » Error exist in S1 message » Duplicated ERAB ID » Conflict with other procedures • Solution: › Contact EPC engineer to locate the problem HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 36 Analysis Of Transport Fault • Possible causes: › Transport admission failure › S1 link failure during S1 message exchange › Incorrect IP path configuration › Wrong QoS configuration in EPC • Solutions: › Check transport admission algorithm, consider extend S1 bandwidth › Check S1 interface › Check IP path configuration › Check relevant QoS configuration, AMBR should be more than 0, and for initial ERAB setup, the QCI must be 6~9 HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 37 Content Poor Accessibility Reasons Checklist of Required Action for Access Problem Access Performance Evaluation Analysis of Tracing Case Study HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 38 Analysis Of Tracing • Driver test tracing analysis › We can get all UU interface messages, internal UE message as well as RSRP value • eNdoeB tracing analysis › We can get UU interface message and S1 interface message • Form the above tracing analysis, we can locate the problem with the following causes: › Random access failure › RRC setup failure › NAS procedure failure › ERAB setup failure HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 39 Random Access Failure • Generic scenario: There is no “RRC connect request ”message • Possible cause: › UE doesn’t support the band » Scenario: UE doesn't receive any system message » Solution: Check if UE band is identical with eNdoeB configuration › Poor coverage » Scenario :Due to poor DL or UL coverage, UE or eNodeB miss receiving the relevant random access message » Solution: Perform RF tuning. Use TMA on uplink › Cell is barred » Check the cell status, should be not barred. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 40 RRC Connection Failure eNodeB UE RRC_CONN_REQ RRC_CONN_REJECT • Scenario 1: eNodeB directly send reject message › Possible cause: No radio resource due to no enough resource for PUCCH and SRS › Solution: Check the cell load status, if it is very high, consider capacity extension HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 41 RRC Connection Failure (Cont.) eNodeB UE RRC_CONN_REQ RRC_CONN_SETUP RRC_CONN_REQ • Scenario 2: UE doesn’t receive “RRC connection setup” message, and repeat sending request message until timer is out • Possible cause: › Poor DL coverage, check RSRP and RSRQ • Solution: › Perform RF tuning HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 42 RRC Connection Failure (Cont.) eNodeB UE RRC_CONN_REQ RRC_CONN_SETUP Waiting “RRC Compelet”time out • Scenario 3: eNodeB send RRC setup message, but doesn’t get complete message • Possible cause › If UE doesn’t reply RRC complete, it should be UE problem › If UE already send RRC complete, then it should be poor UL coverage HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 43 NAS Procedure Failure MME eNodeB UE S1AP_INITIAL_UE_MSG S1AP_DL_INFO_TRANSF RRC_DL_INFO_TRANSF RRC_UL_INFO_TRANS S1AP_UL_INFO_TRANSF S1AP_UE_CONTEXT_REL_CMD S1AP_UE_CONTEXT_REL_CMP • Note: NAS failure is not counted in performance statistic HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 44 eRAB Setup Failure eNodeB MME UE Uu:RRC/NAS RRC_SECUR_MODE_CMD S1-MME:S1AP S1AP_INITIAL_CONTEXT_SETUP_REQ RRC_SECUR_MODE_CMP RRC_UE_CAP_ENQUIRY RRC_UE_CAP_INFO RRC_UE_CAP_INDICATION RRC_CONN_RECFG RRC_CONN_RECFG_CMP S1AP_INITIAL_CONTEXT_SETUP_RSP HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 45 eRAB Setup Failure Cause • If any failure occurs during ERAB setup, we can directly get the failure cause form performance statistic, the relevant counters are: › L.E-RAB.FailEst.NoReply (No response from UE) › L.E-RAB.FailEst.MME (EPC fault) › L.E-RAB.FailEst.TNL (Transport fault) › L.E-RAB.FailEst.RNL (Radio network fault) › L.E-RAB.FailEst.NoRadioRes (No radio resource) › L.E-RAB.FailEst.SecurModeFail (Security mode setup fault) HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 46 Faulty Signaling of No UE Response HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 47 Fault Signaling of Other Cause • Scenario: eNodeB receives “initial context setup request” or “E-RAB setup request” message, after that, if failures happen, then eNB replies response message with failure cause HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 48 Content Access Performance Evaluation Poor Accessibility Reasons Checklist of Required Action for Access Problem Typical Cases Analysis Case Study HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 49 Case 1 – IP Path Configuration Leads To Low Access Ratio • Description: In one live network, ERAB setup ratio is very low, but it’s not zero. • Alarm info: None • Analysis: › Check the performance statistic of ERAB release, we found that most of failures are caused by transport resource not available › From the message tracing, we can also confirm this result HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 50 Case 1 –IP Path Configuration Leads To Low Access Ratio (Cont.) • Now we can locate that the problem is due to IP path configuration. We check eNodeB configuration and find a valid IP path, the connection is valid. And it is also weird that this problem occurs with a probability • Then we analyze the message again, and find that in the “UE context setup request” message delivers variable GTPU address, and these address is not identical with eNodeB configuration. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 51 Case 1 –IP Path Configuration Leads To Low Access Ratio (Cont.) • Conclusion :As the SGW deliveries multiple GTUP address to eNodeB, but we only configure one IP path to SGW, so it causes the partly ERAB setup failure • Solutions: We confirm this with EPC engineer, SGW pool function is used, so there are multiple IP addresses for SGW. Then we make up the IP path for all address, the problem is cleared. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 52 Case 2 – Multi-mode UE Attach Failure S1 trace UU trace • Description: During the commissioning of one live network, we found that UE attach fails. • Alarm info: None • Message Tracing: From the message tracing, we can see that most of access procedures are normal, after ERAB setup, MME release the connection with the cause “normal release” HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 53 Case 2 – Multi-mode UE Attach Failure (Cont.) • Analysis • Since the most of procedures are normal, and eNodeB consider that it’s a normal release, so we locate that the problem is due to NAS failure. • So we continue to analyze the previous NAS message, and in the DL NAS message, we can see that MME response the attach with the cause “MSC-temporatily-not-reachable”, as show above. now we can confirm that this is root cause of attach failure HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 54 Case 2 – Multi-mode UE Attach Failure (Cont.) • Analysis (Cont.) › Why should UE need attach to MSC ? We check the UE model, it ‘s Huawei E398, with multi-modes(GSM/UMTS/LTE). So we assume that this UE performs combined attach. From the attach request message we verify our assumption. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 55 Case 2 – Multi-mode UE Attach Failure (Cont.) • Conclusion: › We check that there is no CS domain configuration in current EPS network, so MME only replies PS attach accept, and also inform that MSC can’t reachable • Temporary solution: › Change UE attach mode with PS only › Add CS domain configuration in EPC • Final solution: › Update MME to compatible with combined attach even there is no CS domain HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 56 Case 3: eRAB Setup Low due to RRC License Limited • In Thailand True LTE Network, several Clusters cannot pass KPI E-RAB Setup Success Rate; • Checked cell level KPI and found the failures, several sites have much high number of eRAB Setup failures, which cause the KPI not pass; • The major faiure is due to “No Resource”; • Checked the number of RRC user, which reached the licensed number; • After expanded license, the KPI became normal. HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 57 57 Page Thank You HUAWEI CO., LTD. HISILICONTECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCTOR Page 58