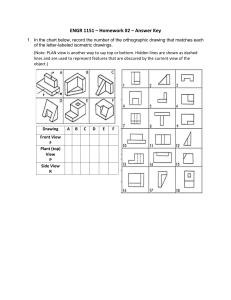
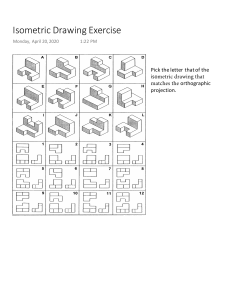
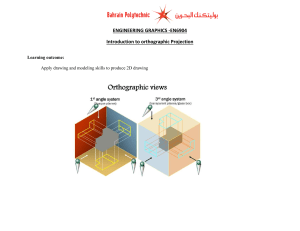
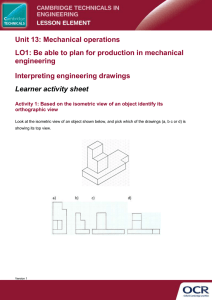
Communication skills PurPose of graPhics… As part of the design process you are required to illustrate your ideas. This is known as a universal language, meaning that people who don't always speak the same language as you, find it easier to understand what you mean through pictures. And since it is considered as a universal language there has to be certain conventions or rules which need to be followed for all 2D and 3D drawings. Convention Line Types Line type Example Construction lines are feint lines (light line), used to start a drawing and then are later erased. Construction lines; Outlines are dark thin / thick lines used to show the edges of the product. They are also known as object, visible or final lines. Outline; Dashed lines; Chained lines Function ---------------------- - - - Dashed lines are used to show the important details that we cannot see (the inside or back of the drawing) Chained Lines are known as Centre lines. They show symmetry (the middle of the object) on a sketch. DIMENSIONS Dimensioning is the convention we use to indicate measurement on our drawings. They are thin feint lines that show us how long, high or deep a drawing is. Unless stated otherwise, dimensions are given in mm SCALE DRAWINGS A scale is a tool used to create a relationship between measurements on a drawing and measurements on the real object. It is the size to which the sketch is drawn. For example; If a scale is 1:100 It means that everything in the sketch is 100 times smaller than in reality. and If the scale is 5:1 It means that everything in the sketch is 5 times larger in reality. Isometric drawing There is a difference between a 3D oblique drawing and a 3D isometric drawing ➢ 3D – Oblique: starts at a 45° angle (flat with depth) and shows the true length of B and C but not A and B. ➢ 3D – Isometric: starts at a 30° angle (slanted with depth) and shows the true length of B and C, A and B and C and D ISOMETRIC DRAWING This is a 3D representation or view of an object. It must always show THREE sides of the object at the same time and is always drawn at a 30̊ angle. Isometric drawings are very useful for designers – particularly architects, industrial and interior designers and engineers, as they are ideal for visualising rooms, products, and infrastructure. First angle orthographic projection Orthographic Projection is a way of drawing an 3D object from different directions. Usually a front, side and top view are drawn so that a person looking at the drawing can see all the important sides. Orthographic drawings are useful especially when a design has been developed to a stage whereby it is almost ready to manufacture.