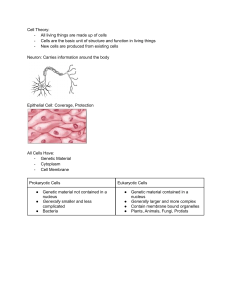
Title: Comprehensive Study Guide on Cells ## I. Introduction to Cells ### A. Definition - Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms. - They are classified into prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ### B. Cell Theory 1. The cell is the fundamental unit of life. 2. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. ## II. Prokaryotic Cells ### A. Characteristics 1. Lack a true nucleus. 2. Simple structure. 3. Examples: bacteria and archaea. ### B. Components 1. Cell membrane. 2. Cytoplasm. 3. Ribosomes. 4. DNA in a nucleoid region. ## III. Eukaryotic Cells ### A. Characteristics 1. Have a true nucleus. 2. Complex structure. 3. Examples: plants, animals, fungi, and protists. ### B. Cell Organelles 1. Nucleus: Control center of the cell. 2. Mitochondria: Powerhouse of the cell. 3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Site of protein and lipid synthesis. 4. Golgi Apparatus: Packages and transports cellular products. 5. Vacuole: Storage organelle. 6. Chloroplasts (in plant cells): Site of photosynthesis. 7. Lysosomes: Digestive organelles. ## IV. Cell Membrane ### A. Structure 1. Phospholipid bilayer. 2. Proteins and carbohydrates. 3. Selective permeability. ### B. Functions 1. Maintains cell shape. 2. Controls entry and exit of substances. ## V. Cell Cycle ### A. Phases 1. Interphase: G1, S, G2. 2. Mitosis: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase. 3. Cytokinesis: Division of the cytoplasm. ### B. Regulation 1. Checkpoints. 2. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). ## VI. Cellular Respiration ### A. Glycolysis 1. Occurs in the cytoplasm. 2. Breaks down glucose into pyruvate. ### B. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) 1. Takes place in the mitochondria. 2. Generates NADH and FADH2. ### C. Electron Transport Chain 1. Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. 2. Produces ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. ## VII. Photosynthesis ### A. Light Reactions 1. Occur in the thylakoid membrane. 2. Generate ATP and NADPH. ### B. Calvin Cycle 1. Takes place in the stroma. 2. Produces glucose from CO2. ## VIII. Cell Division in Prokaryotes ### A. Binary Fission 1. Simple cell division process. 2. Chromosome replication and cell division. ## IX. Stem Cells ### A. Types 1. Totipotent. 2. Pluripotent. 3. Multipotent. ### B. Applications 1. Regenerative medicine. 2. Cell-based therapies. ## X. Cell Communication ### A. Signaling Pathways 1. Reception. 2. Transduction. 3. Response. ### B. Cell Signaling Molecules 1. Hormones. 2. Neurotransmitters. ## XI. Cellular Transport ### A. Passive Transport 1. Diffusion. 2. Osmosis. 3. Facilitated diffusion. ### B. Active Transport 1. Sodium-potassium pump. 2. Endocytosis and exocytosis. ## XII. Disorders Related to Cells ### A. Cancer 1. Uncontrolled cell growth. 2. Causes and prevention. ### B. Genetic Disorders 1. Examples: Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis. ## XIII. Laboratory Techniques ### A. Microscopy 1. Light microscopy. 2. Electron microscopy. ### B. Cell Culture 1. Techniques for growing cells outside the body. ## XIV. Ethical Considerations ### A. Cloning 1. Reproductive cloning. 2. Therapeutic cloning. ### B. Genetic Engineering 1. CRISPR technology. 2. Ethical implications. ## XV. Conclusion - Recap of key concepts. - Importance of understanding cell biology. This comprehensive study guide covers various aspects of cell biology, providing a solid foundation for understanding the structure and function of cells, as well as their role in living organisms.