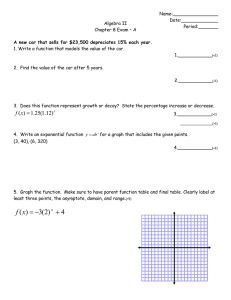
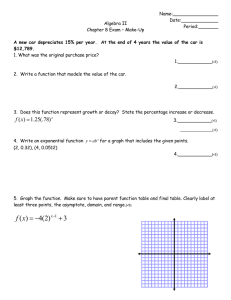
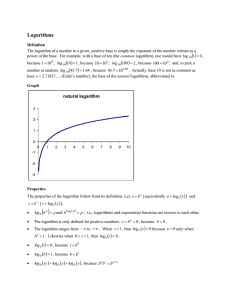
Power Rules and Logarithm Rules Definition Definition a times itself n times = Examples The power to which a number has to be raised n a a⋅a = a a⋅a⋅a = a 2 log a ( an ) = n 3 Examples log 10 (100) = 2 7 a⋅a⋅a⋅a⋅a⋅a⋅a = a log 3 (27) = 3 Reciprocal Rule 1 = a−x ax 3 1/5 = 5 −3 n −n log a ( 1/a ) = log a ( a log 5 ( ) = −n 1 ) = −3 125 Product Rule x a ⋅a y 2 ( x+ y) = a 3 5 2 ⋅2 = 2 x y log a ( a ⋅a ) = x + y 2 3 log 2 (2 ⋅2 ) = 5 4⋅8 = 32 Quotient Rule a x ay ( x− y) = a 54 (4−2) 2 = 5 = 5 2 5 log ( a x ay log 5 ( ) = x− y 54 ) = 2 2 5 625 = 25 25 Power and Logarithm Rules Page 1 of 5 Power Rule (a x ) y = a xy log a ( (a x ) y ) = xy (32 )3 = 36 log 3 ( (32 )3 ) = 6 Product Distribution Rule x log c (ab) = log c a + log c b x x log c ((ab) ) = x (log c a + log c b) (3⋅5)2 = 32⋅5 2 log c ((3⋅5)2) = 2(log c 3 + log c 5) (ab) = a ⋅b Quotient Distribution Rule a log c ( ) = log c a − log c b b a x ax ( ) = b bx 3 x 3 2 2 ( ) = 3 5 5 Power Distrubtion Rule a x log c ( ( ) ) = x (log c a − log c b) b 2 3 log ( ( ) ) = 3( log 2 − log 5) 5 b log c a = b log c a log 2 53 = 3 log 2 5 Identity Rule a 0 = 1 Power and Logarithm Rules log 1 = 0 a Page 2 of 5 Base Reciprocal Rule log (1 / a) b = − log a b log (1 /2 ) 8 = − log 2 8 = −3 Radical Rule (1/n) a 125 (1 /3) = n n √a log a ( √a) = 1 /n √3 125 = 5 log 3 ( √3) = 1/ 2 = Decay Rule (half-life) (t /h) A = A 0 (1/2) Where A is the current quantity A0 is the starting quantity t is the time that has passed h is the half life log A = log A 0 − (t / h) log( 2) log 2 A = log 2 A0 − t / h Growth Rule (doubling time) (t /d) A = A 0 (2) where A is the current quantity A0 is the starting quantity t is the time that has passed d is the doubling time Power and Logarithm Rules log A = log A 0 + ( t/d ) log 2 log 2 A = log 2 A0 + (t / d ) Page 3 of 5 Change of Base log x (b)⋅ log b (a) = log x (a) log b a = log 16 1024 = log 3 16 = log x a log x b log 2 1024 10 = = 2.5 log2 16 4 log 2 16 4 = = 2.523 ... log 2 3 1.585 ... Compound Interest A = P⋅(1+i)n PV = Where A n (1+i) A is the final amount P is the principal PV is the Present Value i is the interest rate n is the number of interest periods Power and Logarithm Rules Page 4 of 5 Annuity A = R = Where R⋅[(1+i)n − 1] i Ai [( 1+i )n − 1] A is the final amount R is the regular payment i is the interest rate n is the number of payments Power and Logarithm Rules Page 5 of 5