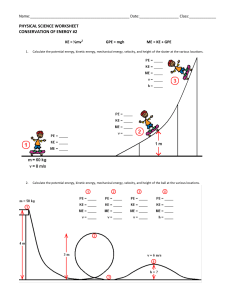
AL-Ma’rifa . Int . School Physics Am – G12 Unit 11/ ( ENERGY and its Conservation ) . Section1: the many forms of energy Objectives : To know how is a system’s motion related to its kinetic energy To write the rotational kinetic energy formula To obtain what is the gravitational potential energy To define the reference level . Kinetic energy : Translational kinetic energy : 𝑲𝑬𝒕𝒓𝒂𝒏𝒔 = Rotational kinetic energy : 𝑲𝑬𝒓𝒐𝒕 = Total kinetic energy : 𝑲𝑬𝑻𝒐𝒕 = 𝟏 𝟐 𝟏 𝟐 𝟐 𝑰𝝎 𝒎𝝑 + 𝟏 𝟐 𝟐 𝟏 𝟐 𝒎𝝑𝟐 𝑰𝝎𝟐 Q1: A 52kg skater moves at 2.5m/s and glides to a stop over a distance Of 24m. find the skater’s initial kinetic energy . how much of her kinetic Energy is transformed into other forms of energy by friction as she stop? How much work must she do to speed up to 2.5m/s again? Q2 : A 875kg car speeds up from 22m/s to 44m/s . what are the initial and final kinetic energies of the car? How much work is done on the car to increase the speed? 1 Q3: A comet with a mass of 7.85x1011kg strikes earth at a speed of 25km/s .find the kinetic energy of the comet in joules , and compare the work that is done by earth in stopping the comet to the 4.2x1015J of energy that was released by the largest nuclear weapon ever exploded . Q4: A 2kg wheel rolls down the road with linear speed of 15m/s. find its translational and rotational kinetic energies ( Hint: 𝑰 = 𝒎𝒓𝟐 ) . Potential energy: Is an energy stored due to interactions between objects in a system. In physics , potential energy divides into three parts : 1. Gravitational potential energy : 𝑷𝑬𝒈 = 𝒎𝒈𝒉 2. Elastic potential energy ( in springs ) : 𝑷𝑬𝒔 = 𝟏 𝟐 𝒌𝒙𝟐 3. Electric potential energy : 𝑷𝑬𝒆𝒍 = −𝒒∆𝑽 Gravitational potential energy ( GPE ) : Reference level : the position where GPE is defined to be zero. 𝑮𝑷𝑬 = 𝒎𝒈𝒉 Work done by gravity ( Wg ) : Upward : 𝑾𝒈 = −𝒎𝒈𝒉 Downward : 𝑾𝒈 = +𝒎𝒈𝒉 2 A diagram representation between KE and GPE under gravity : Q5: 3 Q6: if you slowly lower a 20kg bag of sand 1.2m from the truck of a car to the driveway . how much work do you do? Q7: A boy lifts a 2.2kg book from the desk , which is 0.8m high to a bookshelf that is 2.1m high. What is the potential energy of the book – earth system relative to the desk when the book on the shelf? Q8: If a 1.8kg brick falls to the ground from a chimney that is 6.7m high . what is the change in the potential energy of the brick-earth system? Elastic potential energy ( EPE ) : Is an energy stored due to pulled or compressed strings . Mass : Albert Einstein recognized yet another form of potential Energy that is proportional to the object’s mass . He demonstrated that mass represents a form of energy . The energy is called the rest energy ( Eο ) and can be calculated using the following formula : 𝑬° = 𝒎𝑪𝟐 4 Q9: A 25kg shell is shot from a cannon at earth’s surface . the reference level is earth’s surface. 1. What is the shell- earth system’s gravitational potential energy when the shell’s height is 425m? 2. What is the change in the system’s potential energy when the shell fails to a height of 225m? Q10: A 90kg rock climber climbs 45m upward , then descends a 85m . the initial height is the reference level . find the potential energy of the climber – earth system at the top and at the bottom . draw bar graphs for both situations. Other forms of energy : Chemical energy : released from the burning of fossil fuels and during digestion. Nuclear energy : released with the structure of an atom’s nucleus changes. Thermal energy : the sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy of the particles in a system. Radiant energy : carried by electromagnetic waves. Electrical energy : associated with charged particles. 5 Section2: Conservation of energy. The law conservation of energy states that : ( in a closed , isolated system energy can neither be created nor Destroyed , rather energy is conserved ). That’s mean energy can change its forms , but remains a constant in All total energy system’s forms. Mechanical energy : Its an energy comes from the motion and the interactions between Objects. Mechanical energy equal to the sum of all shapes of kinetic and Potential energies. But here we will study only the translational KE and GPE . 𝑴𝑬 = 𝑲𝑬 + 𝑮𝑷𝑬 Assume that a 10 N system of a bowling ball falls to the earth , in this case you can find the ( ME =20J ) as shown in the figure below . Important point : If the friction does not work on the ball the final Kinetic energy is equal to the initial GPE regardless of which the path it follows. ( show the figure ) . 6 Conservation of mechanical energy : The sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy before event is equal to the sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy after event. 𝑴𝑬𝒊 = 𝑴𝑬𝒇 𝑲𝑬𝒊 + 𝑮𝑷𝑬𝒊 = 𝑲𝑬𝒇 + 𝑮𝑷𝑬𝒇 Conservation and other forms of energy : 1. Roller-coaster : if a hill farther along the Track were higher than the first one , the Car – coaster would not be able to climb the Higher hill because the energy required to do So would be greater than the total mechanical Energy of the system. 2. Skiing : when you ski down a steep slope you begin from rest at the top of the slope and ( ME=GPE ) . Once you start skiing downhill this GPE transformed to( KE ) . as you ski down the slope Your speed increases as more GPE is transformed to ( KE ). 3. Pendulums : we can choose the lowest point of the bob Bob is the reference level , where GPE = 0 . At the instant the bob is released from point A Where ME=GPE transformed to KE at point C Where GPE = 0 . 7 Q11: Q12: A bike rider approaches a hill at a speed of 8.5m/s. the combined mass of the bike and the rider is 85 kg . choose a suitable system . 1. Find the initial kinetic energy of the system. 2. If the rider coasts up the hill , assuming the friction is negligible . at what height will the bike come to rest? 8 Q13: A skier starts from rest at the top of 45m – high hill . skis down a 30ο incline into a valley , and continues up a 40m – high hill . the heights of both hills are measured from the valley floor. Assume that friction is negligible and ignore the affect of the ski poles . 1. How fast is the skier moving at the bottom of the valley? 2. What is the skier’s speed at the top of the second hill? 3. Do the angles of the hills affect your answers? Q14: the spring in a pinball machine exerts an average force of 2N on a 0.08kg pinball over 5cm. as a result the ball has both translational and rotational kinetic energy . if the ball is a uniform sphere ( 𝑰 = table’s tilts ). 9 𝟓 𝟐 𝒎𝒓𝟐 ) . what is the linear speed after leaving the spring? ( ignore the Analyze Collisions : Perfectly elastic collision Normal elastic collision Momentum is Conserved Momentum is Conserved Perfectly inelastic collision Momentum is Conserved m11i m22i m11 f m22 f m11i m22i m11 f m22 f Objects still separate after Collision . Kinetic energy is Conserved KE i KE f Objects still separate after Objects join together after Collision . Collision . Kinetic energy is not Conserved Kinetic energy is not Conserved KE i KE f KE i KE f 10 m11i m22i (m1 m2 ) f Q15: Q16: An 8g bullet is fired horizontally into a 9kg block of wood on an air table and is embedded in it. After the collision , the block and bullet slide along the frictionless surface together with a speed of 10cm/s. what was the initial speed of the bullet? 11 Q17: A 91kg hockey player is skating on ice at 5.5m/s . another hockey player of equal mass moving at 8.1m/s in the same direction hits him from behind , they slide off together . 1. What are the total mechanical energy and momentum of the system before the collision? 2. What is the velocity of the two hockey players after the collision? 3. How much was the system’s kinetic energy decreased in the collision? Q18: As shown in the beside figure a child slides down a playground slide. At the bottom of the slide she is moving at 3m/s . how much energy was transformed by friction as she slid down the slide? 12 Q19: the driver of the car in figure suddenly applies the brakes , and the car slides to a stop. The average force between the tires and the road is 7100N . how far will the car slide after the brakes are applied? Q20: A rock sits on the edge of a cliff as shown in figure . 1. What potential energy does the rock – earth system Possess relative to the base of the cliff? 2. The rock falls without rolling from the cliff . What is its kinetic energy just before it strikes the ground? 3. What is the rock’s speed as it hits the ground? GOOD LUCK 13