Macroeconomics Lecture Notes: Measuring GDP & National Income
advertisement

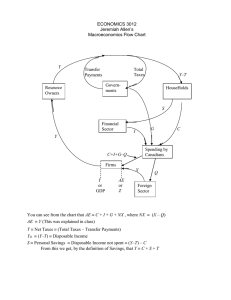
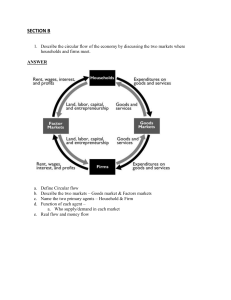
Lecture Notes: C6 Economics of Public Policy-II Week: 2: Measurement of macroeconomic variables 1. National income accounting why? Formal structure of the economy for building macro models; Helps in assessing the magnitude of different economic transactions and the economy at large. 2. Gross Domestic Product: It is the gross money value of all final goods and services produced in an economy (economic territory by residents and non-residents) in a given period (usually a year we also have quarterly GDP estimates, important: it is produce of residents in a country and current not past produce). Gross National Product is the gross money value of all final goods and services produced by the residents of an economy in a given time period. GDP Factor Cost + Net indirect taxes = GDP Market Prices Net Indirect Taxes = Indirect taxes paid – subsidies received GNP = GDP + net factor income from abroad GDP real and nominal and GDP deflator GDP – Depreciation = Net Domestic Product (NDP); Depreciation is the value of capital used up in the production in that year. Net National Product NNP = NDP + net factor incomes from abroad (Net factor income from abroad= factor income received from abroad- factor income paid abroad) Net Domestic Product FC = Domestic Income Net National Product FC = National Income (NY) 3. Disposable Income: Is the money in the hands of people, what they earn and what they get as transfers, money that they can spend as they like. 1 Domestic product accruing to the private sector = NDPFC – property and entrepreneurial income of govt. enterprises - savings of non-departmental enterprises of the government. Private Income: It is the total income that accrues to the private sector i.e. private enterprises and households. Private Income = Domestic product accruing to the private sector + net factor income from abroad + interest on national debt + net current transfers from the government + net current transfers from the rest of the world. Personal Income: Is the total income (factor and transfers) that accrues to the households. Personal Income = Private Income - corporate taxes- retained earnings or savings of the private corporate sector. Personal Disposable income = personal Income- direct taxes paid by the households – miscellaneous receipts of the government from households (contribution to provident fund) Personal Disposable Income = Consumption + Savings Net National Disposable Income = NY / NNPFC + net indirect taxes + net current transfers from the rest of the world. 4. Goods: Final and Intermediate: Final goods are purchased by consumers and firms for their own use Final goods do not undergo any further change in the production process. Intermediate goods are those that are used in furthering the production of final goods and services. They are non-durable goods and services used in the production of other goods. Distinction between final goods and intermediate goods is purely on the basis of how the good is used. Consumption and capital goods (fixed capital, change in stock and buildings) Durable and non-durable; Services: single-use and multiple use 5. Examples on National Income Accounting 2 (i) If for a country GNPFC = Rs. 1000 million. Indirect taxes = Rs. 200 million. Net factor incomes from abroad = Rs 50 million Subsidies = Rs 100 million Consumption of fixed capital (depreciation) = Rs 100 million; Calculate GNPMP, NNPFC, and NDPMP (ii) On the basis of following data, calculate Personal Income and Personal Disposable Income: (figures in Rs million) NNPFC = 54,500 Corporate tax = 1520 Undistributed profits of companies = 3500 Income from domestic product accruing to government sector =1680 National debt interest = 700 Current transfers from government = 1,200 Current transfers from the rest of the world = 300 Personal income tax = 250 Net factor incomes from abroad = 50 6. Income = Private Consumption + Government Consumption + Investment + Net Exports Y = C + G + I + (X-M) or NX G = Transfer Payments + Purchase of goods and services I= Public and Private = Addition to physical stock of capital = Machines and buildings (Capital can also be broadly defined to include both physical and human or social capital) = Inventory + change in stock of capital ( here only the inventory of firms is included as investment. Inventory maintained by households is treated as consumption. Share of Y between C, G and I and X-M is important to see the trends in the economy. USA: C is 70 per cent, I is about 17 per cent, G is 19 per cent and NX is negative. India: C is about 50 to 55 per cent, G is about 10 to 12 per cent, I is about 30 per cent has gone up to 40 per cent. 3 7. Three methods for estimating national income: Production or value added; Income Method Expenditure method Circular flow of income: Production (generation of income within production units) Expenditure (disposal of income by households) Income (distribution of income to factors of production) 8. Product Method or value added method: National income is the net value added at factor cost by each production unit in an economy. Value of output = Sales (Q* MP) + Change in stocks Value of output- value of Inputs = Value added by a firm It is the Gross value added at market prices. GVAMP- Net Indirect Taxes = GVAFC - Depreciation = NVAFC NVAFC =NDP FC GVAMP =GDP MP Precautions/issues: Double counting; imputed value of own account production or imputed rent of owner-occupied houses to be included; sale of second hand goods not to be included, production of illegal activities not included, services rendered by housewife is not included. 9. Income method: Factor incomes paid to the different factors of production by various production units. NVAFC = Wages (compensation to Employee) +Interest income + Rent/Royalty + Profits Operating surplus= Interest income + Rent+Royalty + Profits 4 Wages = Cash + kind + Employer’s contribution to social security Mixed Income of self employed (MISE)viz. doctor practicing from home will earn salary, rent and profits. Precaution/issues: Transfer earnings should not be included (pensions, scholarships etc.), income from sale of second hand assets not to included as only a transfer of ownership takes place- the capital gains is not treated as income but commission or brokerage is included as income in that year.; income from sale of bonds/shares is also not included as only a transfer of ownership takes place; windfall gains not included as income because no productive service is involved; Imputed value of own services or production to be included (rental). 10. Expenditure method: Total expenditure on final goods and services: C+I +G+ X-M I= Gross Fixed Investment + Change in stocks Precautions/issues: expenditure only on final goods and services, exp on second hand goods excluded, imputed values of owner account consumption or production to be included and expenditure on financial assets not to be included. Reconciliation of Methods: Product Method GVAMP for all sectors -NIT -Deprecation NDPFC + NFIFA National Income Income Method Compensation to Employees +Operating surplus +MISE NDPFC + NFIFA National Income Expenditure Method Pvt. C+G+I+Net Exports GDP MP -NIT Depreciation NDPFC + NFIFA National Income 11. GDP is not a good measure of economic activity or of economic wellbeing and is a poor measure of human wellbeing (welfare) in general. 12. Problems of GDP Measurement Some outputs are poorly measured as they are not traded Some activities add to GDP but are ‘bads’, including pollution and environmental degradation. Reflecting the improvement in the quality of goods 5