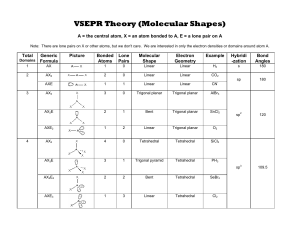
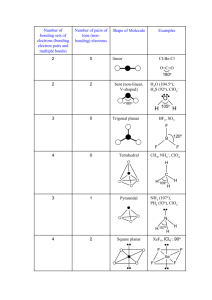
VSEPR Theory (Molecular Shapes) A= the central atom, X = an atom bonded to A, E =a lone pair on A Note: There are lone pairs on X or other atoms, but we don't care. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom A. Total Domains Formula 1 AX 2 AX2 3 Example Shape Electron Geometry Linear Linear H2 2 Linear Linear CO, AXE 1 Linear Linear CN AX 3 Trigonal planar Trigonal planar AIBrs AX,E 2 Bent Trigonal planar SnClh Generic KY-o Picture AX XAX Bonded Lone Atoms Pairs 1 0 Molecular AXE, 1 2 Linear Trigonal planar AX4 4 0 Tetrahedral Tetrahedral SiCL AX,E 3 1 Trigonal pyramid Tetrahedral PH, AX,Ez 2 2 Bent Tetrahedral SeBr2 AXE 1 3 Linear Tetrahedral Cl, Hybridi Bond -zation Angles 180 Sp 180 sp 120 sp 109.5 Total Generic Picture Domains Formnula 5 Bonded Lone Atoms Pairs AX 5 0 AX.E 4 1 AXJE2 Molecular Electron Shape Geometry Trigonal bipyramid Trigonal bipyramid See Saw Trigonal bipyramid Example Hybridi -zation Bond Angles sp°d 90 and AsFs SeH 2 T shape Trigonal bipyramid ICl3 120 X 6 AX,Es 2 3 Linear Trigonal bipyramid BrF2 AX 6 0 Octahedral Octahedral SeCle AX,E 5 1 Square pyramid Octahedral IFs 2 Square planar Octahedral XeF AX4E Notes sp°a? 90 1. There are no stable AXE4, AX,Ej, AX,E, or AXE, molecules. 2. All bonds are represented in this table as a line whether the bond is single, double, or triple. 3. Any atom bonded to thc center atom counts as one domain, even if it is bonded by a double or triple bond. Count atoms and lonc pairs to determinc the number of domains, do not count bonds. 4. The number of bonded atoms plus lone pairs always adds up to the total number of domains.