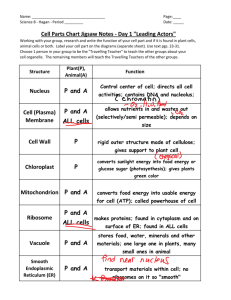
DIRECTIONAL TERMS IN ANAPHY: 1.) Sagittal / Median Plane – Divides left and right 2.) Parasagittal Plane – Parallel to Sagittal 3.) Coronal / Frontal Plane – Divides front and back 4.) Axial – Aligned with center (head, neck, body) 5.) Appendicular – Ends of appendages (arms, legs) 6.) Anterior / Ventral – Front of body 7.) Posterior / Dorsal – Back of body 8.) Superior / Cranial – Towards the top 9.) Inferior / Caudial – Towards the bottom 10.) Medial – Towards the midline 11.) Lateral – Away from midline 12.) Contralateral – opposite sides of midline 13.) Deep – Away from the body’s surface / body part 14.) Intermediate – between two structures 15.) Proximal – Closer 16.) Distal – Away 17.) Superficial – Close to the surface of the body 18.) Supine – Lying on the back with the face upward CELL AND TISSUE FUNCTION: ● ● DEFINITION OF TERMS: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Anatomy – The study of the STRUCTURE and relationships between body parts Physiology – The science of how those parts come together to FUNCTION and keep that body alive. Pathology – Structural and functional changes in cells, tissues, and organs of the body that cause or are caused by disease. Pathophysiology – Physiology of altered health Anatomical Position – Body is erect and facing forward with the arms at the side and palms forward. Homeostasis – Maintain stable, internal conditions no matter what changes are occurring outside the body. Synthesis – Combination or composition of parts or elements so as to form as a whole. HIERARCHY OF ORGANIZATION: 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) 6.) 7.) 8.) Atoms Molecules Organelles Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems The Human Organism ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Cell – Smallest functional unit that an organism can be divided into and retain the characteristics necessary for life. Tissues – Cells with similar embryonic origin or function are often organised into larger functional units. Tissues combine to form the various body structures and organs. Eukaryotic Cells – Have at least one nucleus; Cells with a true nucleus. MAJOR COMPONENTS OF A EUKARYOTIC CELL: ⮚ NUCLEUS ⮚ CYTOPLASM ⮚ CELL MEMBRANE Prokaryotic Cells – Lack nucleus and nuclear membrane. Protoplasm – Composed of water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and electrolytes. ⮚ Water makes up 70% to 85% of the cell’s protoplasm. Cell Protein – The second most abundant constituents of protoplasm (10% to 20%). Proteins – Can also be found complexed to the other compounds such as nucleoproteins, glycoproteins, lipoproteins. Lipids – Comprises 2% to 3% of most cells; Combine with proteins to form the cell membrane and the membranous barriers that separate different cell compartments. MOST IMPORTANT LIPIDS: ⮚ PHOSPHOLIPIDS ⮚ CHOLESTEROL Triglycerides – Constitute up to 95% of the total cell mass; Fat stored in these cells represents stored energy. ⮚ Few Carbohydrates are found in the cell, and these are primarily used for fuel. MAJOR INTERCELLULAR ELECTROLYTES: ⮚ POTASSIUM ION ⮚ MAGNESIUM ION ⮚ PHOSPHATE ION ⮚ SULFATE ION ⮚ BICARBONATE ION THREE TYPES OF RNA: ✔ Messenger RNA (mRNA) – Copies and carries the DNA instructions for protein synthesis to the cytoplasm. ✔ Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – Moves to the cytoplasm and becomes the site for protein synthesis. ✔ Transfer RNA (tRNA) – Also moves into the cytoplasm, where it transports amino acids to the elongating protein as it is being synthesized. These electrolytes facilitate generation and transmission of electrochemical impulses in nerve and muscle cells. Intracellular electrolytes participate in reactions that are necessary for cellular metabolism. ● ● ⮚ Small quantities of sodium, chloride, and calcium ions are also present in the cell. Cellular Metabolism – The set of chemical reactions that occur in living organisms in order to maintain life. ⮚ Cellular metabolism involves complex sequences of controlled biochemical reactions, better known as metabolic pathways. Nucleus – Membrane-enclosed organelle within a cell that contains the chromosomes. ⮚ Appears as rounded or elongated structure ⮚ Situated near the center of the cell ⮚ Enclosed in a nuclear membrane ⮚ Contains CROMATIN and a distinct region called NUCLEOLUS Cromatin – The nuclear matrix where complex structure of DNA and DNA-associated proteins are dispersed. ⮚ Each DNA molecule is made up of two extremely long, double-stranded helical chain containing variable sequences of four (4) nitrogenous bases which forms the genetic code. ⮚ DNA must be replicated before Mitosis ● ● ● ● Nucleolus – Darkly-stained round body / Euchromatic ⮚ Control center of the cell ⮚ Contains DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) WHY IS DNA ESSENTIAL TO THE CELL? Because its genes contain the information necessary for the synthesis of proteins that the cells must produce to stay alive. These proteins include structural proteins and enzymes used to synthesize other substances including Carbohydrates and Lipids. ● ⮚ Site of RNA synthesis PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: Transcription and Translation Mitosis – Cell division ⮚ During replication, complementary pairs of DNA are generated such that each daughter cell receives am identical set of genes. Nucleoli – Structures composed of regions from five (5) different chromosomes, each with a part of a genetic code needed for the synthesis of rRNA, which is transcribed exclusively in the nucleolus. Nuclear Envelope / Nuclear Membrane – A double – layered membrane that surrounds the nucleus. Cytoplasm – The gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. ⮚ Surrounds the nucleus ⮚ Work of the cell takes place ⮚ Contains water, electrolytes, suspended proteins, neutral fats, and glycogen molecules. ⮚ Pigments accumulate in the cytoplasm (such as melanin, which gives the skin color are normal constituents of the cell.) Organelles – Organs of a cell; Include Ribosomes, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Complex, Lysosomes and Peroxisomes, and Mitochondria. THE CYTOPLASM AND ITS ORGANELLES: ● Ribosomes – Sites of protein synthesis in the cell; Small particles of nucleoproteins (rRNA and ● ● ● ● proteins) that can be found attached to the wall of the endoplasmic reticulum or as free ribosomes. Polyribosomes – Formed because of free Note: Ribosomes & ribosomes are scattered singly in the cytoplasm mRNA synthesize or joined by strands of mRNA. proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – An extensive system of paired membranes and flat vesicles that connects various parts of the inner cell. ⮚ The fluid-filled space between the paired ER membrane layers is connected with the space between the two membranes of the double-layered nuclear membrane, the cell membrane, and various cytoplasmic organelles. ⮚ Functions as a tubular communication system through which substances can be transported from one part of the cell to another. ⮚ A large surface area and multiple enzyme systems attached to the ER membranes also provide the machinery for a major share of the metabolic functions of the cell. ⮚ 2 types of ER: Rough ER and Smooth ER Rough ER – Studded with ribosomes attached to specific binding sites on the membrane. ⮚ Proteins produced by the rough ER are usually destined for incorporation into cell membranes and lysosomal enzymes or for exportation from the cell. The rough ER segregates these proteins from other components of the cytoplasm and modifies their structure for a specific function. ⮚ All cells require a rough ER for the synthesis of lysosomal enzymes. Smooth ER – Involved in glycogen storage and metabolism of lipid soluble drugs. ⮚ Free of ribosomes and is continuous with the rough ER. ⮚ Does not participate in the protein synthesis. ⮚ Involved in the synthesis of lipid molecules including: Lipoproteins, Steroid Hormones, Regulation of Intracellular Calcium, Metabolism and Detoxification of Certain Hormone and Drugs. ⮚ The sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal and cardiac muscular cells is a form of smooth ER. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum - a complex network of specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum that is important in transmitting the electrical impulse as well as in the storage of calcium ions. ● ● ⮚ Calcium ions needed for needed for muscle contraction are stored and released from cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Golgi Complex – Golgi Apparatus ⮚ Consists of stacks of thin, flattened vesicles or sacs ⮚ Found near the nucleus ⮚ Functions in association with the ER ⮚ Substances produced in the ER are carried to the Golgi Complex in small, membrane-covered transfer vesicles. ⮚ Modifies certain substances and packages them into secretory granules or vesicles. ⮚ Produces large carbohydrate molecules that combine with proteins produced by the rough ER to form Glycoproteins. Lysosomes – Play an important role in the normal metabolism of certain substances in the body. ⮚ Can be viewed as the digestive system of the cell. ⮚ Consists of small, membrane-enclosed sacs containing hydrolytic enzymes capable of breaking down worn-out cell parts so they can be recycled. ⮚ Breaks down foreign substances such as bacteria taken into the cell. ⮚ All lysosomal enzymes are acid hydrolases which requires an acid environment (5 pH in their interior) NOTES: ⮚ The pH of cytoplasm is approximately 7.2, which protects other cellular structure in this activity. ⮚ Lysosomal enzymes are synthesized in the rough ER and then transported into the Golgi Apparatus, where they are biochemically modified and packaged as lysosomes. ⮚ The type of enzyme packaged in the lysosome by the Golgi Complex Determines this diversity. ⮚ Some materials remain undigested even though lysosomal enzymes can break down most proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids to their basic constituents; These undigested materials may remain in the cytoplasm as residual bodies or be extruded from the cell. ⮚ Found close to the site of energy consumption in the cell ⮚ The number of mitochondria in a given cell type is largely determined by the type of activity the cell performs and how much energy is needed to undertake this activity. ⮚ Contain their own DNA and ribosomes and are self-replicating. LONG LIVED CELLS: ⮚ NEURONS ⮚ HEART-MUSCLE CELLS ⮚ Composed of two (2) membranes: ✔ An outer membrane that encloses the periphery of the mitochondrion. Large quantities of residual bodies accumulate as lipofuscin granules or age pigment. INDIGESTIBLE PIGMENTS: ⮚ INHALED CARBON PARTICLES ⮚ TATTOO PIGMENTS May accumulate and persist in residual bodies for decades. ● ● Peroxisomes – Smaller than lysosomes, these are spherical membrane – bound organelles. ⮚ Contains a special enzyme that degrades peroxides ⮚ Function in the control of free radicals ⮚ These highly unstable chemical compounds would damage other cytoplasmic molecules, unless degraded. ⮚ Contains enzymes needed for breaking down very-long-chain fatty acids, which are ineffectively degraded by mitochondrial enzymes. Mitochondria – Powerhouse of the cell ⮚ Transfers organic compounds into energy that is easily accessible to the cell. ⮚ Contains enzymes needed for capturing most of the energy in foodstuffs and converting it into cellular energy. This multi-step process requires oxygen and is referred to as Aerobic Metabolism. ⮚ Most of this energy is stored in the high-energy phosphate bonds of compounds such as Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) that power the various cellular activities. ✔ An inner membrane that forms shelflike projections called Cristae. MITOCHONDRIAL DNA: ● ⮚ Distinct from the chromosomal DNA found in the nucleus. ⮚ Known as the “other human genome” ⮚ Double stranded, circular molecule that encodes the rRNA and tRNA required for intramitochondrial synthesis function of the mitochondria. ⮚ Directs the synthesis of 13 of the DNA proteins required for mitochondrial function. ⮚ DNA of the nucleus encodes the structural proteins of the mitochondria and other proteins needed to carry out Cellular Respiration. ⮚ Inherited matrilineally and provides a basis for familial lineage studies. Cytoskeleton – Controls cell shape and movements. ⮚ Network of microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments, thick filaments.