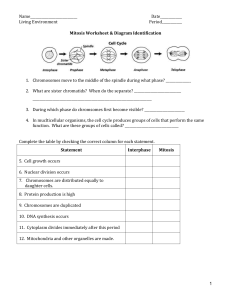
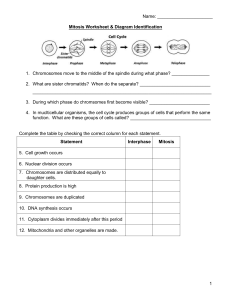
Mitosis Mitosis is the process through which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. A simplified breakdown: Simple definition: Mitosis is cell division that creates two identical cells, each having the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. Simple Explanation: Imagine a cell splitting into two, each retaining the same genetic information. It is like making a copy of a book; the original book stays intact, and you get an exact duplicate. Five Phases of Mitosis: In the context of cell division, the IPMAT acronym represents the phases of mitosis. Each letter corresponds to a specific phase: 1. Interphase: - Cell grows and prepares for division. - DNA duplicates. 2. Prophase: - Chromosomes condense and become visible. - Nuclear membrane breaks down. - Spindle fibres form. 3. Metaphase: - Chromosomes line up along the center of the cell. - Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes. 4. Anaphase: - Chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. - Spindle fibers help in separation. 5. Telophase: - Chromatids decondense. - Nuclear membranes form around chromosomes. Notable Mention: Cytokinesis (not part of IPMAT): - Cell divides into two daughter cells. - Each daughter cell contains a complete set of chromosomes. Examples of Mitosis: 1. Growth: Mitosis helps in the growth of organisms by creating new cells. 2. Repair: it is crucial for repairing damaged cells or tissues. 3. Asexual Reproduction: Some single-celled organisms can reproduce through mitosis. Mitosis is like the ‘copy and divide’ process ensuring cells have the right genetic material to function correctly.