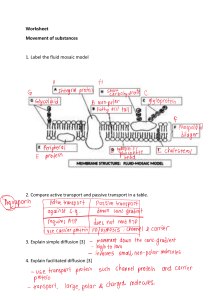
Practice Exam 2 & Equation Sheet Practice Exam 2 Discussion Introduction Use this discussion board to discuss ONLY about the Practice Exam 2 problems with your classmates. Please help your classmates if their answers or explanations do not seem right as well. Anyone should feel free to provide answers or suggestions to various questions. If you have questions related to the structure or technical issue of the exam, please post in the Q&A Discussion. If you have questions of a personal nature, please email your instructor privately. Practice Exam 2 (Chapter 4, 5, 6, 7 and 9) Not providing solution. Allow for discussion in practice exam 2 discussion board. Practice Exam 2 1. During plastic deformation, the number of dislocations ____________. a. Increases b. Decreases c. Stays the same 2. According to Fick’s 1st law, if the concentration gradient is zero, the diffusion flux will be: a. The second derivative of the concentration with respect to position b. Infinite c. Zero d. Equal to the diffusion coefficient 3. Which choices are zero-dimensional or point defects? (select all that apply) a. External surface b. Void c. Twin boundary d. Crack e. Interstitial f. Vacancy g. Screw dislocation 4. The questions below refer to the Fe-Fe3C phase diagram below For an alloy with a composition of 1.5 wt% C and just above the eutectoid temperature, answer the following questions: a. what is (are) the approximate chemical composition(s) of each phase, and b. what is (are) the mass fraction(s) of the phase(s) present? 5. A sheet of steel 1.5 mm thick has nitrogen (N) atmospheres on both sides at 1200°C and is permitted to achieve a steady-state diffusion condition. The diffusion flux is found to be 1.2 × 10-7 kg/m2-s. Also, it is known that the concentration of nitrogen in the steel is 4.0 kg/m3 at the high-pressure surface and 2.0 kg/m3 at 1 mm into the sheet away from the high pressure surface. What is the diffusion coefficient of N through steel under these conditions? Assume a linear concentration profile. 6. What are the primary differences between elastic, anelastic, and plastic deformation behaviors? 7. An α-iron-carbon alloy initially containing 0.10 wt.% C is carburized at an elevated temperature of 1027°C and in an atmosphere wherein the surface carbon concentration is maintained at 1.0 wt.%. How long does it take for the concentration of carbon to reach 0.35 wt.% at a position 3.0 mm below the surface? 8. Short answer: What is the composition in weight percent (wt%) of Sn in an alloy that contains 98.0 g tin and 65.0 g lead? How does this compare to the composition in (at%)? 9. Essay: What are the four Hume-Rothery Rules? 10. Explain these lines: a. Solvus line b. Liquidus line c. Tie line d. Phase boundary line e. Solidus line f. Eutectic temperature line a. Eutectoid temperature line 11. Rank the magnitudes of the diffusion coefficients from greatest to least for the following systems: A. N in Fe at 700°C B. Cr in Fe at 700°C C. N in Fe at 900°C D. Cr in Fe at 900°C Now justify this ranking. (Note: Both Fe and Cr have the BCC crystal structure, and the atomic radii for Fe, Cr, and N are 0.124, 0.125, and 0.065 nm, respectively. You may also want to refer to Section 4.3.) 12. What reaction, upon cooling, isothermally and reversibly transforms one solid phase into two new solid phases that are intimately mixed? 13. Given that the activation energy for vacancy formation in Copper is 0.90 eV/atom, calculate the temperature (in Kelvin) at which 1 of every 10,000 Copper lattice sites is vacant. Show your work for full credit. 14. Below is shown a plot of the logarithm (to the base 10) of the diffusion coefficient versus reciprocal of the absolute temperature, for the diffusion of iron in chromium. Determine values for the diffusion coefficient at 0.60 and 0.65 reciprocal temperature (1000/K). 15. Using the Fe-Fe3C phase diagram, draw the microstructure of the following alloys that were cooled slowly from liquid to their final state. Include grain boundaries in your image (if applicable) and label the phases present. a. 3 wt% C, 1200 oC b. 0.5 wt% C, 730 oC c. 2 wt% C, 600 oC 16. Answer the following questions based on the given diagram: a. What is the elastic modulus of this alloy? b. What is the maximum load a cylindrical sample with a 10mm diameter will see? c. If a sample was initially 100 mm long what is the final length of this material just before fracture has occurred? d. Explain in words, how the answer in previous question would change if the sample had already fractured before its final length was measured? 17. Which microstructure below indicates a material within a two-phase region but did not undergo a eutectic reaction? Formula sheet – Exam 2 Physical Constants and Conversions: kB = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K = 8.62 x 10-5 eV/K NA = 6.022 x 1023 atoms/mol R = 8.31 J/mol∙K = 1.987 cal/mol∙K T(K) = T(°C) + 273 K 1 nm = 10-9 m 1 mm = 10-3 m 4 Volume of a sphere = πR 3 3 Chapter 4 𝑁𝑁𝑣𝑣 = 𝑁𝑁 exp �− 𝐶𝐶1 (𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤%) = 𝑄𝑄𝑣𝑣 � 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑚𝑚1 × 100 𝑚𝑚1 + 𝑚𝑚2 𝐶𝐶"1 (𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑚𝑚3 ) = � 𝐶𝐶1 𝐶𝐶′1 (𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎%) = 𝐶𝐶1 𝐶𝐶2 + 𝜌𝜌1 𝜌𝜌2 � × 103 𝑛𝑛𝑚𝑚1 × 100 𝑛𝑛𝑚𝑚1 + 𝑛𝑛𝑚𝑚2 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 𝜕𝜕𝜕𝜕 𝜕𝜕 2 𝐶𝐶 = 𝐷𝐷 2 𝜕𝜕𝜕𝜕 𝜕𝜕𝑥𝑥 𝐶𝐶𝑥𝑥 − 𝐶𝐶0 𝑥𝑥 = 1 − 𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒 � � 𝐶𝐶𝑠𝑠 − 𝐶𝐶0 2√𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷 𝐷𝐷 = 𝐷𝐷0 𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒 �− 𝑄𝑄𝑑𝑑 � 𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 ν Chapter 9 %𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸 = � 𝑙𝑙𝑓𝑓 − 𝑙𝑙0 � × 100 𝑙𝑙0 WL = cα − c0 cα − cL 𝐴𝐴0 − 𝐴𝐴𝑓𝑓 %𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 = � � × 100 𝐴𝐴0 Wα = c0 − cL cα − cL You will be given these on the exam if needed. You do not need to include them on your cheat sheet. z 0.00 0.025 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 erf(z) 0 0.0282 0.0564 0.1125 0.1680 0.2227 0.2763 0.3286 0.3794 0.4284 0.4755 0.5205 z 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.0 1.1 1.2 erf(z) 0.5633 0.6039 0.6420 0.6778 0.7112 0.7421 0.7707 0.7970 0.8209 0.8427 0.8802 0.9103 z 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 erf(z) 0.9340 0.9523 0.9661 0.9763 0.9838 0.9891 0.9928 0.9953 0.9981 0.9993 0.9998 0.9999