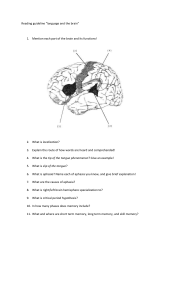
LANGUAGE AND THOUGHT 9.1 What is language? -grouping of spoken written or gestured symbols used to convey information -important for social communication -share information and improve upon others’ ideas -productivity allows humans to produce new messages and connect unrelated information -connects emotional cognitive and perceptual areas -early development is devoted to language because we are very social creatures that thrive through interrelatedness + our thought process depends on language -combine information to communicate new information 9.2 The development of language -sensory and auditory system develops prenatally -2 to 7yr old girls outperform boys in comprehension and sentence complexity -differences between cultures influence thought patterns and perception -system becomes fine-tuned to the sounds its exposed to and can differentiate between their native language -English speakers use pitch to convey feeling -around 3 months children can narrow their perception and connect speech sounds with objects -English speakers can be familiar with German as the language is similar but not with Cantonese 9.2.1 Theories of language development -bf skinner said environment influences language development -Chomsky talked about biological constraints on development 9.2.1.1 Nurture: the role of environmental factors on behavior -study humans by only focusing on behavior as its observable and measurable -skinner said speech is verbal behavior -operant conditioning argues that children utter and repeat phrases if they are reinforced -verbal behavior decrease if it’s followed by punishment -the tone adults use becomes associated with praise or punishment -difference in pitch and rhythm-higher pitch to encourage and lower pitch to scold -Stephen Opsal and Bernstein trained mothers to talk more slowly to children with speech disorders to see if it would positively impact ability to easily produce words-rate of speaking didn’t decrease but time spent struggling to produce words decreased -mothers to praise child’s behavior reach speech millstones faster -fathers positive interaction benefits child’s language -when parents engage in conversations with child it helps in better neural connectivity and comprehension 9.2.1.2 Nature: the role of genetic factors on behavior -nativism is the belief that certain abilities are built into our brains -7-12 months has slower acquisition -5yrs they start to absorb words-critical period to ensure children fully develop language skills, children need environmental stimulation to promote healthy development -after puberty if someone hasn’t learned a second language it’ll be hard for them to do so -critical period is also called sensitive period-neurological system is more malleable during early development but can be modified later with proper environmental stimulation -children across cultures acquire nouns faster as that’s most common -sign language can either be SOV (subject object verb) or SVO (subject verb object) -sign language advancement shows the impact of environmental influences 9.2.1.3 An emergentist perspective -language is an interaction between inherited biology, environmental factors and social pressures -includes nativist environmentalist and behavioral approaches -without auditory input humans would only develop complex sign language -genetics help us develop language and environment specializes us 9.3 Language and the brain 9.3.1 Broca’s area -aphasia is the inability or difficulty to produce speech -damage to the lower frontal lobe -called Broca’s aphasia or non-fluent aphasia -he found that there’s a module in the brain controlling speech and language production is predominantly controlled by the left hemisphere -other primates can’t verbally speak because they haven’t developed Broca’s area like humans have -primates haven’t developed the version of FOXP2 that humans have 9.3.2 Wernicke’s area -his patient had damage to temporal lobe but could produce speech even though it wasn’t coherent -melody (prosody) of speech pattern stays intact but the ability to convey meaning is damaged -called Wernicke’s aphasia or fluent aphasia -this area organizes speech and projects a comprehensible message to Broca’s area for motor output and production -helps with processing and differentiating understandable sounds from nonsensical ones 9.4 Classifying words and objects -mental lexicon is the storage of words and concepts -it’s organized by using phenomes (smallest units of sound information) and morphemes (smallest unit of language comprehension) -semantic network of stored information lets us put words in context, get responses and detect errors -Wittgenstein says we store general information and define categories according to similarity -a prototype is the most common form a word assumes when we imagine it 9.4.1 The influence of language and culture on classification -Sapir-Whorf hypothesis says that language can influence perception (linguistic relativity) -references of time and space influence how we perceive time Eg: English speakers speak of time horizontally while mandarin speakers use it vertically -Haviland and Levinson discovered that GY speakers (compass oriented) accurately remember spatial information and outperformed English speakers (self-referenced directions) in spatial recognition tasks -dual task interference occurs when a person is trying to simultaneously complete tasks that compete for mental or physical resources 9.5 Problem solving -nature of problem, past experiences, general knowledge, way to approach a problem, available strategies contribute to your ability to solve problems 9.5.1 The approach to a problem -participants used the same strategy for problem 2 that they used in problem 1 -they were less likely to apply a new strategy -those who didn’t have problem 1 were less likely to use the same solution -their mental set was influences by past experience and created a set effect/fixation -this limited their application of new solutions 9.5.2 Functional fixedness -limits us from using objects for purpose outside of their normal use 9.5.3 Strategy -algorithm is a set of rules applied to solve a problem and individual differences+ environment will dictate the algorithm -trial and error is an exhaustive technique that requires you to go through every solution one at a time 9.5.3.1 Heuristics -used to create shortcuts to the lengthy decision-making process -means end heuristics lets us envision the goal and take whatever measures necessary to attain that goal -representative heuristics let us mentally compare something to our stored prototype of an event object or person-solve problems quicker but also leads to errors as we ignore the probability/base rate information -Bornstein and Elmer say those in medical field should be aware of this as they make quick high-pressure decisions and can make errors based on assumptions -we also assess the likelihood of something happening-availability heuristics say that we make judgements based on how easily we can retrieve same events from our memory or how easily available those memories are 9.5.4 Creativity -Robert Sternberg says creativity is a habit, process and approach to life -preparation is when we gather knowledge on the topic -incubation requires the idea to sit in your mind while you think of other things, memory helps you process information and make connections -illumination is when you are unaware of insight striking and it occurs suddenly -procrastinators have high creativity -evaluation is when you assess if it’s a creative solution 9.6 Decision making -confirmation bias is when we tend to seek out information that confirms our ideas and information which isn’t consistent with that is ignored -our bias is altered based on the framing of options 9.6.1 The dual process of decision making -intuition is the reliance on experience and emotions -our mind can unconsciously tap into information to help us make faster intuitive decisions (system 1 thinking) -this system relies on emotional system and stored experiences to guide thinking -cognitive reflection test assesses the likelihood that a person will overrule our initial decision -system 2 is logical thinking which contradicts initial instincts -language helps to allow us to slow down and use system 2