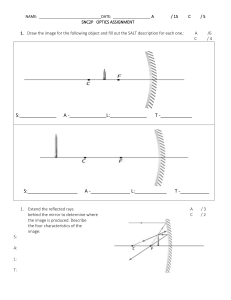
LESSON 3: Light and Mirrors OBJECTIVES: 1. Predict the qualitative characteristics (orientation, type, and magnification) of images formed by plane and curved mirrors and lenses (S10FE-IIg-50); and 2. Apply ray diagramming techniques in describing the characteristics and position of images formed by mirrors and lenses. LIGHT mirrors and lenses LIGHT • Light is a form of energy which helps us to see objects. • When light falls on objects, it reflects the light and when the reflected light reaches our eyes then we see the objects. • Light travels in straight line. • The common phenomena of light are formation of shadows, formation of images by mirrors and lenses, bending of light by a medium, twinkling of stars, formation of rainbow etc. Reflection of light :The bouncing back of light as it hits a smooth and shiny surfaces like mirror. Laws of reflection of light :1. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. 2. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane. 1. What is the value of the angle of incidence? 2. What is the value of the angle of reflection? Types of Reflection Specular/Regular reflection ➢ defined as light reflected from a smooth surface at a definite angle. Diffused/Irregular ➢ It is produced by rough surfaces that tend to reflect light in all directions Image formed by a plane mirror :1. The image is located behind the mirror. •2. The image is virtual. 3. The image is the same size as the object. 4. The image is upright, with the same height as the object. 5. The image undergoes a lateral inversion in relation to the object. 6. The image is situated at the same distance from the mirror as the object. Formation of Image by a Plane Mirror - Ray Diagrams The following rays are usually considered while constructing ray diagrams. • A ray of light incident on a plane mirror at 90o gets reflected from the mirror along the same path. • A ray of light falling on a plane mirror at any angle gets reflected from the mirror such that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection A Ray Diagram Showing the formation of an Image by a Plane Mirror Spherical mirrors Spherical mirror is a curved mirror which is a part of a hollow sphere. Spherical mirrors are of two types. They are concave mirror and convex mirror. Concave mirror :- is a spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards. Rays of light parallel to the principal axis after reflection from a concave mirror meet at a point (converge) on the principal axis. Convex mirror :- is a spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outward. Rays of light parallel to the principal axis after reflection from a convex mirror get diverged and appear to come from a point behind the mirror. F F Terms used in the study of spherical mirrors :Center of curvature :- is the center of the sphere of which the mirror is a part (C). Radius of curvature :- is the radius of the sphere of which the mirror is a part (CP). vertex:- is the centre of the spherical mirror (V). Principal axis :- is the straight line passing through the centre of curvature and the pole (X-Y). Principal focus :In a concave mirror, rays of light parallel to the principal axis after reflection meet at a point on the principal axis called principal focus(F). In a convex mirror, rays of light parallel to the principal axis after reflection get diverged and appear to come from a point on the principal axis behind the mirror called principal focus (F). Focal length :- is the distance between the pole and principal focus (f). In a spherical mirror the radius of curvature is twice the focal length. R = 2f or f = R 2 X C F f V Y C – center of curvature V- vertex XY – principal axis F – principal focus f – focal length Contsruction Rules for Ray Diagram 1. In a concave mirror a ray of light parallel to the principal axis after reflection passes through F. In a convex mirror a ray of light parallel to the principal axis after reflection appears to diverge from the F. C F V V F C 2. In a concave mirror a ray of light passing through the focus after reflection goes parallel to the principal axis. In a convex mirror a ray of light directed towards the focus after reflection goes parallel to the principal axis. C F V P F C 3. In a concave mirror a ray of light passing through C after reflection is reflected back along the same direction. In a convex mirror a ray of light directed towards C after reflection is reflected back along the same direction. C F V V F C • In a concave or a convex mirror a ray of light directed obliquely at the pole is reflected obliquely making equal angles with the principal axis. C F i r P i r P F C Images formed by concave mirror Case 1: When the object is at infinity C F • The image is at F, just a point. V Case 2: When the object is beyond C C F V • The image is between C and F, smaller, real and inverted. Case 3: When the object is at C C F V •The image is at C also, same size as the object, real and inverted. Case 4: When the object is between C and F C F V The image is beyond C,enlarged, real and inverted. Case 5: When the object is at F C • NO IMAGE F V Case 6: When the object is between F and V C F V The image is formed behind the mirror, erect, it is enlarged, and virtual. Images formed by convex mirror :• When the object is at infinity P F •The image is formed at F behind the mirror, it is highly diminished, virtual and erect. •When the object is between infinity and pole, P F C •The image is formed behind the mirror, it is reduced, virtual and erect. 9) New Cartesian sign convention for spherical mirrors :i) The object is always placed on the left of the mirror and light from the object falls from the left to the right. ii) All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole. iii) All distances measured to the right of the pole are taken as + ve. iv) All distances measured to the left of the pole are taken as – ve. v) The height measured upwards perpendicular to the principal axis is taken as + ve. vi) The height measured downwards perpendicular to the principal axis is taken as – ve. Object Direction of incident light Height upwards ( + ve ) Distance towards the left ( - ve Distance towards the right ( + ve ) ) Height downwards ( - ve ) Image Concave mirror 10a) Mirror formula for spherical mirrors :The mirror formula for spherical mirrors is the relationship between the object distance (u), image distance (v) and focal length (f). The mirror formula is expressed as :1 1 1 + = v u f b) Magnification for spherical mirrors :Magnification for spherical mirrors is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object. Height of the image hi Magnification = m= Height of the object ho The magnification is also related to the object distance and image distance. It is expressed as :hi v Magnification m = = ho u Wrap-up Activity A. Below are the qualitative characteristics of images. Determine whether it is REAL or VIRTUAL type of images: VIRTUAL 1. ____________is upright. REAL 2. ____________is inverted. VIRTUAL 3. ____________is behind the mirror. VIRTUAL 4. ___________ is formed by convex mirror. REAL 5. ___________ can be projected onto a screen. REAL is inverted with the respect to the 6. ______ object. A. Below are the qualitative characteristics of images. Determine whether it is REAL or VIRTUAL type of images: REAL 7. __________ is on the same side of the mirror as the object. 8. __________rays of light do not actually pass VIRTUAL through the image. REAL 9. __________can be larger, smaller, or the same size as the object. REAL 10.______rays of light actually converge and pass through the image. B. Identify whether the following is PLANE, CONCAVE or a CONVEX MIRROR CONVEX & CONCAVE 1. is a curved mirror _________________ PLANE 2. is flat, smooth mirror _______________________ PLANE & CONVEX 3. forms only virtual images____________________ 4. forms real or virtual images__________________ CONCAVE 5. forms images that are always upright _________ CONVEX & PLANE CONVEX 6. forms images that are always reduced _________ CONVEX & PLANE 7. forms images that are behind the mirror________ CONCAVE 8. forms images that are upright or inverted_______ CONCAVE 9. forms images that are either real or virtual_______ PLANE 10. forms images that have left to right reversal____