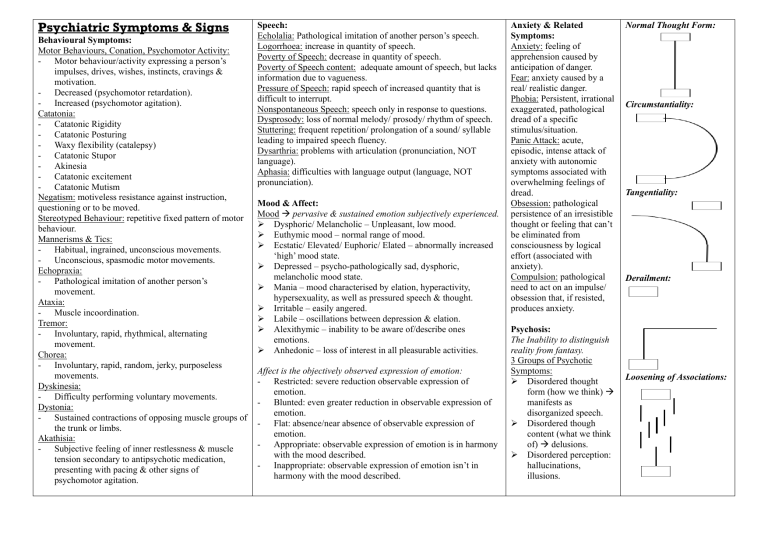
Psychiatric Symptoms & Signs Behavioural Symptoms: Motor Behaviours, Conation, Psychomotor Activity: - Motor behaviour/activity expressing a person’s impulses, drives, wishes, instincts, cravings & motivation. - Decreased (psychomotor retardation). - Increased (psychomotor agitation). Catatonia: - Catatonic Rigidity - Catatonic Posturing - Waxy flexibility (catalepsy) - Catatonic Stupor - Akinesia - Catatonic excitement - Catatonic Mutism Negatism: motiveless resistance against instruction, questioning or to be moved. Stereotyped Behaviour: repetitive fixed pattern of motor behaviour. Mannerisms & Tics: - Habitual, ingrained, unconscious movements. - Unconscious, spasmodic motor movements. Echopraxia: - Pathological imitation of another person’s movement. Ataxia: - Muscle incoordination. Tremor: - Involuntary, rapid, rhythmical, alternating movement. Chorea: - Involuntary, rapid, random, jerky, purposeless movements. Dyskinesia: - Difficulty performing voluntary movements. Dystonia: - Sustained contractions of opposing muscle groups of the trunk or limbs. Akathisia: - Subjective feeling of inner restlessness & muscle tension secondary to antipsychotic medication, presenting with pacing & other signs of psychomotor agitation. Speech: Echolalia: Pathological imitation of another person’s speech. Logorrhoea: increase in quantity of speech. Poverty of Speech: decrease in quantity of speech. Poverty of Speech content: adequate amount of speech, but lacks information due to vagueness. Pressure of Speech: rapid speech of increased quantity that is difficult to interrupt. Nonspontaneous Speech: speech only in response to questions. Dysprosody: loss of normal melody/ prosody/ rhythm of speech. Stuttering: frequent repetition/ prolongation of a sound/ syllable leading to impaired speech fluency. Dysarthria: problems with articulation (pronunciation, NOT language). Aphasia: difficulties with language output (language, NOT pronunciation). Mood & Affect: Mood → pervasive & sustained emotion subjectively experienced. ➢ Dysphoric/ Melancholic – Unpleasant, low mood. ➢ Euthymic mood – normal range of mood. ➢ Ecstatic/ Elevated/ Euphoric/ Elated – abnormally increased ‘high’ mood state. ➢ Depressed – psycho-pathologically sad, dysphoric, melancholic mood state. ➢ Mania – mood characterised by elation, hyperactivity, hypersexuality, as well as pressured speech & thought. ➢ Irritable – easily angered. ➢ Labile – oscillations between depression & elation. ➢ Alexithymic – inability to be aware of/describe ones emotions. ➢ Anhedonic – loss of interest in all pleasurable activities. Affect is the objectively observed expression of emotion: - Restricted: severe reduction observable expression of emotion. - Blunted: even greater reduction in observable expression of emotion. - Flat: absence/near absence of observable expression of emotion. - Appropriate: observable expression of emotion is in harmony with the mood described. - Inappropriate: observable expression of emotion isn’t in harmony with the mood described. Anxiety & Related Symptoms: Anxiety: feeling of apprehension caused by anticipation of danger. Fear: anxiety caused by a real/ realistic danger. Phobia: Persistent, irrational exaggerated, pathological dread of a specific stimulus/situation. Panic Attack: acute, episodic, intense attack of anxiety with autonomic symptoms associated with overwhelming feelings of dread. Obsession: pathological persistence of an irresistible thought or feeling that can’t be eliminated from consciousness by logical effort (associated with anxiety). Compulsion: pathological need to act on an impulse/ obsession that, if resisted, produces anxiety. Psychosis: The Inability to distinguish reality from fantasy. 3 Groups of Psychotic Symptoms: ➢ Disordered thought form (how we think) → manifests as disorganized speech. ➢ Disordered though content (what we think of) → delusions. ➢ Disordered perception: hallucinations, illusions. Normal Thought Form: Circumstantiality: Tangentiality: Derailment: Loosening of Associations: Inappropriate/ Irrelevant Answer: Thought Blocking: Flight of Ideas: Thought Form Disorders: Overinclusiveness: speech containing unnecessarily excessive detail. Perseveration: persisting response to a previous stimulus, even following a new stimulus. Verbigeration: meaningless repetition of specific words or phrases. Word salad: incoherent mixture of words/ phrases. Neologisms: made up words that don’t form part of any language. Echolalia: pathological repeating of words/ phrases of one person be another. Delusions: Fixed, false beliefs, based on incorrect inferences about external reality that cannot be corrected by reasoning. Types: Delusions of Persecution: belief of being harassed, cheated or persecuted. Delusion of Grandeur: belief of exaggerated importance, power or identity. Delusion of Reference: belief of behaviour of others refers to him/herself. Delusion of Poverty: belief of being bereft of all material possessions. Nihilistic Delusion: Belief that one’s self, others or the world is non-existent or is coming to an end. Somatic Delusion: belief surrounding a part of the body. Delusion of Control: belief of one’s will, thoughts or feelings are being controlled by external forces. Bizarre Delusion: absurd, totally implausible, strange belief. Perceptual Disturbances: Hallucination: false sensory perception not associated with real external stimuli. Types according to senses: - Auditory hallucination: perception of sound, usually voices. - Visual hallucination: perception of seeing images. - Olfactory hallucination: perception of smell. - Gustatory hallucination: perception of taste. - Tactile hallucination: perception of touch. Other Hallucinations: - Cenesthetic Hallucination: perception of sensation in an organ unable to experience sensation. - Hypnagogic Hallucination: non-pathological perception occurring while falling asleep. - Hypnopompic Hallucination: non-pathological perception occurring while awake from sleep. Illusion: Misperception/ misinterpretation of real external sensory stimuli.