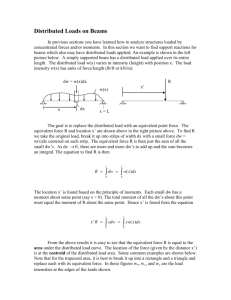
KWARA STATE UNIVERSITY, MALETE FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CES 822 ASSIGNMENT 5 COMPILED BY SUBMITTED TO PROF. A.A. ADEDEJI Q: What type of steel profile member should be designed for: i. ii. Universal Beam Universal Column The type of steel profile member that should be designed for depends on the specific application. Universal beams are typically used to support loads that are applied in one direction, such as the weight of a floor or roof. They are also used to resist bending moments. Universal beams have an I-shaped cross-section, with the flanges (the horizontal parts) being wider than the web (the vertical part). This shape makes them strong in bending. Universal columns are typically used to support loads that are applied in the vertical direction, such as the weight of a building. They are also used to resist buckling. Universal columns have an H-shaped cross-section, with the flanges being equal to or greater than the width of the web. This shape makes them strong in compression. In general, universal beams are more versatile than universal columns and can be used in a wider range of applications. However, universal columns are stronger in compression and are therefore better suited for applications where this is a major concern. Table 1.0 below summarizes the key differences between universal beams and universal columns Table 1.0: Key differences between Universal beams and universal columns Feature Universal Beam Universal Column Cross-section I-shaped H-shaped Strength Strong in bending Strong in compression Versatility More versatile Less versatile Typical Supporting loads in one direction, applications resisting bending moments Supporting loads in the vertical direction, resisting buckling Ultimately, the best type of steel profile member to use will depend on the specific requirements of the application. A structural engineer can help you determine the best choice for your project. Here are some additional considerations that may affect the choice of steel profile member: The magnitude of the loads that need to be supported The direction of the loads The need for resistance to bending or buckling The available space The cost of the different options