Newborn Screening Act 9288 Reviewer: Metabolic Disorders
advertisement
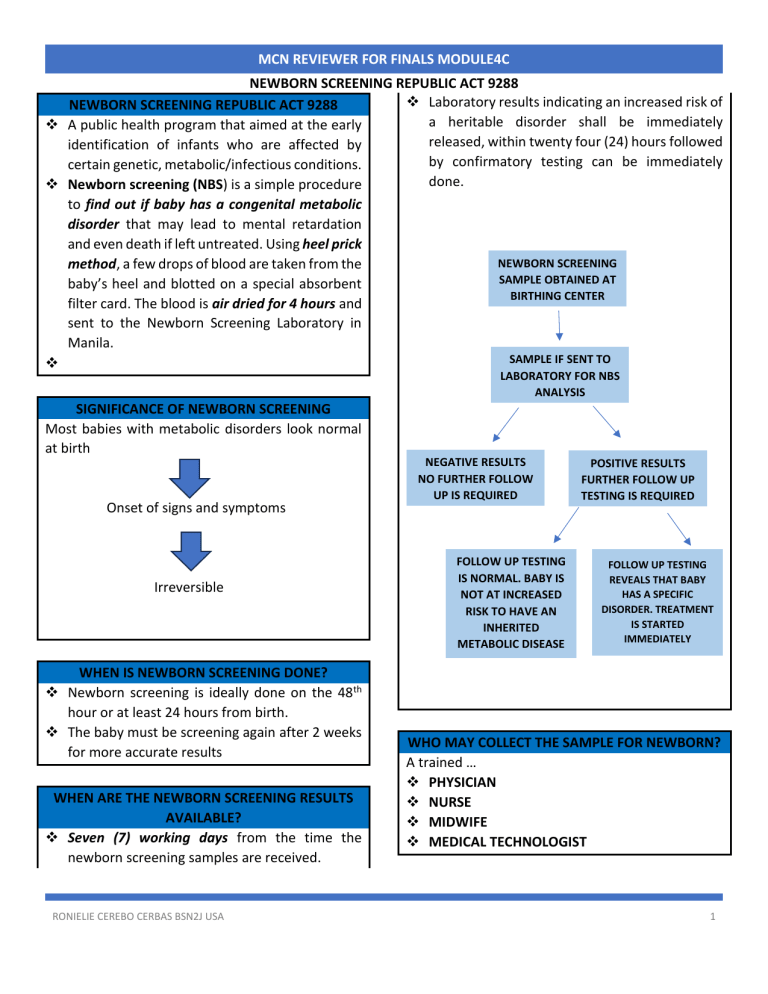
MCN REVIEWER FOR FINALS MODULE4C NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 ❖ Laboratory results indicating an increased risk of NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 a heritable disorder shall be immediately ❖ A public health program that aimed at the early released, within twenty four (24) hours followed identification of infants who are affected by by confirmatory testing can be immediately certain genetic, metabolic/infectious conditions. done. ❖ Newborn screening (NBS) is a simple procedure to find out if baby has a congenital metabolic disorder that may lead to mental retardation and even death if left untreated. Using heel prick NEWBORN SCREENING method, a few drops of blood are taken from the SAMPLE OBTAINED AT baby’s heel and blotted on a special absorbent BIRTHING CENTER filter card. The blood is air dried for 4 hours and sent to the Newborn Screening Laboratory in Manila. SAMPLE IF SENT TO ❖ LABORATORY FOR NBS ANALYSIS SIGNIFICANCE OF NEWBORN SCREENING Most babies with metabolic disorders look normal at birth Onset of signs and symptoms Irreversible WHEN IS NEWBORN SCREENING DONE? ❖ Newborn screening is ideally done on the 48th hour or at least 24 hours from birth. ❖ The baby must be screening again after 2 weeks for more accurate results WHEN ARE THE NEWBORN SCREENING RESULTS AVAILABLE? ❖ Seven (7) working days from the time the newborn screening samples are received. RONIELIE CEREBO CERBAS BSN2J USA NEGATIVE RESULTS NO FURTHER FOLLOW UP IS REQUIRED FOLLOW UP TESTING IS NORMAL. BABY IS NOT AT INCREASED RISK TO HAVE AN INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE POSITIVE RESULTS FURTHER FOLLOW UP TESTING IS REQUIRED FOLLOW UP TESTING REVEALS THAT BABY HAS A SPECIFIC DISORDER. TREATMENT IS STARTED IMMEDIATELY WHO MAY COLLECT THE SAMPLE FOR NEWBORN? A trained … ❖ PHYSICIAN ❖ NURSE ❖ MIDWIFE ❖ MEDICAL TECHNOLOGIST 1 MCN REVIEWER FOR FINALS MODULE4C NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 c)main regulator of body temperature d) helps maintain heart rate THE 5 METABOLIC DISORDERS BEING IDENTIFIED e) helps in normalcy of bowel movements. BY NEWBORN SCREENING ❖ TRI-IODOTHYRONINE (T3) ❖ THYROXIN (T4)- crucial for normal growth and development of the body and brain among newborns. Thyroid gland is regulated by… a)HYPOTHALAMUS- produces THYROTROPIN RELEASING HORMONE TRH b)PITUITARY GLAND- produces THS ❖ TRH stimulates the pituitary gland to produce THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE TSH 1) CONGENITAL HYPOTHYROIDISM NORMAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Low thyroid hormone level in circulation Hypothalamus releases TRH Pituitary gland releases TSH ❖ Congenital means existing at birth (inherited). ❖ Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the person does not make enough thyroid hormone. Caused by… a)defective development of thyroid gland b)development of thyroid gland in an abnormal location c)maternal intake of anti-thyroid medication or excess iodine d) an inherent defect in manufacturing the thyroid hormone Thyroid hormone functions… a)responsible for normal function of certain body organs and is essential for normal brain development. b)controls the development of muscles and bones as well as growth of teeth. RONIELIE CEREBO CERBAS BSN2J USA Stimulates thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) into bloodstream PT gland detects adequate hormone levels in body Slows down production of TSH Clinical Manifestation… A)JAUNDICE B)POOR MUSCLE TONE C)LOW BODY TEMPERATURE D)LONG PROTUDING TONGUE E)LARGE ANTERIOR FONTANEL 2 MCN REVIEWER FOR FINALS MODULE4C NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 F)UMBILICAL HERNIA ❖ Hyperplasia means an abnormal increase in the Goals of treatment… number of cells that make up an organ or tissue. a)maintain the T4 level of the client above the This causes the organ or tissue to enlarge. normal range Adrenal Glands releases hormones… b)maintain TSH level in normal range (below 10 a.)Epinephrine or Adrenaline-Secreted by adrenal mIU/L) medulla, the fight or flight hormones. Prepares the c) avoid overtreatment body for vigorous physical activity. -premature closure of cranial sutures and b.)Cortisol- the “Stress hormones” helps body cope fontanelles with stressful situations protective mechanism of d)provide psychological support to the family the body against illness or injury. Helps control Management… blood pressure, blood sugar and heart function. Thyroid Replacement before 2 weeks old Not having enough cortisol can be life threatening TREATMENT: because it can lead to shock (dangerously low blood L-THYROXINE tablet from for babies with pressure), which is also known as an “adrenal crisis” CH- crushed into food or dissolved into a small c.)Aldosterone- the salt retaining hormone amount of formula, juice or other liquid. BLOOD PRESSURE DROPS NOTE: DO NOT GIVE Soy-based formulas and iron supplementsreduce the amount of absorption. SECOND SENSE BY PITUITARY GLAND 2.)CONGENITAL ADRENAL HYPERPLASIA RELEASE ACTH STIMULATES ADRENAL GLANDS ❖ A disorder present at birth and characterized by abnormalities in the production of certain hormones of the adrenal glands. ❖ An endocrine disorder caused by abnormalities in specific enzyme caused by abnormalities in specific enzyme of the adrenal gland that causes serve salt lose, dehydration and abnormally high levels of male sex hormones in both boys and girls. ❖ If not detected and treated early, babies may die within 7-14 days. RONIELIE CEREBO CERBAS BSN2J USA DIRECTS OUR KIDNEYS TO PULL SALT AND WATER OUT OF URINE AND PUT IT BACK INTO THE BLOOD RAISES BP BACK TO NORMAL AND PREVENTS BODY FROM LOSING TOO MUCH LIQUID Adrenal cortex hormones…. ANDROGEN MALE HORMONE- stimulate the development of male sexual characteristics. PITUITARY GLAND- responsible for giving commands to different glands of the body 3 MCN REVIEWER FOR FINALS MODULE4C NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 -releases hormones ACTH (Adrenocorticotrophic hormone) -Stimulates the production of adrenal hormones. Clinical Manifestation… ❖ SALT WASTING -deficient aldosterone – will start losing too much water and salt via urine- dehydration and very low blood pressure. This can be life-threatening if not treated right away. ❖ Listlessness and drowsiness ❖ Dehydration ❖ Weight loss ❖ Low blood pressure ❖ Low blood salt ❖ Too much acid in the blood, called metabolic acidosis. If not treated… Severe dehydration leads to shock, a serious situation in which not enough blood is getting to the brain and other organs called the “adrenal crisis”. The signs of an adrenal crisis include; ❖ Confusion ❖ Irritability ❖ Rapid heart rate ❖ Coma RONIELIE CEREBO CERBAS BSN2J USA 4 MCN REVIEWER FOR FINALS MODULE4C NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 ❖ Gal is a condition in which the body is unable to process galactose, the sugar present in the milk. Accumulation of excessive galactose in the body can cause many problems, including liver damage, brain damage and cataracts. ❖ An inherited disorder that lacks an enzyme (galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase/Gal1-PUT) which helps the body break down the galactose. 3.)GALACTOSEMIA/GAL RONIELIE CEREBO CERBAS BSN2J USA 5 MCN REVIEWER FOR FINALS MODULE4C NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 Management…. ❖ Avoid milk and milk products substituted with lactose free or galactose free milk such us Soybased milk formula. ❖ ❖ Galactose-restricted diet must be followed for life and requires close supervision and monitoring. 4.)PHENYLKETONURIA/PKU ❖ PKU is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which the body cannot properly use one of the building block of protein called phenylalanine, and essential amino acid that converts into tyrosine causing evaluation of phenylalanine in the blood. ❖ Phenylalanine is neurotoxic ❖ Excessive accumulation of phenylalanine in the body causes brain damage. RONIELIE CEREBO CERBAS BSN2J USA 6 MCN REVIEWER FOR FINALS MODULE4C NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 5.)G6PD Deficiency ❖ Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency ❖ Is an inherited condition in which the body lacks the enzymes g6pd, which helps red blood cells function normally. ❖ This deficiency can cause hemolytic anemia, usually after exposure to certain medications, foods, or even infections. ❖ Is an X-linked hereditary disease, which means it is cause by a defective gene effects males almost exclusively and is transmitted by the mother only to sone or daughter who will become another carrier. ❖ Is one of many enzymes that helps the body process carbohydrates and turn them into energy. ❖ Also protects red blood cells from potentially harmful byproducts that can accumulate when a person takes certain medications or when the body is fighting an infections ❖ Without enough G6PD to protect the blood, RBCs can be damaged or destroyed. ❖ Hemolytic anemia is a disorder in which the red blood cells are destroyed faster than the bone marrow can produce them. RONIELIE CEREBO CERBAS BSN2J USA 7 MCN REVIEWER FOR FINALS MODULE4C NEWBORN SCREENING REPUBLIC ACT 9288 RONIELIE CEREBO CERBAS BSN2J USA 8