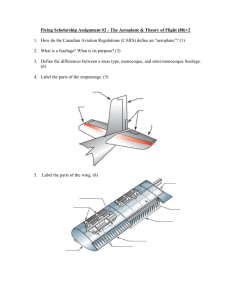
Introduction to Aircraft Flight Aircraft have become an integral part of our daily lives, transporting people and goods across the world at incredible speeds. But have you ever wondered how these massive machines take flight and navigate through the air? In this presentation, we'll explore the fundamental principles behind aircraft flight and gain a deeper understanding of how they work. Basics of Lift and Drag The two main forces that act on an aircraft during flight are lift and drag. Lift is the force that acts perpendicular to the direction of motion, while drag is the resistance force acting in the opposite direction. These forces are created by the interaction between air molecules and different parts of the aircraft. Bernoulli's Principle One of the key principles behind lift is Bernoulli's principle, which states that as the speed of a fluid (such as air) increases, its pressure decreases. This is why airplanes are designed with curved wings on top and flat wings on the bottom - as air flows over the curved surface, it has to travel a longer distance, resulting in higher velocity and lower pressure on top of the wing. Angle of Attack The angle at which the wing meets the oncoming air, known as the angle of attack, also plays a crucial role in generating lift. Too small of an angle and there won't be enough lift to keep the aircraft in the air, but too large of an angle can result in stall - a dangerous situation where airflow over the wing becomes turbulent and causes loss of lift. Thrust and Weight In order for an aircraft to take off and maintain level flight, the thrust generated by its engines must be greater than its weight. This is known as the thrust-to-weight ratio. During takeoff, the pilot will increase engine power in order to reach a speed where enough lift is generated to overcome the weight of the aircraft. Role of Control Surfaces To control the direction and stability of an aircraft, various control surfaces such as ailerons, elevators, and rudders are used. These surfaces work by altering the airflow over the wings and tail, allowing pilots to make precise adjustments and maneuvers. Influence of Drag While lift is essential for flight, drag can have both positive and negative effects. Drag is a force that acts in the opposite direction of motion and can be both beneficial, such as when it slows down an aircraft during descent, or detrimental, such as when it hinders forward motion. Conclusion In summary, the principles of lift and aerodynamics play a crucial role in how aircraft are able to fly. From Bernoulli's principle to the angle of attack and thrust-to-weight ratio, all of these factors work together to keep an aircraft in the air and under control. So next time you're flying in a plane, take a moment to appreciate the science behind it all! So, it is clear that there are many variables at play when it comes to flight. From the shape of the wing and the angle of attack, to the control surfaces and drag, each element works together to create lift and keep the aircraft in motion. It is truly remarkable how these principles are applied in order to defy gravity and allow us to travel through the skies. As technology continues to advance, we can only imagine what new developments will further improve upon these fundamental concepts of flight. The next time you take to the skies, remember the incredible science behind it all and appreciate the wonders of flight. Let's continue to soar towards new heights! So keep on flying, because the sky is truly the limit. Blue skies and tailwinds! References 1. "How Do Planes Fly?", NASA Glenn Research Center. [Online]. Available: https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/howfly.html 2. "Airfoil", Encyclopedia Britannica. [Online]. Available: https://www.britannica.com/science/airfoil 3. "Angle of Attack", Boldmethod. [Online]. Available: https://www.boldmethod.com/learn-to-fly/aerodynamics/angle-of-attack/ 3. "Drag", NASA Glenn Research Center. [Online]. Available: https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/drag1.html 4. "Thrust-to-Weight Ratio", Aerospaceweb.org. [Online]. Available: https://www.aerospaceweb.org/question/performance/q0118.shtml 5. "Flight Control Surfaces", Boldmethod. [Online]. Available: https://www.boldmethod.com/learn-to-fly/aerodynamics/flight-control-surfaces/ 6. "A Brief History of Aviation", Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum. [Online]. Available: https://airandspace.si.edu/exhibitions/wrightbrothers/online/fly/1903/principles/controls.cfm 7. "Jet Engine", Encyclopedia Britannica. [Online]. Available: https://www.britannica.com/technology/jet-engine 8. "The Future of Flight", Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum. [Online]. Available: https://airandspace.si.edu/exhibitions/future-flight/