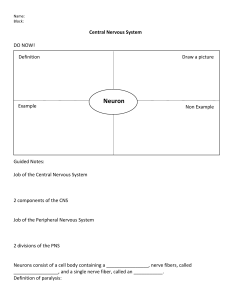
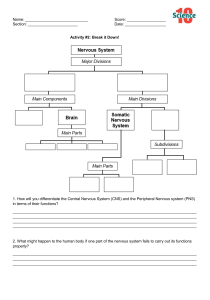
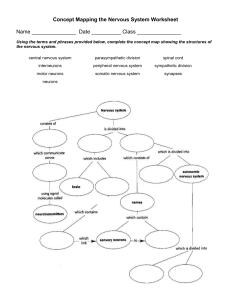
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. G. U. Israel 1. Introduction TABLE OF CONTENT 2. cellular architecture i. Neuron ii. Neuroglial cells iii. Synapse iv. Reflex arc 3. central nervous system i. The brain ii. The spinal cord 4. peripheral nervous system i. Autonomic nervous system ii. Somatic nervous system INTRODUCTION The nervous system is the chief controlling and coordinating system of the body. It is responsible for judgement, intelligence and memory, this made it the most complex system of the body. This system is composed of highly specialized cells called neurons which can detect, receive and transmit different kind of stimuli. Neves are composed of groups of individual specialized neurons, which transmit motor and sensory information back and forth between the peripheral and central nervous system. Divisions of the Nervous System 1. Central nervous system (CNS) 2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE NEURON This is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. It’s a specialized cell which can detect, receive and transmit different kind of stimuli. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, using biochemical neurotransmitters. Structure of the Neuron Cell body (soma); contains a nucleus, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, endoplasmic retinaculum, ribosomes, Nissl's granules, etc. Dendrites; cytoplasmic extension of the soma. It receives action potential and carry them towards the body. Axon; it carries action potential away from the soma. CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE NEURON CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE Classification of Neurons 1. According to the number of their processes. i. Multipolar neurons ii. Bipolar neurons iii. Pseudounipolar neurons iv. Unipolar neurons CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE Classification of Neurons 1. According to the length of axon. i. Golgi type I ii. Golgi type II iii. Amacrine neuron Does not have axon, only dendrite Found in retina CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE Classification of Neurons 1. According to function. i. Sensory neuron ii. motor neurons iii. Relay or Interneurons CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE Classification of Neurons 1. According to Shape. i. Stellate ii. Basket iii. Fusiform iv. Pyramidal CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE Classification of Neurons 1. According to Size. i. Macroneuron: more than 7um, eg. Betz cells ii. Microneuron: less than 7um, eg. Granular cells CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE NEUROGLIAL CELLS These are supportive cells that surround the cell bodies, dendrites, and axons of neurons in both CNS and PNS. They include: 1. Astrocytes 2. Oligodendrocytes 3. Microglia 4. Ependymal cells 5. Schwann cells CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE SYNAPSE This is the site of contact between neurons. Neurons are connected to one another by their processes. The contact between neurons is by contiguity and not continuity. Impulse is transmitted across a synapse through biochemical neurotransmitters (acetylcholine). REFLEX ARC This is the functional unit of the nervous system. It is neural pathway that controls an action reflex An involuntary motor response to a sensory stimulus is called reflex action. It consist of: • A receptor, e.g. skin • The sensory neuron • The interneuron • The motor neuron • The effector, e.g. muscle CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM This is the body’s processing center. Function 1. Reception of sensory information (touch, pressure, pain, temperature, vibration) 2. Receiving and perceiving special sensations (taste, smell, vision, sound) 3. Integration and processing of sensory information 4. Responds generation Components 1. Brain 2. Spinal cord CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM BRAIN Parts of the brain Parts Subdivisions Principal Structure Ventricle Forebrain (prosencephalon) Telencephalon Cerebrum, Basal ganglia, limbic system Lateral Diencephalon Thalamus, hypothalamus, metathalamus, epithalamus Third Midbrain (mesencephalon) Mesencephalon Crus cerebri, substantia Cerebral aqueduct nigra, tegmentum, tectum Hindbrain (rhombencephalon) Metencephalon Pons, cerebellum Myelencephalon Medulla oblongata Fourth CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM BRAIN CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM SPINAL CORD • It is the long cylindrical lower pat of the CNS • it’s the main pathway for information connecting the brain and the PNS Meningeal Coverings • Outermost dura mater • Middle arachnoid mater • Innermost pia mater Enlargements • Cervical enlargement • Lumbar enlargement Spinal Nerves • 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Each nerve arises by dorsal and ventral nerve rootlet CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM SPINAL CORD CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Tracts of the Spinal Cord • A collection of nerve fibres that connects two masses of grey matter within the cns is called a tract. Descending Tracts Ascending Tracts Pyramidal or corticospinal tracts • Lateral spinothalamic tract • Lateral corticospinal tract • Anterior spinothalamic tract • Anterior corticospinal tract • Fasciculus gracilis Extrapyramidal tracts • Fasciculus cuneatus • Rubrospinal tract • Dorsal spinocerebellar tract • Medial reticulospina tract • Ventral spinocerebellar tract • Lateral reticulospina tract • Spino-olivary tract • Olivospinal tract • Spinotectal tract • Vestibulospinal tract • Tectospinal tract CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM SPINAL CORD TRACTS PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The peripheral nervous system is divided into; Somatic Nervous System • It is made up of 12 pairs of cranial nerve and 31 pairs of spinal nerves It’s divided into: Sensory or afferent nervous system Motor or efferent nervous system Autonomic Nervous System; it’s divided into: Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Cranial Nerves There are twelve (12) cranial nerves , arising from the brain, as follows; Forebrain: Olfactory nerve (CN I), optic nerve (CN II) Midbrain: Oculomotor nerve (CN III), trochlear (CN IV) Hindbrain • Pons: Trigeminal nerve (CN V), abducent nerve (CN VI), facial nerve (CN VII), vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). • Medulla oblongata: Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (X), accessory nerve (CN XI), hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Spinal Nerves RECEPTORS RECEPTORS THE EAR RECEPTORS THE TONGUE RECEPTORS THE NOSE AND SMELLING PATHWAY RECEPTORS THE EYES AND VISION PATHWAY RECEPTORS THE SKIN THANK YOU