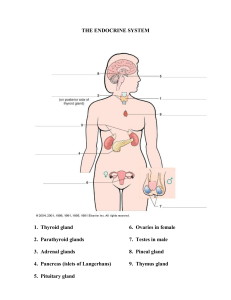
Chapter 21 ➢ Male system - testes (sperm production), seminiferous tubules, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicle, prostate, and bulbourethral gland ➢ Male system - hormonal regulation -GnRH stimulates release of LH and FSH which stimulate testes to produce testosterone, sperm and inhibin (controlled by negative feedback) ➢ Female system – urethra, vagina, uterus, oviducts/fallopian tubes, and ovaries ➢ Oogenesis – primary oocyte (in prophase I at birth), Meiosis I at puberty, M II at fertilization, role of follicle and corpus luteum in hormone production ➢ Female system – hormonal regulation – roles of GnRH, LH, FSH, estrogen and progesterone; also understand the ovarian cycle and the uterine cycle and hormonal regulation Chapter 16 Know the organs/structures of the excretory system Functions of the excretory system and its various parts Kidney structure – veins, arteries and capillaries, cortex, medulla, nephron, and renal pelvis Filtration, reabsorption, and secretion – what are they and how do they work? Conservation of salt and water via reabsorption and osmosis. What are diuretics and how do they cause their effect? Disorders of the Kidney Dialysis – via a dialysis machine (hemodialysis) vs. via Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Chapter 17 Nervous System Structure – Central and Peripheral Nervous System. PNS with Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System (ANS). ANS with Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Neuron Structure/Function – Sensory, motor, and inter-neurons, with dendrites, cell body, axon, and axon terminals; axons wrapped in Schwann cells to form myelin Nerve propagation – resting potential (polarized) and action potential (depolarization) based on movement of sodium and potassium ions Synapse function via calcium and vesicles filled with neurotransmitters Spinal cord, vertebrae, meninges with cerebrospinal fluid, ganglia, gray matter, white matter Cerebrum as seat of consciousness with primary motor area and primary somatosensory area as examples; Diencephalon and brainstem control involuntary processes Somatic system; reflexes Autonomic system with control via the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems Chapter 18 Types of Receptors: Chemo-, photo-, mechano-, and thermoSomatic sensing relies on proprioceptors, cutaneous, and pain receptors Taste depends on chemoreceptors in taste buds which bind “taste” molecules and depolarize nerve cells Olfaction (sense of smell) utilizes ~1,000 different odor receptors which can discriminate ~10,000 different odors Eye structure and vision; optic chiasma Photoreceptors: types and location; vision disorders Ear structure; hearing and equilibrium How many senses do we have? Chapter 20 Endocrine glands and Hormones (peptide vs. steroid); understand basic functions of endocrine secretion and hormone action – including peptide vs. steroid mechanism of action Examples of glands: Hypothalamus & Pituitary gland (posterior and anterior), Thyroid, Thymus, Pineal, Adrenal, Testes and Ovaries, & Pancreas Hypothalamus connection with posterior (ADH and oxytocin) and anterior pituitary (TSH, ACTH, FSH, & LH; also PRL & hGH) Thyroid gland and its hormones (thyroxin (T4), T3) and role; Thyroid imbalance Thymus gland and its hormones (thymosins) and role Pineal gland and its hormone (melatonin) and role Adrenal Gland and its hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine; glucocorticoids and mineralcorticoids) and roles Pancreas and its hormones (glucagon and insulin) and roles; diabetes Pancreas as an endocrine and exocrine gland Chapter 22 Biological Development Stages and structures – - Fertilization - cleavage (morula, blastula, blastocoel) - gastrulation (gastrula with endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm, and blastopore) - Human embryonic and fetal development - Fates of embryonic germ layers - Definitions: zygote, embryo, fetus - Fertilization to Implantation - Embryonic development across species: similarities Fetal development of organs and body systems Features of Fetal Circulation (foramen ovale, ductus arteriosus, umbilical vessels) Prenatal testing: Amniocentesis, Chorionic villus sampling - Embryo Adoption - Reproductive biotechnology: IVF, PGD, egg and sperm donation, designer babies Chapter 26 Biotechnology tools – restriction enzymes, ligase, plasmid DNA, recombinant DNA Polymerase Chain Reaction – enabled by thermostable DNA polymerase; used to amplify DNA Electrophoresis to separate DNA fragments; DNA sequencing Cloning: gene, therapeutic, reproductive Stem cells DNA“fingerprinting” Ancestry Determination using AIMS, HapMaps; what is a haplotype? Genetically Modified Organisms, Transgenic Organisms Genetic Modification of Humans – therapy vs enhancement - somatic vs germ-line genetic engineering Gene Therapy using Vectors – how they work & what can go wrong Gene editing with CRISPR; editing somatic vs. germ-line cells