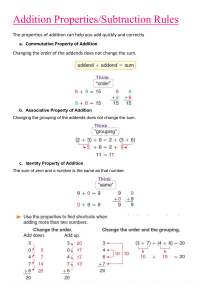
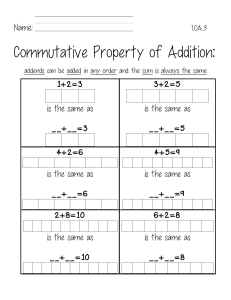
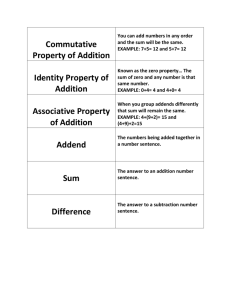
Title: Learning Simple Addition Objective: The purpose of this document is to introduce and teach the concept of simple addition to beginners. By the end of this guide, learners should be able to perform basic addition with confidence. Introduction: Addition is a fundamental mathematical operation that involves combining two or more numbers to find their total or sum. In simple terms, addition helps us understand how quantities can change when combined. Terminology: Addends: The numbers being added together. Sum: The result of adding two or more numbers. Plus Sign (+): The symbol used to indicate addition. Basic Addition Rules: 1. Order Doesn't Matter: The sum remains the same regardless of the order in which the numbers are added. For example, 3 + 5 is the same as 5 + 3, and both equal 8. 2. Associative Property: When adding three or more numbers, the grouping of addends does not affect the sum. For example, (2 + 4) + 3 is the same as 2 + (4 + 3), and both equal 9. Example Problems: Let's go through a few examples to understand how addition works. 1. Adding Two Numbers: Problem: 4 + 7 Solution: Start with the larger number (7) and count up by the value of the smaller number (4). Count 4: 7, 8, 9, 10, 11. Answer: 4 + 7 = 11 2. Adding Three Numbers: Problem: 2 + 5 + 3 Solution: You can add the numbers in any order. Start with 2: 2 + 5 = 7 Add 3: 7 + 3 = 10 Answer: 2 + 5 + 3 = 10 3. Adding with Zero: Problem: 6 + 0 Solution: Adding zero to any number results in the same number. Answer: 6 + 0 = 6 Practice Exercises: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 3+8 2+6+4 9+0 5+7 1+2+3 Conclusion: Congratulations! You've learned the basics of addition. Regular practice with addition will enhance your mathematical skills and lay the foundation for more advanced concepts. Keep practicing and exploring different number combinations to strengthen your understanding of addition.