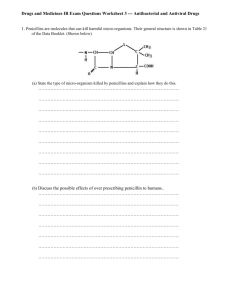
Penicillin Breakthrough in Medicine Penicillium Penicillin is the oldest and one of the most commonly used groups of antibiotics at present. They are derived from the mold/fungi Penicillium. Penicillin can be divided into two groups, namely natural and semisynthetic penicillins. Natural penicillins are produced from the fermentation of the fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. The semisynthetic penicillins, on the other hand, are prepared from (+)-6aminopenicillanic acid. History Discovery fi ff Starting in the late 19th century there had been reports of the antibacterial properties of Penicillium mould, but scientists were unable to discern what process was causing the e ect.Scottish physician Alexander Fleming at St Mary's Hospital in London (now part of Imperial College) was the rst to show that Penicillium rubens had antibacterial properties. History Medical application fi The rst successful use of pure penicillin was when Fleming treated Harry Lambert of fatal infection of the nervous system (streptococcal meningitis) in 1942. By that time the Oxford team could produce only small amount. Florey willingly gave the only available sample to Fleming. Lambert showed improvement from the very next day of the treatment, and was completely cured within a week.Fleming published his clinical trial in The Lancet in 1943. Following the medical breakthrough the British War Cabinet set up the Penicillin Committee on 5 April 1943 that led to projects for mass production. History Mass production fi P zer scientist Jasper H. Kane suggested using a deep-tank fermentation method for producing large quantities of pharmaceuticalgrade penicillin. Large-scale production resulted from the development of a deep-tank fermentation plant by chemical engineer Margaret Hutchinson Rousseau.As a direct result of the war and the War Production Board, by June 1945, over 646 billion units per year were being produced. History Mass production Penicillin was being mass-produced in 1944. History Structure determination and total synthesis fi fi The chemical structure of penicillin was rst proposed by Edward Abraham in 1942 and was later con rmed in 1945 using X-ray crystallography by Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin, who was also working at Oxford. She later in 1964 received the Nobel Prize for Chemistry for this and other structure determinations. History Structure determination and total synthesis Dorothy Hodgkin's model of penicillin's structure. Thank you for your attention!