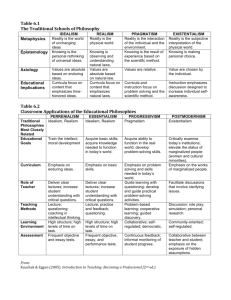
Idealism derived from “Ideal” an “idea” Idealism is a philosophy which adheres to the view that nothing exists except an idea in the mind of a man. Idealism asserts that reality consists of ideas, thoughts, minds or selves rather than material objects and force. Naturalism is opposed to idealism. It subordinated mind to matter and holds that ultimate reality is physical not spiritual Pragmatism is derived from Greek word “pragma” which means “action”. Pragmatism is a philosophy which recognizes truth only according to its practical results. Brightman- It is a theory which tests truth according to practical results. An idea or theory can be considered true only if its results are satisfactory and useful. REALISM Realism regards the physical world as real and this real, factual and practical life is more important than any other things. NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Democritus Aristotle Huxley Darwin Irwin Lamarck Spencer Rousseau Bacon Hobbs Pierce W. James Dewey Kilpatrick Russel Socrates Berkeley Ross Plato Kant Fichte Hegal Gandhi Vivekanand Ghosh Aristotle Aquinas Locke Karl Marx Metaphysics Epistemology Axiology • NaturalismNature is ultimate reality. • Pragmatismreality is still in process • Idealism• Mind idea and spirit are true • Realism- Real world is the world of Nature • Senses are the gateways of knowledge. • Knowledge is experience based. • No belief in values • Mind is treasure of knowledge • Values are eternal • Knowledge obtained through senses is real. • Values are permanent and fundamental values don’t change. • Values are being changed NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Nature alone is reality and it is readymade. Reality lies in process. It is still in process and not readymade. Mind and thought are real. Every reality is proved by observation, experience, experiment and scientific reasoning The outlook is materialistic. Social outlook spiritual outlook Intelligence is significant to formulate concepts Essence of Human life is animality Essence of human life is practicability Essence of human life is spiritual Essence of human life is experiences Ultimate reality is physical Ultimate reality is utility Ultimate reality is spiritual Ultimate reality is physical NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Do not believe in the Believe in the existence of God. existence of God to some extent. Full belief in God. Do not believe in values, soul, religion or divine spirit. Values are changeable and created by men. They change with time, place and circumstances. No law is universal Values are eternal and they never change. Truth, goodness and beauty are eternal values. Spiritual laws are universal Values are permanent and objective. Right and wrong should be taught Universe is created by man Universe is created by God Physical universe is operated by natural laws. Physical and natural laws are universe. Universe is created by nature Soul and God do not exist Physical and natural laws are universal NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Nature is the base . The slogan is “Follow the nature” Society is the base. Emphasis is on physical and social environment Preparation for complete and real life Chid-centred education Experience Teacher centered/ centred child centered education Child centered Opposes bookish knowledge Experiences Emphasis and bookish experimentati knowledge ons Vocational and technical education Spiritualism is base of education. Emphasis is on spiritual and moral environment NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM Believes in negative education Believes in Believes in education based positive on experiences education Self experience Emphasis on uncontrolled freedom of child Emphasis on restricted freedom Emphasis on good discipline to follow rules and regulations of school Emphasis on strict discipline REALISM NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Individual development Dynamic development Character development Personality Development Sensory Development Social development Development of will power Development of insight and scientific attitude Sublimation of instincts Creation of new values Development of inventive sense Self thinking and decision making Attainment of present and future life Development of resourceful mind Simple living high thinking Socialistic feelings NATURALISM t PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Autonomous development Social development Spiritual development Personality Development Perfection of human machine Creation of new values and ideals development of moral sense Socialistic values Self expression Social efficiency Self realisation Art of living for complete life Adaptation to environment Adjustment with present and to change the present Preservation and development of culture Insight for self thinking and decision making Preparation for struggle of existence Rich present life Based on moral, spiritual and intellectual values Vocational and technical skills to earn his livelihood NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Learning by doing, Observation method Learning by activity Project method Questioning method, story telling, dramatics Inductive-Deductive Logic, going from the particular facts of sensory experience to the more general laws Play-way method Learning by experiences Conversation method Observation Direct method Heuristic method Method of Lecture method, integration debate Inductive method discussion Analysis Synthesis Insight NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Uncontrolled freedom Restricted freedom Regulated freedom Good Discipline Discipline through natural consequence Social discipline Self discipline Social Discipline NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Teachers place behind the scene Teacher has an importance place Place of a teacher is very high Teacher must be educated and well versed with the customs of beliefs and right and duties of people and the trends of all ages and places Teacher guides, directs, suggests and control the nature of child Guidance of hard realities of life, must be able to expose problems of life and world Teacher is not to Teacher puts the interfere with pupil’s in the pupil’s activity position of discover NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Emphasis on science Emphasis on practical Emphasis on ethics Science Emphasis on Physical sciences Higher place to science not to culture Important place to scientific important place to study Vocational Subjects Related to interest, abilities, aptitudes and nature of child Based on utility, integration, child’s natural interest and experiences Based on humanistic, moral, spiritual and intellectual values Emphasis on mother tongue Subjects according to ability and interest NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Broad based curriculum Games Physical education Physical & Life Sciences Mathematics Social Sciences Literature Music Sculpturing Painting Language Health Sciences, Physical Education Social sciences Mathematics Agriculture Languages Arts Social sciences Ethics Literature Sciences Physical Education Vocational subjects Mother tongue Social Sciences NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Child centred New concept of school Child centred Teacher centred Objective attitude Individual development Practical subjects Morality based Practical aims Wider and higher aims Curriculum according to nature and capabilities of students Utility based subjects Based on needs of technology Based on ideas and ideals Realistic school organisation Humanistic Attitude towards learning Complete development Universal education Technical and vocational subjects Emphasis upon psychology Democratic outlook Restored dignity to man Sense training Emphasis upon free choice Progressive attitude Self discipline Scientific teaching methods NATURALISM PRAGMATISM IDEALISM REALISM Too much freedom Do not believe in eternal values Ideals and aims can neither be achieved Too much emphasis on objectivity Too much emphasis on present Opposition to spiritual values Neglects science and technology Emphasis on Sciences Ignores text books No pre determined goals Teacher centred approach Too much emphasis on facts No importance to teachers Negation of past Theoretical methods No place for intuition and meditation Not clear cut aims Negation of Humanities Undue importance to teacher No faith in eternal values and high ideals of life Focus on natural consequences Anti intellectual Main concern is market place of daily life Difficult concepts Ignorance of emotions and imagination which are equally important in life Negative education Overloading teachers Neglects social aspects of life Ignorance of spiritual aims Nandra, I.S. & Kaur, P. (2015). Philosophical Perspective in Education. Twentyfirst Century Patiala https://onlinenotebank.wordpress.com https://wandofknowledge.com