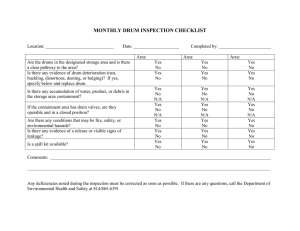
“Heaven’s light is our guide” Rajshahi University of Engineering & Technology DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL AND FOOD PROCESS ENGINEERING Course Code : CFPE 3122 Course Name : Unit Operations in Chemical and Food Process Engineering Sessional Topic name : Rotary drum filter Submitted by Name & Roll : Mst.Nusrat Jahan(1911004) MD.Nasibur Rahman(1911005) Shauvik Das Shuvo(1911006) Submitted to Sajib Dey Lecturer Department of Chemical and Food Process Engineering Rajshahi University of Engineering & Technology Date of submission : 27 November 2023 Table of contents: Serial number Contents Page 01 Introduction Page no 3 02 Underlying Theories Page no 3 Working Principles 03 Page no 4 (schematic diagram) 04 Advantages & Disadvantages Page no 5 05 Conclusion Page no 5 06 References Page no 6 Introduction Filtering is the process of passing a liquid through a filter in order to remove solid particles, where the solids are collected. Separating the liquid and solid phases of a suspension is known as solid-liquid separation. The reason this process is called “Mechanical Separation” is that it uses physical techniques to separate the materials. The initial separation is accomplished by physical techniques, though it can be enhanced by chemical or heat treatments. [1] The most common type of continuous vacuum filter is the Rotary drum filter. This is a type of filter that can accommodate a large thickness of cake and can take a precoat of filter aid which is up to 150 mm in depth. [2] Many other filters are made specifically to extract particles from liquid solutions. In addition to being utilized for this purpose, the rotary drum filter is also employed in solids recovery and compression, drying .There are two types of rotary drum filters: pressurized (pressure drum filters) and vacuum (rotary drum vacuum filters). [3] These filters have minimal power needs, effective cake washing, and continuous operation. They can handle a variety of discharge techniques for filter cakes with varying consistencies and work with a variety of filter cloths. [3] The rotary filter is most suitable for continuous operation on large quantities of slurry. If the slurry contains considerable amount of solids, that is, in the range of 15-30% [4] . The vacuum-driven ones are available in a variety of sizes and types to meet the needs of a wide range of industries, including food processing, wastewater treatment, mineral engineering, and even laboratory settings. [3] Examples of pharmaceutical applications include the collection of calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate and starch. The separation of the mycelia from the fermentation liquor in the manufacture of antibiotics. Also, Block and instant yeast production. [4] Underlying Theories : A rotary drum filter works on the principle of slurry filtration through a sieve-like mechanism on the surface of a rotating drum, under vacuum conditions . [5] Sieving is a physical mechanism of particle removal, where a particle is denied access through a pore or passageway that is smaller than the particle itself. The liquid passes through the sieve while retaining larger particle itself. [6] The drum is made up of a perforated plate that supports a filter cloth, and the slurry is introduced into the trough of the drum filter. [5] As the drum rotates, a vacuum is applied to the segment it is submerged in, causing the liquid to be sucked through the filter cloth and leaving solids to cake on the membrane surface in sieving-like mechanism. [5] The sieve-like mechanism of the rotary drum filter is suitable for filtering slurries containing a high proportion of solids up to 15 to 30 percent. [5] 3D Model: Working principle : A rotary vacuum drum filter consists of a horizontal drum with a slotted face turns at 0.1 to 2 rpm in an agitated slurry trough. A filter medium, such as canvas, covers the face of the drum. [7] The filter operates by slowly rotating the drum in a trough of slurry with the drum from 10 to 35% submerged. (189/1063). The drum rotates at creating a vacuum of about 400 to 160 torr. [3] Rotary drum filler is divided into several sections, including a pickup zone, a drain zone, a watering zone, a drying zone, and a cake removal zone. Pick-up zone and draining zone are also called filtration zone. In the first four zones under vacuum and in the last zone, vacuum is released, and compressed air is worked. In pick-up zone, the rotary drum filter is partially submerged in the slurry to be filtered. As the drum begins to rotate, it picks up the incoming liquid along with suspended solids. In draining zone, the drum, with the slurry on its surface, moves into a drainage or vacuum zone. Excess liquid is drawn through the filter medium, leaving behind a layer of filtered solids (cake) on the drum surface. In washing zone, the drum may be subjected to additional liquid, either by spraying water onto the cake or by submerging the drum in a washing liquid which helps improve the purity of the filtrate by removing any remaining impurities on the cake surface. Following the washing zone, the drum rotates further, exposing the cake to air. This allows for partial drying of the cake, reducing its moisture content before the cake removal stage. The cake removal zone involves methods to remove the solid cake from the drum’s surface. This can include scraping the cake off using a blade, vacuum removal, or other techniques. The removed cake may be collected for disposal or further processing. Advantages • • • • • The rotary vacuum drum filter is a continuous and automatic operation, so the operating cost is low. [4] The variation of the drum speed rotating can be used to control the cake thickness. The process can be easily modified (pre-coating filter process). [4] Can produce relatively clean product by adding a showering device. [4] The cake is removed simultaneously during operation. Therefore, suitable for use with concentrated slurries. [5] Disadvantages • • • • • • Due to the structure, the pressure difference is theoretically limited to atmospheric pressure (1 bar), and in practice somewhat lower. [4] The discharge cake contains residual moisture. [4] The cake tends to crack due to their air drawn through by the vacuum system, so that washing and drying are not efficient. [4] High energy consumption by the vacuum pump [4] A rotary drum filter is expensive equipment with complex functioning. It contains moving parts and also requires a number of accessories such as agitators and vacuum pump, vacuum receivers, slurry pumps, traps etc. [5] The rotary filter is suitable only for straightforward slurries. It is less satisfactory if the solids form an impermeable cake or if it is difficult to remove the cake adequately. [5] Conclusion : In conclusion, the rotary drum filter is a reliable method of separating solids from liquids that is well-suited to a variety of industrial settings (drying, compression). Its sturdy construction and modifiable operating parameters, like flow rate and drum speed, provide flexibility in meeting various filtration needs. Sustaining performance and longevity requires proper maintenance, which includes routine cleaning and observation. The ongoing progress in filtering technology offers prospects for additional improvements in efficacy and efficiency. The rotary drum filter is still a viable option for solid-liquid separation as a crucial part of industrial processes, which enhances product quality and operational dependability. References [1 G. V. A. V. K. T. Sivakumar, "ENHANCING THE PERFORMANCE OF ROTARY VACUUM DRUM ] FILTER," International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology, p. 2. [2 A. R. H. A.Rushton, Solid-Liquid Filtration and SeparationTechnology, VCH . ] [3 K. Sutherland, "Rotary drum filter," in Filters and Filtration Handbook, Elsevier Science, 2007, p. ] 117. [4 "Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia," [Online]. Available: ] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotary_vacuum-drum_filter. [5 S. Ray, "Pharmacy Scope," 18 May 2022. [Online]. Available: https://pharmacyscope.com/rotary] drum-filter/. [Accessed 26 November 2023]. [6 "Science Direct," [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and] biologicalsciences/sieving#:~:text=Sieving%20is%20a%20physical%20mechanism,smaller%20than%20the% 20particle%20itself. [7 J. S. P. H. Warren McCabe, "Unit Operations Of Chemical Enigneering," in Mechanical Separations, ] McGraw Hill, 2004, p. 1007. Table of work distribution : Tasks Roll number 1911004 Lab report 1911005 1911006 1911004 Presentation Slide 1911005 1911006 Design 1911005