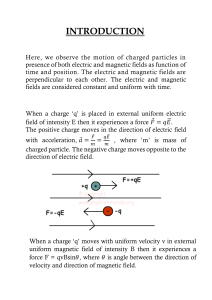
1 MOST IMPORTANT DERIVATIONS + TheoryFollow the following steps - • The derivation marked bold are of more importance. • I have written important theory topics in italics • Treat this as a check list of all derivations and important theory for your Physics board examination. • Refer to my notes. I have written the page number of every derivation in my notes. You can find the link to my notes in the description box of the video. Best of luck ! Unit 1 : Electrostatics Pg No of Notes of that Particular Chapter All Derivations + Imp Theory Topics - Coulomb’s law of Electrostatics ( Normal Derivation & Vector Derivation F21=- 3 F12) - Superposition Principal in Electric Field Intensity 7 Note : Electric Lines of force and it’s properties is very important 8 - Electric field intensity of a dipole at tanA/ Equatorial position 10 - Electric field intensity of a dipole at tanB/ Axial position 11 - Electric field intenisty at any point due to an ideal dipole 12 - Force and torque acting on a dipole in an external uniform electric field 13 - Work done to rotate a dipole in external electric uniform field 14 - Gauss Theorem : It’s definition, verificaiton and application 17 - Electric field intensity due to a thin uniformly charged infinite plane sheet 19 - Electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell 20 - Electric Potential at a point due to a point charge 22 - Prove electric field is conservative in nature 25 - Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor 29 - Capacitance of a single and concentric sphere 30 - Energy stored in a capacitor 31 - Series and Parallel Combination of Capacitors 33 - Effect of dieletric medium on the capacitance of parallel plate capacitor 35 an Am w r ta at Dh al Aman Dhattarwal 2 Current Electricity - Ohm’s Law and its derivations 1,4 - Drift velocity of free electrons & it’s relation with current I=neAvd 3 - Series and Parallel Combination of Resistances 6 - Kirchof’s Law and simple application (defintion & numerical) i) Meter Bridge, Ammeter, Voltmeter n a m t a h D - Learn formulas and Practice Numericals of the following - l a w 8 tar ii) Potentiometer - Principle and Working + Numericals A Magnetic Effects of Current and Electricity - Biot-savart’s law definition (imp) //theory 1 - Magnetic field intensity due to a straight current carrying conductor of finite length 6-7 - Magnetic field intensity due to a circular loop of current carrying conductor 8 - Magnetic field at any point on the axis of a circular loop and coil 9 9-11 - Ampere’s Circuit Law & it’s applications - i) Magnetic field due to an infinitely long straight current carrying conductor. (ii) Magnetic field intensity at any point inside a straight infinitely long solenoid. (iii) Toroid - Lorentz Law and it’s properties (v.imp) // theory l a w r a t t a h D 12 - Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field when the velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field 13 - Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field when the velocity is not perpendicular to the magnetic field. 14 - Cyclotron : Principle + Construction + Working 15 n a m - Force on a Current Carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field A 16 - Force on a Current Carrying Loop in a uniform magnetic field 17 - Torque acting on a current carrying loop/coil in a uniform magnetic field 18 - Moving Coil Galvanometer : Principle + Construction + Working 19 - Force b/w parallel current carrying conductors ( also practice numerical) 20 Aman Dhattarwal 3 Magnetism and Matter - Magnetic field due to a magnetic dipole. i) at any point on the axis or at tanA position. (ii) At any point on equatorial line/tanB. (iii) at any point due to a dipole moment. 24 l a w 26 - Force and torque acting on a dipole moment in an external uniform electric r a field tt a h 27 - Work done in rotating a magnetic dipole in a uniform magnetic D field n a 28 - Terrestrial magnetism ( theory + numerical ) m A Properties of dia, para and ferro magnetic substances + Magnetic Saturation (imp theory) Electromagnetic Induction - Faraday’s Experiment ( very imp). // thery at h D - Motional EMF or induced EMF ( Derivations + Numericals) - Self Inductance and Work done - Mutual Inductance n a m l a w tar A Aman Dhattarwal 4 Alternating Current - AC Generator : Diagram, Principle, Construction and working. Derive the expression for the induced emf and current. // (imp theory) - Transformer : Principle, Construction, working and theory of a transformer. How is current affected in a transformer? What are the energy losses in a transformer? How can they be reduced? //theory (v.imp) - Mathematical treatment of LC-oscillations - Conservation of energy in LC- oscillations - Define power for an a.c circuit. Derive an expression for the average of a series LCR-circuit connected to an a.c source. Discuss the various special cases. - Impedance, reactance and average power in series LCR, LR, LC or CR circuit. Aman Dhattarwal - Derive an expression for the impedance of a series LCR-circuit. Use Phasor Diagram - Resonance condition of a series LCR-circuit. Calculate its resonant frequency - Sharpness of resonance in a series resonant circuit? Find expression for Q-factor of circuit. - AC Circuit containing a i) resistor. (ii) inductor. (iii) Capacitor //draw phasor diagram + graph of E and I versus wt - Average value of a.c over one complete cycle - Relation between the rms value and the peak value of an alternating emf - Relation between the effective and peak value of a.c (note: effective=rms=virtual) - Relation between average value and peak value of a.c Electromagnetic Waves - Derivation of displacement current - Characteristics and Properties of EM Waves - Electromagnetic Spectrum Aman Dhattarwal 5 Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - Reflection from Speherical Mirrors and find relation b/w f & R. 2 - Mirror formula using Concave and Convex Mirror 4-5 - Total Internal Reflection ( definition + applications & numerical ) (v.imp) 11 - Refraction through spherical surfaces (convex and concave) 15 - Lens Makers Formula (derivation & numerical) 17 - Refraction through a glass prism & minimum angle of deviation 21 - Scattering of light (Blue colour of sky, reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset) // theory (imp) l a w - Optical Instruments (Ray Diagram & Numerical) //(gauranteed qs) Wave Optics n a m ar t t a Dh A - Expression for the intensity at any point on the observation screen in Young’s double slit experiment. Hence write the conditions for constructive and destructive interference. - Expression for fringe width in Young’s double slit experiment. How can the wavelength of monochromatic light be found by this experiment? - Diffraction using single slit (derivation + numerical) - Deduce expression for (i)angular width of central maximum (ii) linear width of central maximum (iii) linear width of a secondary maximum - Polarisation (derivation + numerical) Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter - Derivation of de-broglie relation - Relation between threshold frequency, frequency of the incident photon and cutoff potential - Dual nature of radiation - Photoelectric effect - Hertz and Lenard’s Observation - Einstein’s photoelectric equation-particle nature of light Aman Dhattarwal 6 Note : In the following chapters the number of derivations are less but they have a significant theory portion. These chapters are easier , simpler and scoring chapters. Atoms - It is small, easy and scoring chapter. Refer to the notes uploaded on my channel. - Do the whole chapter. - Expression of radius in hydrogen like atoms - Bohr model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum (also do numericals) - Alpha-particle scattering experiment Nuclie t a h D l a w tar n a - N=N’e-lamda t. m A OR State and deduce Radioactive decay law - Relation between mean life and decay constant - Relation between half cycle and decay constant - Decay rate or activity of a radioactive sample. - Mass defect (definition and numerical) - Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion (definition & numerical) (imp) - Binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number (Definition and Numerical Problems) Electronic Devices - Common emitter transistor amplifier - Common base transistor amlifier - Energy bands in conductor,semiconductors and insulators - Semiconductor diode: I-V chacteristics in forward and reverse bias - Diode as rectifier Communication Systems - Frequency modulation and amplitude modulation. - Elements of a communication system - Propagation of electromagnetic waves in the atmosphere, sky & space wave propagation, satellite communication - Types of Modulation and Modulation Index Aman Dhattarwal