Microeconomics Assignment: Elasticity, Consumer Behavior
advertisement

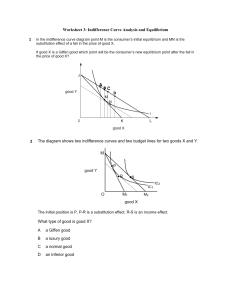
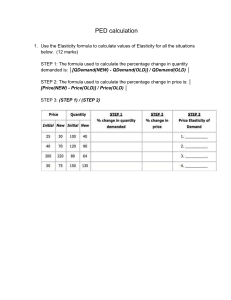
Microeconomics | Assignment 1| Dr. GK 1. Calculate price elasticity of demand curve, P = 100 - 5Q at each of the following price and quantity levels. P = 90 and Q = 2 P = 50 and Q = 10 P = 5 and Q = 19 2. Given: P.Q = 500, what happens to price elasticity of demand as price falls (P = Price, and Q = Quantity Purchased)? 3. An individual spends all his income on two goods, X and Y. If with the rise in price of good X, the quantity purchased of good Y remains unchanged, what is the price elasticity of demand for X? 4. The price elasticity of demand for colour TV is estimated to be – 2.5. If the price of colour TV is reduced by 20 percent, how much percentage increase in the quantity of colour TVs sold do you expect? 5. Studies in the United States of America indicate that price elasticity of demand for cigarettes is 0.4. If a pack of cigarettes currently costs $2 and the government wants to reduce smoking by 20 percent by how much should it increase the price? 6. In the attempts to increase sales and profits, a firm is considering 5 percent increase in the price and 15 percent increase in the advertising expenditure. If the price elasticity of demand is – 1.5 and advertising elasticity is + 0.7, would there be increase or decrease in total revenue? 7. Explain the relationship between the total revenue of firm and the price elasticity of demand for price reduction. 8. Explain why a firm facing a downward sloping demand curve would never produce at the inelastic (ep < 1) portion of the demand curve. 9. Show that on a linear demand curve, price elasticity of demand decreases continuously from infinity at the price axis to zero at the quantity axis. 10. For the demand curve Q(p) = a + bp find the equation for point price elasticity of demand. 11. Show that if indifference curves are concave, a consumer will consume only one of the two goods. 12. Amit’s budget line relating good X and good Y has intercepts of 50 units of good X and 20 units of good Y. If the price of good X is 12, what is Amit’s income? What is the price of good Y? what is the slope of budget line? 13. Wha is marginal rate of substitution? An indifference curve of Sonia contains the following market baskets of apples and bananas. Each of these baskets gives her equal satisfaction. Market basket Apples Bananas 1 2 16 2 3 11 3 4 7 4 5 4 5 6 2 6 7 1 Find out marginal rate of substitution of Sonia. How does marginal rate of substitution vary as she consumes more of apples and less of bananas? Give reasons. 14. Explain consumer’s equilibrium condition with the help of indifference curve approach. How a change in consumer’s income will affects his equilibrium? 15. Explain why a consumer will choose a market basket so that marginal rate of substitution (MRS) equals price ratio. 16. A consumer spends all her income on food and clothing. At the current prices of P f = 10₹ and Pc = 5₹, she maximizes her utility by purchasing 20 units of food and 50 units of clothing. (a) What is the consumer’s income? (b) What is the consumer’s marginal rate of substitution of food for clothing at the equilibrium position? 17. Priya spends all her monthly income of ₹5000 on food and clothing. Price of food is ₹250 and the price of clothing is ₹100 and her monthly consumption of food is 10 units and that of clothing is 25 units. With this consumption of the two commodities her marginal rate of substitution of food for clothing is MRS fc = 1𝐶 1𝐹 . Is she in equilibrium with this consumption? Which commodity she will substitute for the other to reach equilibrium position? Illustrate diagrammatically with indifference curves. 18. What is income consumption curve. Draw indifference curve diagram showing the income consumption curve in the following cases; (a) Both X and Y are normal goods (b) Good X is normal good and good Y is inferior (c) Good X is inferior good and good Y is a normal good 19. Fill in the blanks in the following table: Number of variable inputs 3 4 5 6 7 Total output (No. of units) 130 - Marginal product of the variable input 18 20 5 - Average product of the variable input 30 19.5 20. Consider the following data on output and inputs. What type of returns to scale does it represent and why? K L Q 5 8 3 10 16 6 20 32 12 40 64 24 21. You are given the following production function. Which ones represent constant returns to scale, which one increasing return to scale and which one decreasing returns to scale and why? (a) Q = AK0.5 L0.7 (b) Q = AK 0.25 L0.75 (c) Q = AK0.3 L0.6 (d) Q = 10√𝐿 √𝐾 22. A firm has the following production function: 1 1 Q = 22 𝐿2 Calculate marginal product function for labor and capital. Also calculate MRTSLK. What type of return to scale does it represent?