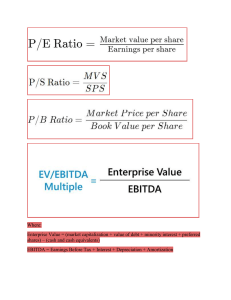
CHAPTER 4 INCOMEBASED VALUATION PRESENTED BY ALBESOR-BERNALDEZ-DELFIN-DIAZ-DINZON-SILVINO-VILLARINA OVERVIEW Introduction WACC DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW Two Opposing Theories CAPM SUMMARY Factors affecting proper asset valuation EVA THEORY QUESTIONS CEM PROBLEMS QUESTIONS Key drivers in IncomeBased Valuation INCOME BASED VALUATION Many investors and analysts find that the best estimate for the value of the company or an asset is the value of the returns that it will yield or income that it will generate. Thus, most of them are more particular in determining the total income that the asset will generate. INCOME Income is based on the amount of money that the company or assets will generate over the period of time. These amounts will be reduced by the costs that they need to incur in order to realize the cash inflows and operate the assets. EXPENSE Being the opposite of income, it represents a decrease in economic benefit during the accounting period in the form of a decrease in asset or an increase in liability that results in a decrease in equity other than distributions from the equity participants. In income based valuation, investors consider the two opposing theories: the dividend irrelevance theory and the birdin-hand theory. DIVIDEND IRRELEVANCE THEORY (MODIGLIANI & MILLER) Stock prices are not affected by dividends or the returns on the stock but more on the ability and sustainability of the asset of the company. DIVIDEND RELEVANCE THEORY/BIRD IN HAND THEORY (GORDON&LINTNER) Dividend or capital gains impact the price of the stock. Once the value of the asset has been established, investors and analysts are also particular about certain factors that can be considered to properly value the asset. Additional value inputted in the calculation that would account for the increase in value of the firm: Potential Growth Price Increases Operating Effeciences Both are considered in the sensitivity analysis. Reduces the value when there are future circumstances that affects the firm negatively. SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS Multiple analysis are done to understand how changes in an input or variable will affect the outcome (firm value). Amount added to the value of the firm in order to gain control of it. Risk that may affect a firm's ability to realize projected earnings. TRUE OR FALSE THEORY QUESTIONS 1. MANY INVESTORS AND ANALYSTS FIND THAT THE BEST ESTIMATE FOR THE VALUE OF THE COMPANY OR AN ASSET IS THE VALUE OF THE RETURNS THAT IT WILL YIELD OR INCOME THAT IT WILL GENERATE. 2. INCOME IS BASED ON THE AMOUNT OF MONEY THAT THE COMPANY OR THE ASSETS WILL GENERATE OVER THE PERIOD OF TIME. 3. IN INCOME BASED VALUATION, INVESTORS CONSIDER TWO OPPOSING THEORIES: THE DIVIDEND IRRELEVANCE THEORY AND THE BIRD-IN-HAND THEORY. 4. THE DIVIDEND IRRELEVANCE THEORY WAS INTRODUCED BY MODIGLIANI AND MYRON GORDON THAT SUPPORTS THE BELIEF THAT THE STOCK PRICES ARE NOT AFFECTED BY DIVIDENDS OR THE RETURNS ON THE STOCK BUT MORE ON THE ABILITY AND SUSTAINABILITY OF THE ASSET OR COMPANY. 5. BIRD-IN-HAND THEORY BELIEVES THAT THE DIVIDEND OR CAPITAL GAINS HAS IMPACT ON THE PRICE OF THE STOCK. IN INCOME BASED APPROACH, A KEY DRIVER IS THE COST OF THE CAPITAL OR THE REQUIRED RETURN FOR A VENTURE COST OF CAPITAL Represents the firm's cost of financing and its minimum rate of return that a project must earn to increase its value. It refers to the cost of the next dollar (or peso) of financing necessary to finance a new investment opportunity. It is an extremely important financial concept. It is the major link between the firm's long-term investment decisions and the wealth of the firm's owners as determined by the market value of thier shares. COST OF CAPITAL INVESTMENT 1 INVESTMENT 2 Investments with a rate of return above the cost of capital will increase the value of the firm. Projects with a rate of return below the cost of capital will decrease firm value. SOURCES OF LONG TERM CAPITAL CAPITAL COST OF CAPITAL Long term Debt After tax rate of interest (1 - tax rate) Common Stock CAPM Preferred Stock Annual dividend per share/Net proceeds from the sale of preferred shares Retained Earnings Addition to RE for the year/Equity Fraction KEY DRIVERS IN INCOME BASED VALUATION 01 WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL OR WACC 02 CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL OR CAPM WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL(WACC) It reflects the expected average future cost of capital over the long run. It is found by weighting the cost of each specific type of capital by its proportion in the firm's capital structure. It can be used to determine the appropriate cost of capital by weighing the portion of the asset funded through equity and debt. FORMULA WACC= (Ke x We) + (Kd x Wd) Ke= cost of equity We=weight of the equity financing Kd= cost of debt after tax Wd=weight of the debt financing WACC may also include other sources of financing like Preferred Stock and Retained Earnings. Including other sources of financing will have to require redistributing the weight based on the contribution to the asset. WACC = (% of debt) (After-tax Cost of Debt) + (% of Preferred share) (Cost of Preferred Shares) + (% of Ordinary Equity) (Cost of Ordinary Equity) Example: Proportion Specific Cost Weighted Cost of Capital Bonds 30% 6.6% 1.98% Preferred Shares 10% 10.21% 1.02% Ordinary Equity Shares 40% 13.33% 5.33% Retained Earnings 20% 13% 2.6% WACC 10.93% CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL (CAPM) Shows the relationship between the market risk and the expected return. It is one of the major developments in modern financial theory widely used in investment analysis. It is a model based on the proposition that any stock's required rate of return is equal to the risk-free rate of return plus a risk premium that reflects only the risk remaining after diversification. FORMULA Ke= Rf+B (Rm-Rf) Ke/Re=Rate of Return Rf= risk free rate B = beta coefficient of an individual stock which is correlation between the votality (price variation) of the stock market and the votality of the price of the individual stock Example: if the price of the individual stock rises 10% and the stock market 15%, the beta is 1.5. Rm = market return (Rm-Rf)=market risk premium or the amount above risk free rate required to induce average investors to enter the market. To illustrate, the risk-free rate is 5% while the market return is roving around at 11.91%, the beta is 1.5. The cost of equity is 15.365% [5% +1.5 (11.91% -5% ) ]. If the prospect can be purchased by purely equity alone the cost of capital is 15.365% already. However, if there will be portion raised through debt, it should be weighted accordingly to determine the reasonable cost of capital for the project to be used for discounting. Ke= Rf+B (Rm-Rf) Ke= 5% + 1.5 (11.91% - 5%) Ke= 5% + 1.5 (6.91%) Ke= 5% + 10.365% Ke= 15.365% The cost of debt can be computed by adding debt premium over the riskfree rate. Kd = Rf + DM Rf= risk free rate DM= debt margin Kd = Rf + DM Kd=5% + 6% Kd= 11% To illustrate, the risk-free rate is 5% and in order to borrow in the industry, a debt premium is considered to be about 6%. Given the foregoing, the cost of the debt is 11% [5% + 6% ] . Now, assuming that the share of financing is 30% equity and 70% debt, and the tax rate is 30%. The weighted average cost of capital will be computed as: WACC= (Ke x We) + (Kd x Wd) WACC = (15.365 % x 30% ) + (11% x (1-30% ) x 70%) WACC = 4.61% + 5.39% WACC = 10% The WACC is 10%. Observe that tax was considered in debt portion to factor in that the interest incurred, or cost of debt is taxdeductible, hence, there is tax benefit from it. You may also note that the cost of equity is higher than cost of debt, this is because cost of equity is riskier as compared to the cost of debt which is fixed. It may be observed that the cost of capital is a major driver in determining the equity value using income based approaches. PROBLEMS QUESTIONS Using Capital Asset Pricing Method (CAPM), compute for the cost of capital(equity) with risk-free rate of 4%, market return of 8% and Beta of 1.5. PROBLEMS QUESTIONS The appropriate WACC of a firm is 6.43% with risk free rate of 4%, market return of 8%, prevailing credit spread of 3%, tax rate of 30% and equity ratio of 30%, compute for the volatility of stocks or beta. PROBLEMS QUESTIONS With risk-free rate of 5%, Beta of 1.5, market return of 8%, prevailing credit spread of 3%, tax rate of 30% and equity ratio of 30% compute for the weighted average of cost of capital. THEORY QUESTIONS True or False 1. WACC may also include other sources of financing like preferred stock and retained earnings. 2. The cost of equity may be also derived using the Capital Asset pricing. 3. cost of capital is a major driver in determining the equity value using income based approaches. 4. The cost of capital can be computed primarily by getting the weight of cost of sources of fund, through weighted average cost of capital and capital asset pricing model. 5. The beta in Capital Asset pricing model is used to represent volatility/risk of the market. In the succeeding discussions, the value of the stocks will be based on the value of the cash flows that the company will generate. The approach is the determination of the value using economic value added, capitalization of earnings method, or discounted cash flows method. ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED (EVA) "EXCESS EARNING" The most conventional way to determine the value of the asset is through its economic value added. In Economics and Financial Management, economic value added (EVA) is a convenient metric in evaluating investment as it quickly measures the ability of the firm to support its cost of capital using its earnings. ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED (EVA) "EXCESS EARNING" EVA is the excess of the company earnings after deducting the cost of capital. The excess earnings shall be accumulated for the firm. The general concept here is that higher excess earnings is better for the firm. The elements that must be considered in using EVA are: Reasonableness of earnings or returns Appropriate cost of capital ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED (EVA) "EXCESS EARNING" The earnings can easily be determined, especially for GCBOS, based on their historical performance or the performance of the similarly-situated company in terms of the risk appetite. The appropriate cost of capital will be lengthily discussed in the succeeding chapters can be determined based on the mix of financing that will be employed for the asset. ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED (EVA) "EXCESS EARNING" Measures the ability of the firm to support its cost of capital using its earnings. EVA= Earnings -Cost of Capital Cost of Capital=Investment Value x Rate of Cost of Capital ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED (EVA) "EXCESS EARNING" ILLUSTRATIONS: Chandelier Co. projected earnings to be Php350 Million per year. The board of directors decided to sell the company for Php1.5 Billion with a cost of capital appropriate for this type of business at 10%. Solve for EVA. EVA= Earnings -Cost of Capital Cost of Capital=Investment Value x Rate of Cost of Capital ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED (EVA) "EXCESS EARNING" EVA= Earnings - (Investment Value x Rate of Cost of Capital) SOLUTION: EVA= Earnings - (Investment Value x Rate of Cost of Capital) = 350M - ( 1.5 B X 10%) = 350M-150M =200M he result of Php200 million means that the value offered by the T company is reasonable to for the level of earnings it realized on an average and sufficient to cover for the cost of raising the capital. Problem: SPPE Corp. is planning to expand and new projects is expecting to earn an average of Php 375,000.00 annually. If the projected requires for Php 5,000,000 investment at 10% cost of capital. Compute for the Economic Value Added. a. Php 125,000 b.(Php 125,000.00) c. Php 875,000.00 d. (Php 875,000.00) Problem: SPRO Corp. is planning to expand and new projects is expected to have an EVA of Php 200,000.00. The annual cost of capital at 10% amounts to Php 400,000.00. What is the average monthly earning projected for this project? a. Php 600,000.00 b. Php 50,000.00 c. Php 60,000.00 d. Php 500,000.00 Problem: SPLI, Inc. has a debt to equity ratio of 3:1. After tax cost of debt is 5% while cost of equity is 10%. The board of directors of the company decided to sell 100% of the company for Php 1 Billion. Compute for the projected monthly average earnings assuming an EVA of Php 57,500,000.00 a. Php 37,500,000.00 b. Php 10,000,000.00 c. Php 120,000,000.00 d. Php 100,000,000.00 CAPITALIZATION OF EARNINGS METHOD The value of the company can also be associated with the anticipated returns or income earnings based on the historical earnings and expected earnings. For green field investments which do not normally have historical reference, it will only rely on its projected earnings. Earnings are typically interpreted as resulting cash flows from operations but net income may also be used if cash flow information is not available. In capitalized earnings method, the value of the asset or the investment is determined using the anticipated earnings of the company divided by the capitalization rate (i.e. cost of capital). This method provides for the relationship of the (1) estimated earnings of the company; (2) expected yield or the required rate of return; (3) estimated equity value. CAPITALIZATION OF EARNINGS METHOD ILLUSTRATIONS: Mobile Inc. expects to earn Php450,000 per year expecting a return at 12%. SOLUTION: EQUITY VALUE= 450,000 / 12% = 3,750,000 Another scenario is that the future earnings are not constant and vary every year, the suggested approach is to determine average of earnings of all the anticipated cash flows. CAPITALIZATION OF EARNINGS METHOD ILLUSTRATIONS: Mobile Inc. projects the following net cash flows in the next five years, with the required return of 12%: SOLUTION: To calculate the equity value with variable cash flows, get the average in the given period: SOLUTION: EQUITY VALUE= 610,000/12% = 5, 083, 333 The equity value calculated is Php5,083,333. In the valuation process, this value include all assets. It is generally assumed that all assets are income generating. In case there are idle assets, this will be an addition to the calculated capitalized earnings. Capitalized earnings only represents the assets that actually generate income or earnings and do not include value of the idle assets. Following through the information of Mobile Inc. with the calculated equity value of Php5,083,333, assume that there is an idle asset amounting to Php 1,350,000. This value should be included in the equity value but on top of the capitalized earnings. Hence, the adjusted equity value is Php6,433,333 computed as follows: Capitalized Earnings Add: Idle Assets Equity Value 5,083,333 1,350,000 6,433,333 Problem: Heinz, Inc. expects to generate earnings over the next five years of Php 50,000.00; Php 60,000.00; Php 65,000.00; Php 70,000.00; and Php 75,000.00. Using the Capitalization of Earnings Method, what is the estimated value of the firm using 10.00% required rate of return? a. Php 640,000.00 b.Php 657,378.72 c.Php 657,738.72 d.Php604,000.00 Problem: Hai-dee is looking to buy a property that costs Php 115,000, and can be leased out of Php 750 a month. She has done some research and has determined the net operating expenses to be Php 5,000 per year. Her desired capitalization rate is 10%. What is the appraisal value of this property using the capitalization of earnings approach? a. Php 40,000.00 b. Php 42,500.00 c. Php 45,000.00 d. Php 50,000.00 DISCOUNTED CASH FLOWS METHOD Discounted Cash Flows is the most popular method of determining the value. This is generally used by the investors, valuators and analyst because this is the most sophisticated approach in determining the corporate value. It is also more verifiable since this allows for a more detailed approach in valuation. The discounted cash flows or DCF Model calculates the equity value by determining the present value of the projected net cash flows of the firm. The net cash flows may also assume a terminal value that would serve as a representative value for the cash flows beyond the projection. SUMMARY Income based valuation theorizes that the best estimate of value is based on the returns that an asset or business can generate in the future. Income based valuation approaches require the use of cost of capital to calculate value of future earnings. Cost of capital can be derived using two means (based on available information): through calculating the weighted average cost of capital or through the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). Income based valuation approaches include economic value added, capitalized earnings approach and discounted cash flow approach. SUMMARY Economic value added calculates the excess of company earnings after deducting cost of capital. Capitalized earnings approach is a simple calculation approach which divides forecasted earnings of the company by the cost of capital. Discounted cash flow approach is the most popular method of determining the value as it considers the present value of future cash flows associated with business operations. TRUE OR FALSE THEORY QUESTIONS 1. THE MOST CONVENTIONAL WAY TO DETERMINE THE VALUE OF THE ASSET IS THROUGH ITS ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED. 2. IN MATHEMATICS, ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED IS A QUICKLY MEASURES THE ABILITY OF THE FIRM TO SUPPORT ITS COST OF CAPITAL USING ITS EARNINGS. 3. EVA IS THE EXCESS OF THE COMPANY EARNINGS AFTER DEDUCTING THE COST OF CAPITAL. 4. THE GENERAL CONCEPT OF EVA IS THAT HIGHER EXCESS EARNING IS BETTER FOR THE FIRM. 5. ONE OF THE ELEMENTS THAT MUST BE CONSIDERED IN USING EVA IS THE REASONABLESNESS OF EARNINGS OR RETURNS. THANK YOU!